Smart intersections are the next big thing in terms of ways to optimize the traffic, especially given the connected car push that’s getting so much traction these days.
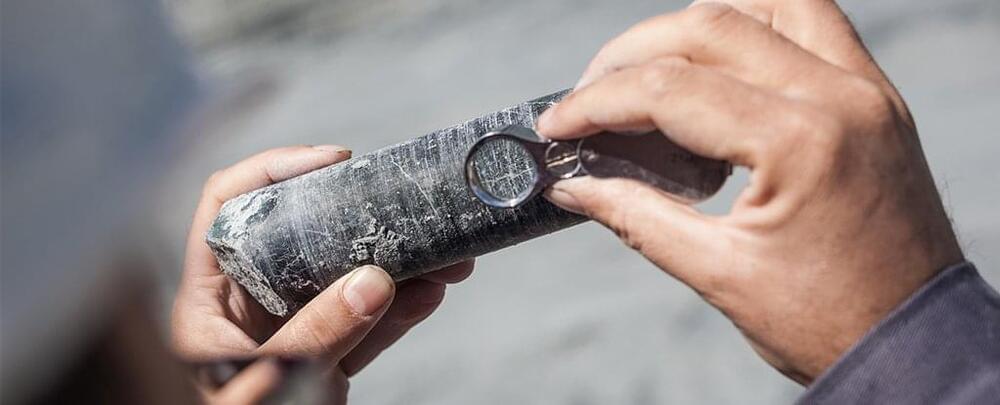



Earlier this year, researchers found a deposit of rare-earth minerals off the coast of Japan that could supply the world for centuries, according to a study.
The study, published in the journal Nature in April 2,018 says the deposit contains 16 million tons of the valuable metals.
Rare-earth minerals are used in everything from smartphone batteries to electric vehicles. By definition, these minerals contain one or more of 17 metallic rare-earth elements (for those familiar with the periodic table, those are on the second row from the bottom).
These elements are actually plentiful in layers of the Earth’s crust, but are typically widely dispersed. Because of that, it is rare to find any substantial amount of the elements clumped together as extractable minerals, according to the USGS.

When automotive chieftains gather in Munich this upcoming week for Europe’s first major car show in two years, they’ll do more than just lift the veil on shiny sheet metal. These are occasions where big deals tend to get done.
Consider one of the last times the auto world descended on a European city for such a forum in March 2019. Just before the action got underway in Geneva, the CEOs of Peugeot maker PSA and Fiat Chrysler met to sow the seeds of what blossomed into a mega merger, vaulting Stellantis NV into the same league as Toyota Motor Corp. and Volkswagen AG.

Tesla’s Gigafactory Nevada has achieved an incredible milestone. As seen in an image recently shared online, the expansive battery facility has formally produced its 1 millionth battery pack. This is a notable achievement, especially considering the uphill battle that Tesla and its battery partner, Panasonic, had to go through to ramp the facility’s battery production activities.
A picture of Gigafactory Nevada’s 1,000,000th battery was posted on the r/TeslaMotors subreddit. The special occasion was commemorated by the Giga Nevada team, with the battery pack being signed by numerous employees. A sign that read, “We have officially built 1,000,000 packs at Gigafactory Nevada,” could also be seen in the image.
Since starting its battery production activities in January 2,017 Gigafactory Nevada has played a key role in Tesla’s overall operations. The facility does not produce vehicles, but it manufactures powertrains and 2,170 battery cells for the Model 3 and Model Y, Tesla’s two mass-market cars. When it was initially pitched by CEO Elon Musk, however, the skepticism surrounding Gigafactory Nevada was notable.
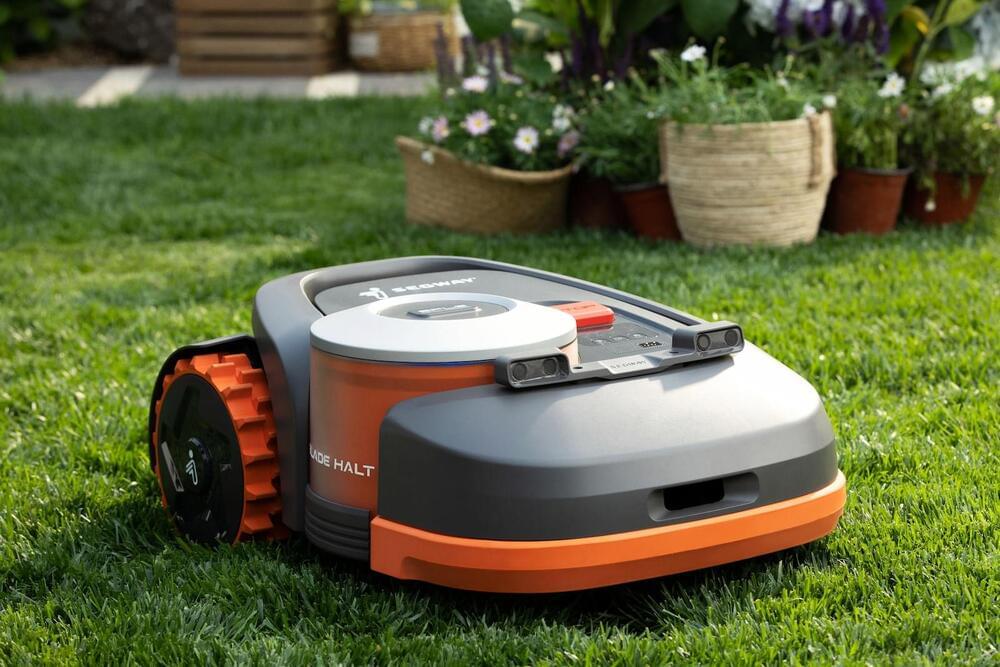

There’s no need to install a perimeter wire with the Navimow.
Is moving into the robot mower market with the Navimow. What sets this model apart from many others is that you don’t need to install a boundary wire. Instead, Navimow uses GPS and other sensors to stay within the perimeter of your lawn.
A so-called Exact Fusion Locating System can maintain Navimow’s position accurate to within two centimeters, according to Segway. If the GPS signal ever dips, the company says the device’s array of sensors and data ensure it will still work. You can tell Navimow where to mow, define the boundaries and instruct it to avoid certain parts of your garden via an app. Segway claims Navimow uses an algorithm to figure out a mowing path so it doesn’t have to criss-cross.
Segway says Navimow operates relatively quietly at 54 dB. There are offset blades to trim edges and corners, while the mower gradually cuts grass from above to reach the height you want (between three and six centimeters). The mower can handle 45-degree inclines and it has an IPX6 water resistance rating, according to Segway.

Arizona, and Georgia will introduce the system first, with Connecticut, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Oklahoma, and Utah also signed up.
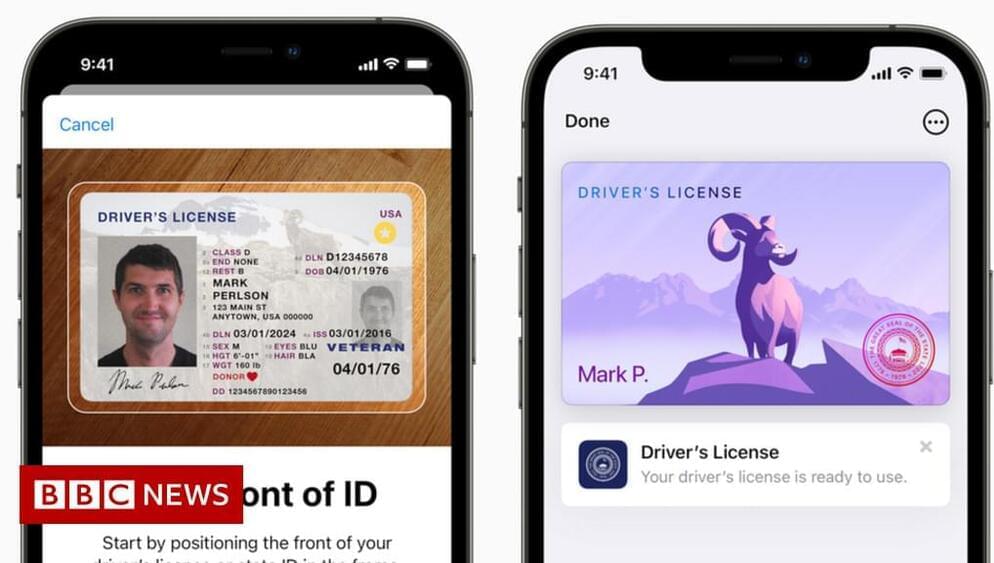
The “first locations” to use the system will be airport security checkpoints run by the Transportation Security Administration (TSA), Apple says.
Americans usually need some form of state ID only to travel by air domestically, unlike other countries, in which a passport is widely used.
Tapping a phone at an identity reader at supported airports will prompt passengers to use their Face ID or fingerprint to authorise sending information to the machine.
“Users do not need to unlock, show, or hand over their device to present their ID,” Apple said.
Apple’s new ID system for its Wallet will be rolled out at airports to start.
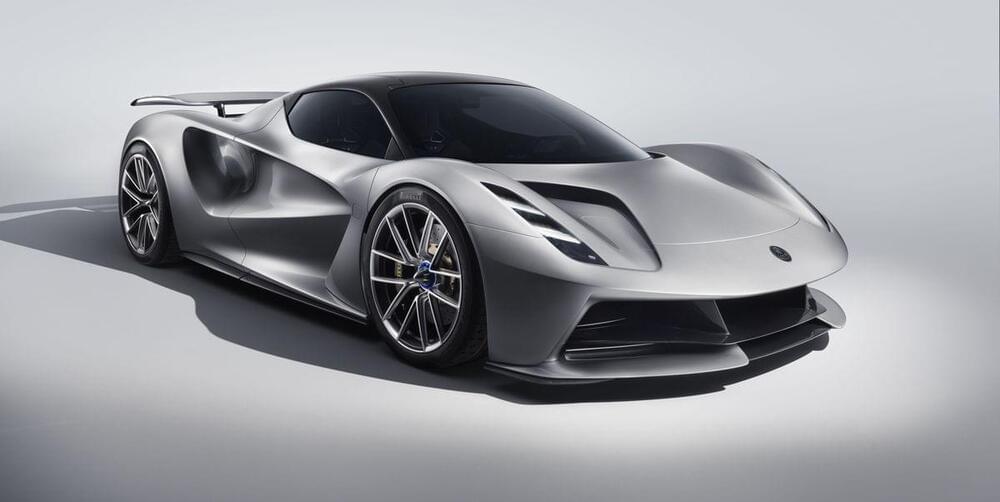

Lotus targets almost2000horsepower for its new hypercar.
Lotus is wary of corporate hubris these days, preferring to remain quiet when previously it would have shouted. Former boss Dany Bahar once introduced five sports-car concepts on the same auto-show stand, none of which made it even close to production. Lotus’s resources have grown massively since the thinly applied gild of the Bahar era; Chinese automaker Geely took a majority stake in the British sports-car maker two years ago. But although the company has recruited hundreds of new engineers, and is known to be working on several new models, few details have been shared so far.
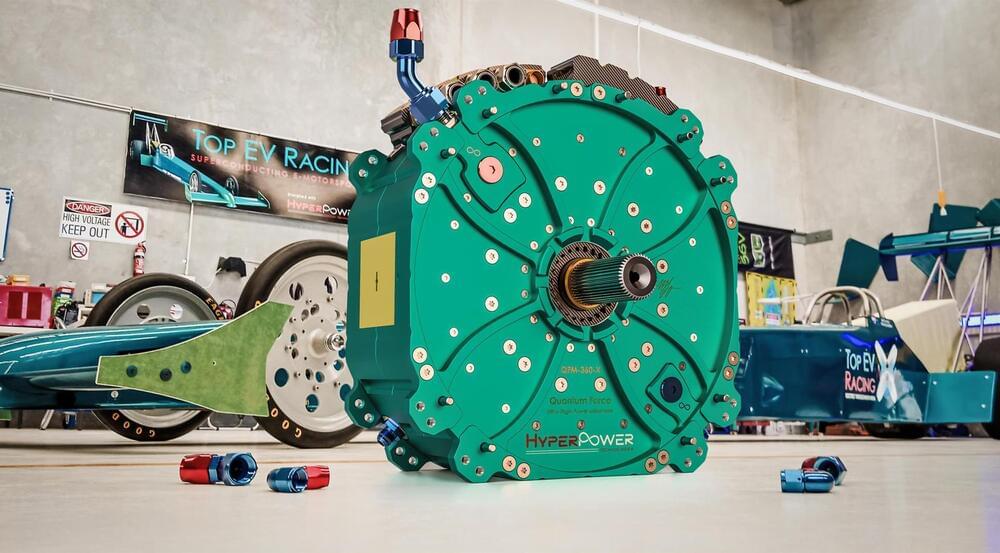
An Australian company by the name of HyperPower Technologies has developed an electric motor that generates a mammoth 1,340 horsepower.
The electric motor, code-named the QFM-360-X, measures about 17 inches in diameter and is designed to be scalable. HyperPower said ten of them could be mounted on a common shaft to deliver 13,400 hp.
To demonstrate the performance, HyperPower teamed up with electric drag racers Top EV Racing and built a Top Fuel-style dragster powered by four of the motors for a combined output of 5,360 hp. Performance estimates for the electric beast include a 0–124 mph time of 0.8 seconds, a 0–330 mph time of 3.7 seconds, and a top speed of 380 mph.

The two companies have raised an initial US$6.5 million toward what could genuinely be a revolutionary powertrain for electric aircraft; a fully FAA-certified hydrogen system would instantly allow electric aircraft to carry several times more energy on board, vastly boosting flight endurance while also enabling fast refueling instead of slow charging.
HyPoint claims its “turbo air-cooled” fuel cell system” will be able to achieve up to 2,000 watts per kilogram (2.2 lb) of specific power, which is more than triple the power-to-weight ratio of traditional (liquid-cooled) hydrogen fuel cells systems. It will also boast up to 1,500 watt-hours per kilogram of energy density, enabling longer-distance journeys.” For comparison, today’s commercially available lithium battery packs rarely break the 300-Wh/kg mark.