Click on photo to start video.





A proposed hypersonic reconnaissance and strike aircraft, the SR-72 would serve as a replacement for the famed SR-71 Blackbird, which was retired by the Air Force back in 1998. The SR-71 Blackbird could fly at 2200 mph (over 3 times the speed of sound).
Lockheed has said they are working on a combined-cycle engine. It uses both a turbine and a scramjet to achieve hypersonic speeds. Lockheed Martin is testing Aerojet Rocketdyne from 2013 to 2017. Two combined-cycle engines are planned to power the SR-72, which is designed to be about the same size of the SR-71 and could achieve first flight in the late 2020s.
More on this #transhumanism AI religion story, w/ some of my quotes in it. This article has 5500 comments on it!
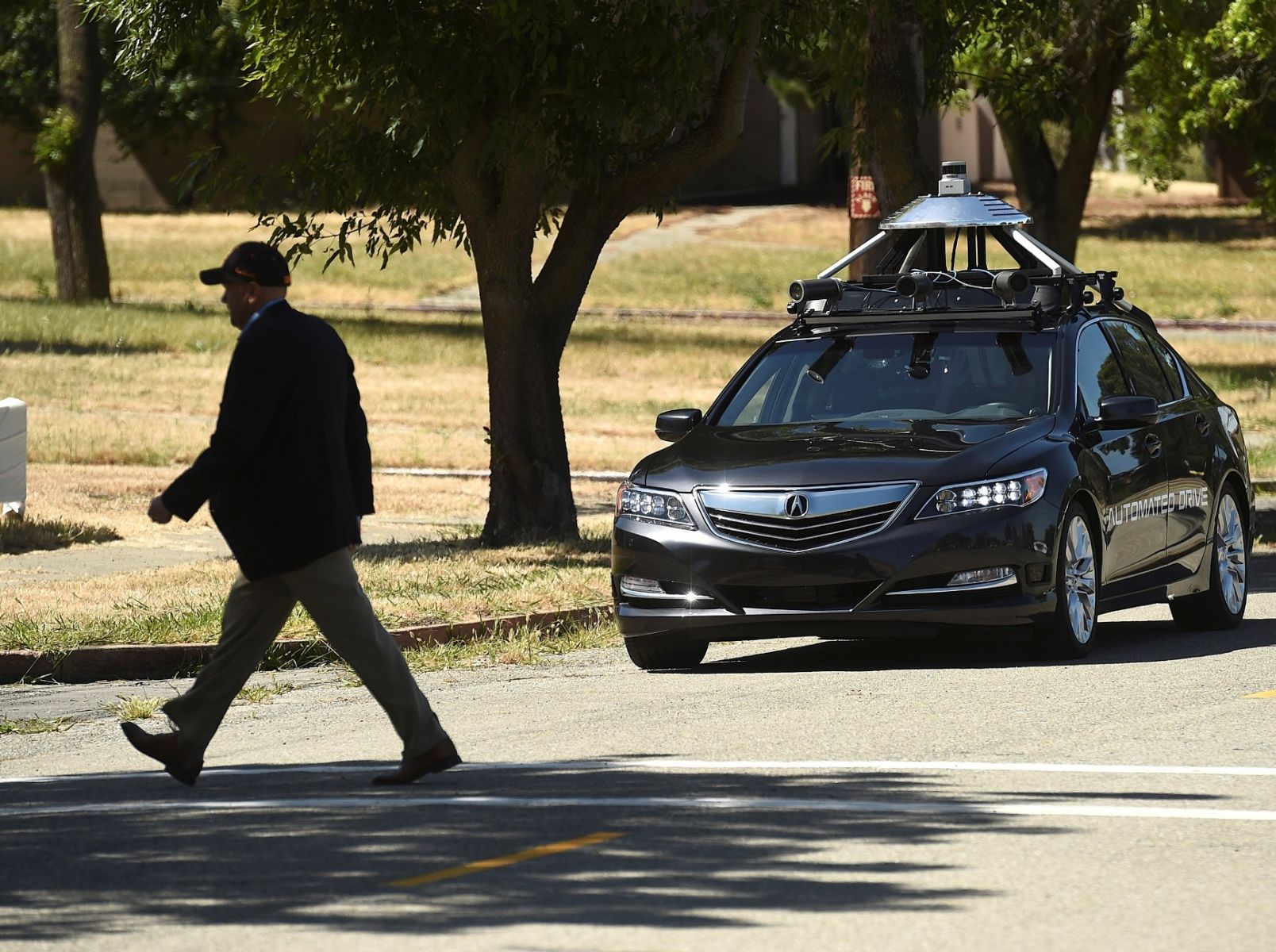
Former Google engineer Anthony Levandowski is emerging from the shadow of a self-driving lawsuit to create a robot god.
The present continues to take inspiration from science-fiction author Isaac Asimov’s visions of the future. In “The Last Question,” Asimov conceived of an artificial intelligence project known as Multivac. Its purpose was to solve for the inevitable heat death of the universe, but in the end, it becomes that answer.
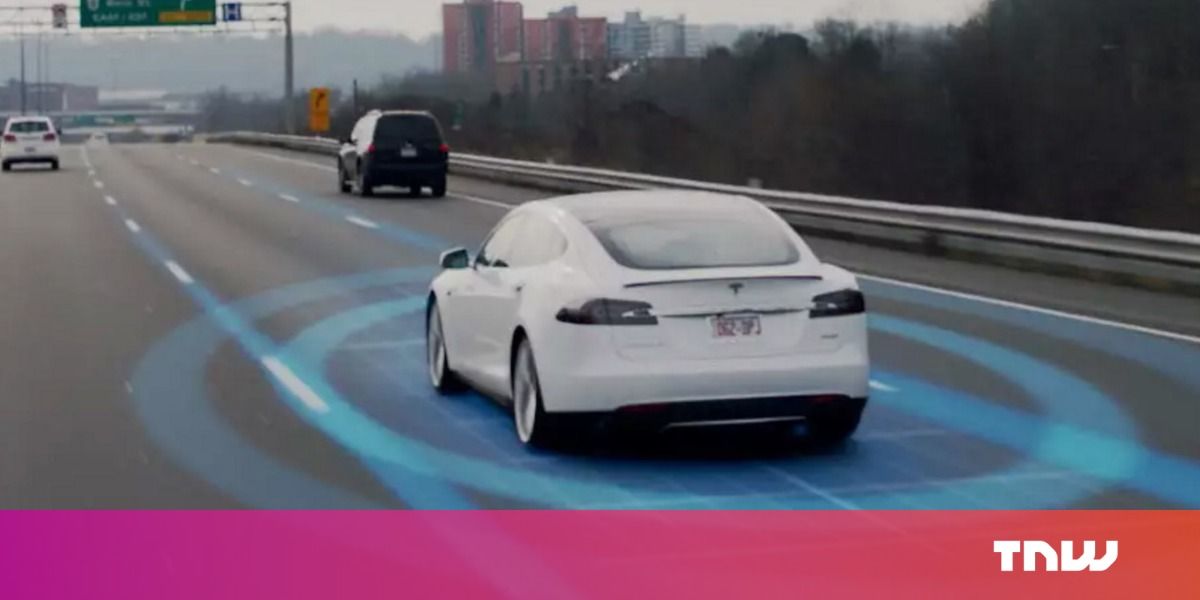
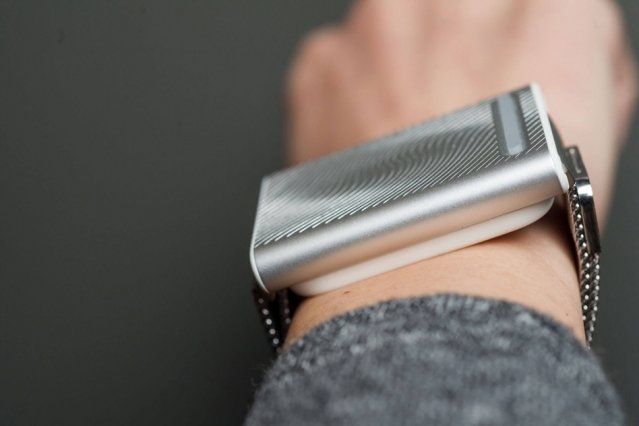



Cool Wearable! Actually does something useful & could help reduce energy waste.
Sitting in a stifling subway car or walking Boston’s cold winter streets may soon become more bearable, thanks to a “personal thermostat” wristband being released by MIT spinout Embr Labs.
For a design competition in 2013, four MIT engineering students created a smart wristband, called Wristify, that makes its wearer feel warmer or cooler through its contact with the skin on the wrist. After much fanfare, and a lot of research and development, the wristband will hit the shelves early next year.
The wristband, now called Embr Wave, has a flat aluminum top that includes a colored display users adjust from blue to red, to provide cooling or warming, respectively. The device works because the wrist is one of the most thermally sensitive parts of body. It’s also an area where people are most comfortable putting new wearable technologies.
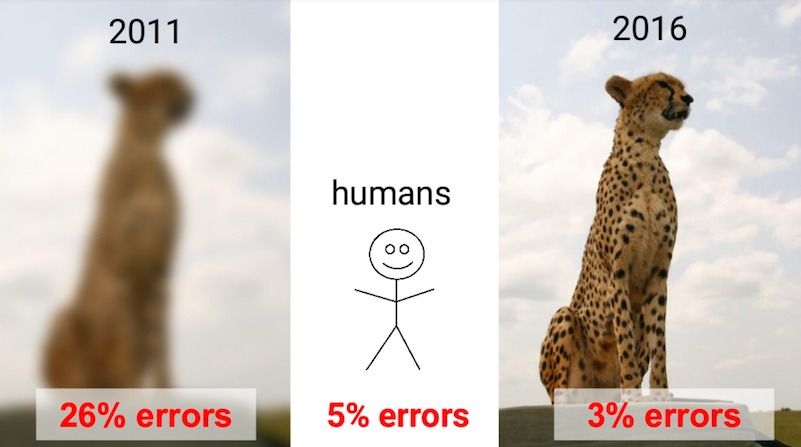

Just five years ago, artificial intelligence-enabled computers could barely recognize images fed to them, much less analyze them anything like people can. But suddenly, they’ve turned the tables.
“In 2011 their error rate was 26 percent,” says Jeff Dean, chief of the Google Brain project, which along with other tech giants has helped lead a recent revolution in image recognition as well as speech recognition and self-driving cars. Now, he says, computers’ ability to view and analyze images (pictured) exceeds what human eyes can do.
“If you ’ d have told me that would be a possible just a few years ago, I would ’ ve never believed you,” Dean said during an appearance at a research event in Heidelberg, Germany. But thanks to AI-enabled computer vision advances, computers “can now see … and that has opened our eyes (about) what is possible.”

Huge queues formed at airports around the world today after an IT system vital to scores of airlines crashed due to one faulty switch.
A program run by a huge tech firm called Amadeus is behind computers for British Airways, Air France, Lufthansa and other carriers, who use it every day to check passengers onto flights.
But the system was sent into meltdown today when the firm accidentally triggered a computer crash, causing long lines of upset passengers to form at airports across the globe.