Get started with these growing tech trends here.



I recently got a private tour of a NASA space shuttle’s cockpit, a quirky mosaic-covered LA home, and a peaceful chapel with light streaming through ornate stained-glass windows—all without leaving my chair.
That chair was in an office at Google’s Silicon Valley headquarters, and I was wearing an HTC Vive virtual-reality headset on my face. But because these places were filmed with a high-resolution prototype camera that reproduces some of the key cues we use to understand depth in the real world, it felt more like actually being there than anything I’ve experienced with any other live-action VR. Which is to say it was pretty damn cool.
I could peer around the seats in the space shuttle Discovery, revealing buttons and switches on the walls of the cockpit that were previously obscured. As I looked closely at mirrored bits of tile on the outside of the mosaic house, I glimpsed reflections of other tiles in the background and saw a dizzying display of shapes and patterns. In the chapel, I gazed at the floor, and the colorful sunbeams moved as I did.

“Five Landmark students, including Hansen, spent a year developing the game-based learning experience that does away with specialized terms, symbols, and formulas of a typical statistics course and replaces it with a Pokemon-like first-person adventure that exercises statistical thinking.”

In many ways, the future is unpredictable. A report by the World Economic Forum reveals that almost 65 percent of the jobs elementary school students will be doing in the future do not even exist yet. Combined with technological automation and the disappearance of traditional jobs, this leaves us with a critical question: how can we survive such a world?
The answer may be imagination.
Initially coined by Rita J. King, the imagination age is a theoretical period beyond the information age where creativity and imagination will become the primary creators of economic value. This is driven by technological trends like virtual reality and the rise of digital platforms like YouTube, all of which increase demand for user-generated content and creativity. It is also driven by automation, which will take away a lot of monotonous and routine jobs, leaving more higher-ordered and creative jobs.
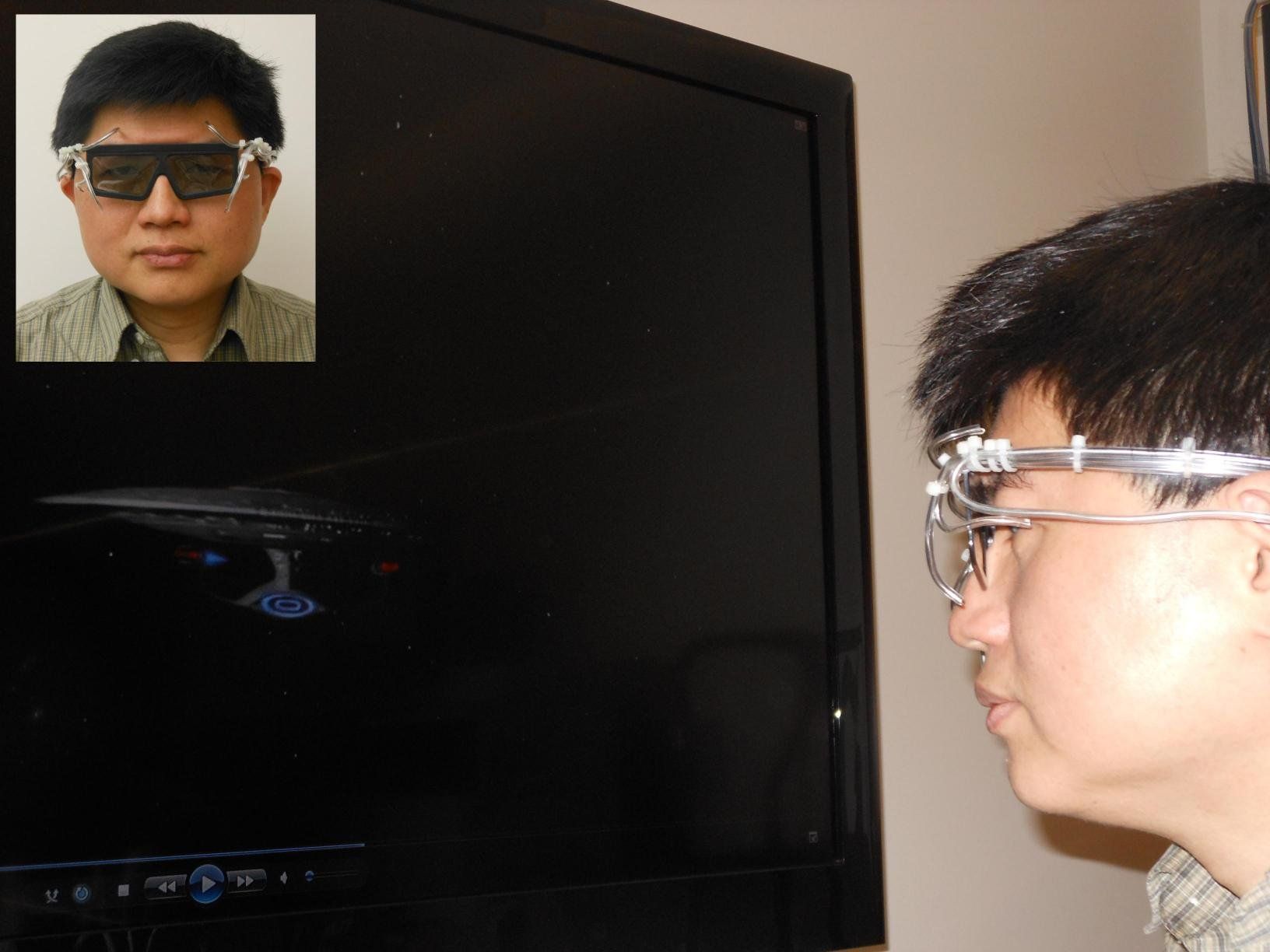

A team of researchers at UC San Diego and San Diego State University has developed a pair of “4D goggles” that allows wearers to be physically “touched” by a movie when they see a looming object on the screen, such as an approaching spacecraft.
The device was developed based on a study conducted by the neuroscientists to map brain areas that integrate the sight and touch of a looming object and aid in their understanding of the perceptual and neural mechanisms of multisensory integration.
But for the rest of us, the researchers said, it has a more practical purpose: The device can be synchronized with entertainment content, such as movies, music, games and virtual reality, to deliver immersive multisensory effects near the face and enhance the sense of presence.
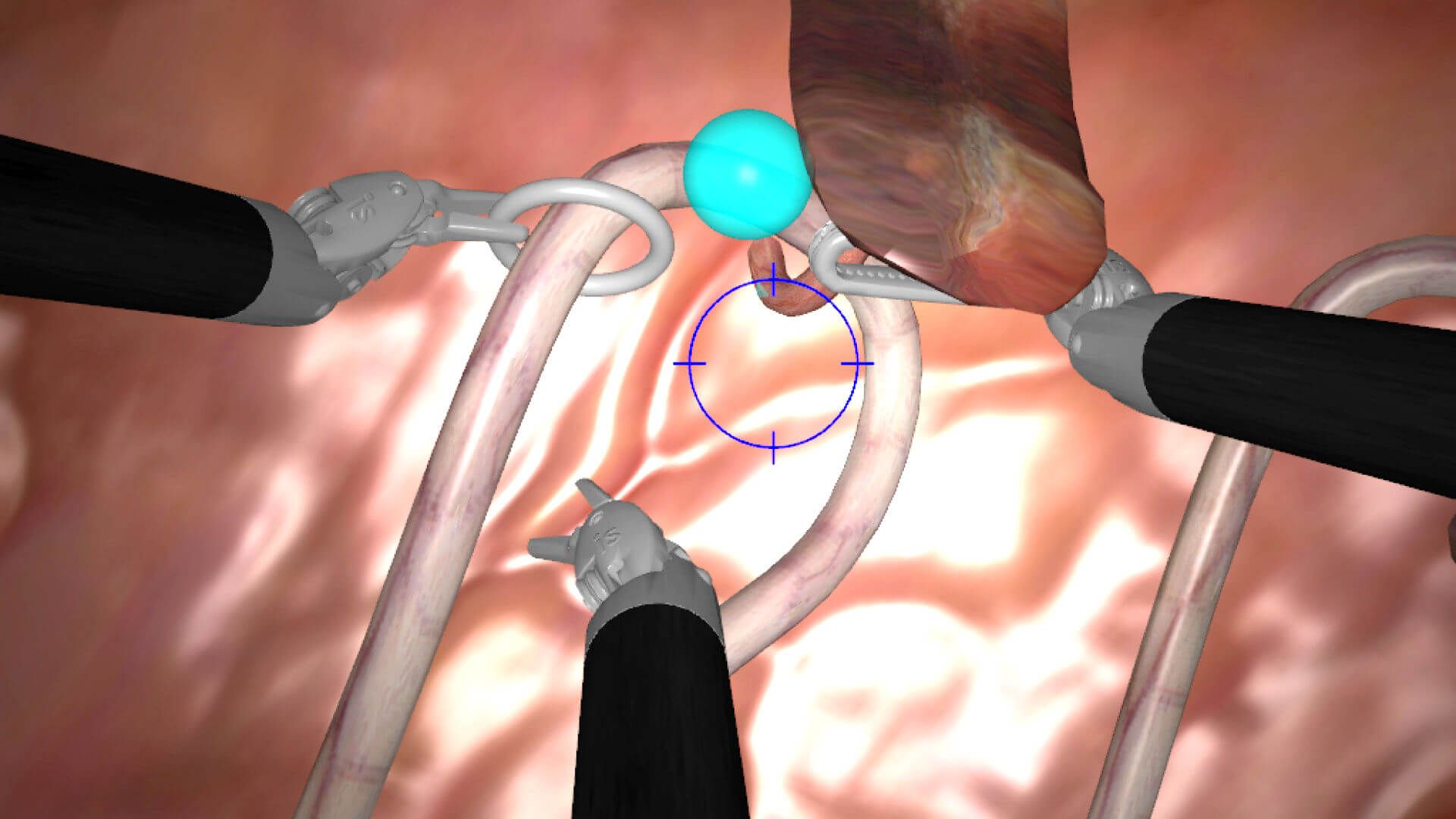
We’re no stranger to robotics in the medical field. Robot-assisted surgery is becoming more and more common. Many training programs are starting to include robotic and virtual reality scenarios to provide hands-on training for students without putting patients at risk.
With all of these advances in medical robotics, three niches stand out above the rest: surgery, medical imaging, and drug discovery. How have robotics already begun to exert their influence on these practices, and how will they change them for good?

Shermer’s journey into the present-day search for human domination over death and society’s ills introduces readers to all forms of what he calls “techno-optimism,” meaning the belief that technological progress means an end to death — or, at the very least, to aging and social decay. There are the cryonicists who want to freeze us, and those who want simply to freeze our brains, with all their neural connections and associated memories (the connectome). The transhumanists want to enhance us so thoroughly — through means both natural and artificial — that we become godlike, “taking control of evolution and transforming the species into something stronger, faster, sexier, healthier and with vastly superior cognitive abilities the likes of which we mere mortals cannot conceive”; the Omega Point theorists think we will all one day be brought back to life in a virtual reality. Believers in “the singularity” contend that it is possible to upload the human brain to a server without losing the essence of what makes you you. And, of course, there are those who try to cure us of aging, so that our bodies and minds will cease to deteriorate and our life spans will increase ad infinitum. Shermer visits each of these and other utopian theories with detail and considered analysis, drawing readers along increasingly unrealistic (or are they?) possibilities for our future evolution. It’s a journey as boggling as it is engrossing.
In “Heavens on Earth,” Michael Shermer explores the lengths to which mankind will go to ensure our souls’ survival beyond existence on this mortal coil.

Even as autonomous robots get better at doing things on their own, there will still be plenty of circumstances where humans might need to step in and take control. New software developed by Brown University computer scientists enables users to control robots remotely using virtual reality, which helps users to become immersed in a robot’s surroundings despite being miles away physically.
The software connects a robot’s arms and grippers as well as its onboard cameras and sensors to off-the-shelf virtual reality hardware via the internet. Using handheld controllers, users can control the position of the robot’s arms to perform intricate manipulation tasks just by moving their own arms. Users can step into the robot’s metal skin and get a first-person view of the environment, or can walk around the robot to survey the scene in the third person—whichever is easier for accomplishing the task at hand. The data transferred between the robot and the virtual reality unit is compact enough to be sent over the internet with minimal lag, making it possible for users to guide robots from great distances.
“We think this could be useful in any situation where we need some deft manipulation to be done, but where people shouldn’t be,” said David Whitney, a graduate student at Brown who co-led the development of the system. “Three examples we were thinking of specifically were in defusing bombs, working inside a damaged nuclear facility or operating the robotic arm on the International Space Station.”


“Eventually such systems may not require conscious input to capture and respond to shifting user preferences, though user intervention might still remain an option. The notion of ‘virtual’ fails to accurately describe such a world.”