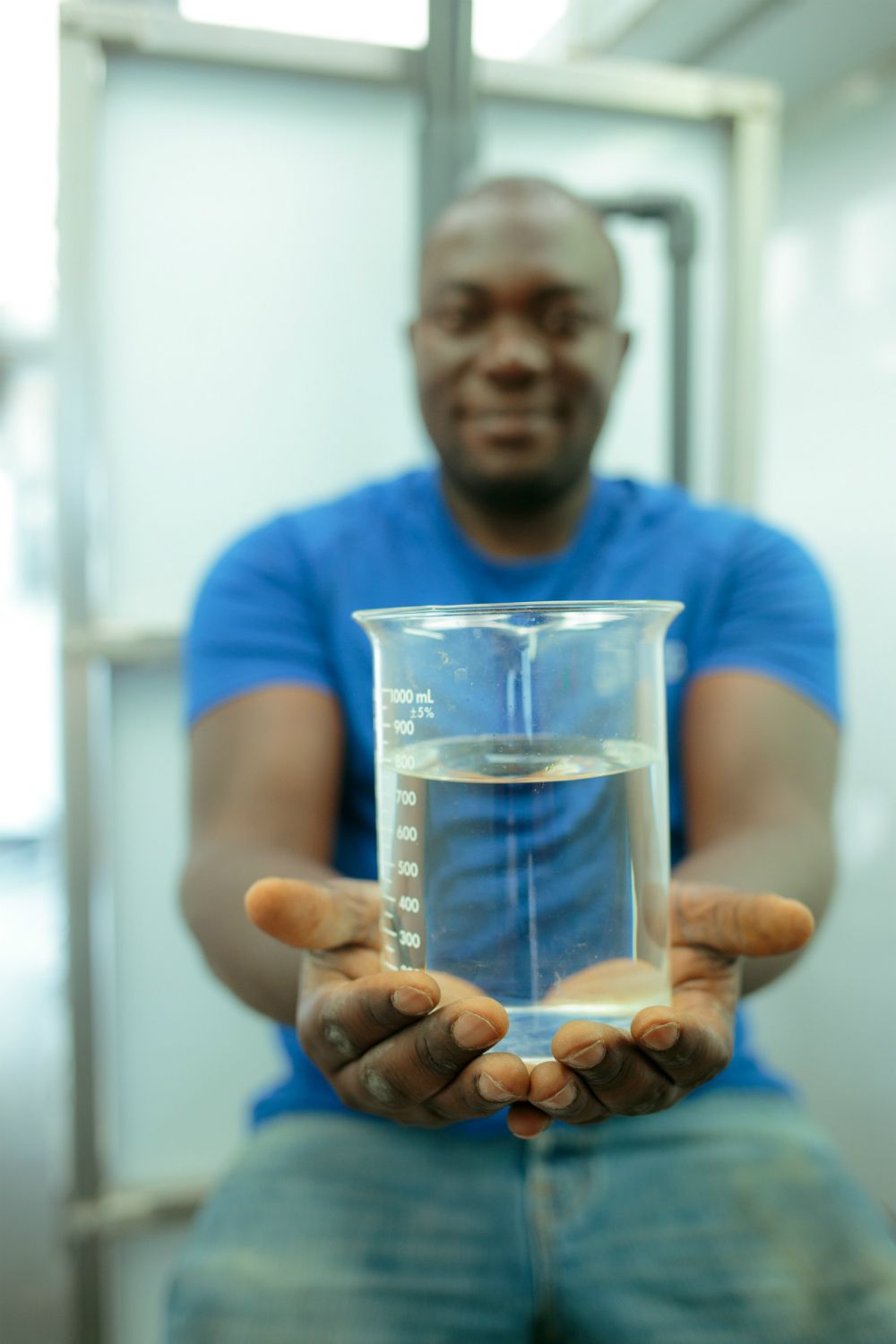
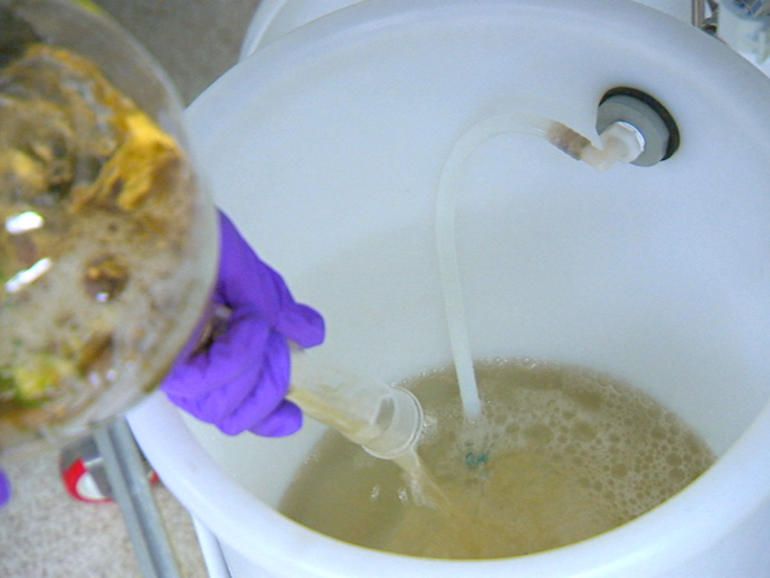
Hoppy beers do that to me. This beer was different. The water used for the brew came not from a river, a reservoir, or even a well. Instead, the water was sourced from a wastewater treatment plant located along the South Platte River. This simple fact didn’t bother me at all.
To be clear, I’m not a risk taker. Never skydived. Never paddled down Class V rapids. Never swallowed goldfish on a dare. But from what I’ve learned about purification processes for reclaimed water, drinking this limited-edition beer was eminently safe. The pilsner, blonde and translucent, like a Coors, looked and tasted like any number of beers made from water freshly obtained from creeks and rivers tumbling from Colorado’s mountain peaks. As for the strawberry-kiwi wheat beer ordered by my companion, I would have nothing of it. “That’s not beer,” I harrumphed, “that’s a fruit bowl. Undrinkable.”
I was at Declaration Brewing Co., located in Denver’s Overland neighborhood. The brewery and also a winery, InVINtions, located in Greenwood Village, were part of a regional effort. Water for the one-time specialty beverages produced by both came from the PureWater Colorado Demonstration Project. In the demonstration that was conducted in spring of 2018, water providers, engineering companies and water reuse advocates collaborated to showcase direct potable reuse treatment technologies. The water was treated using five different processes until it met federal and state drinking water standards, suitable for human consumption.