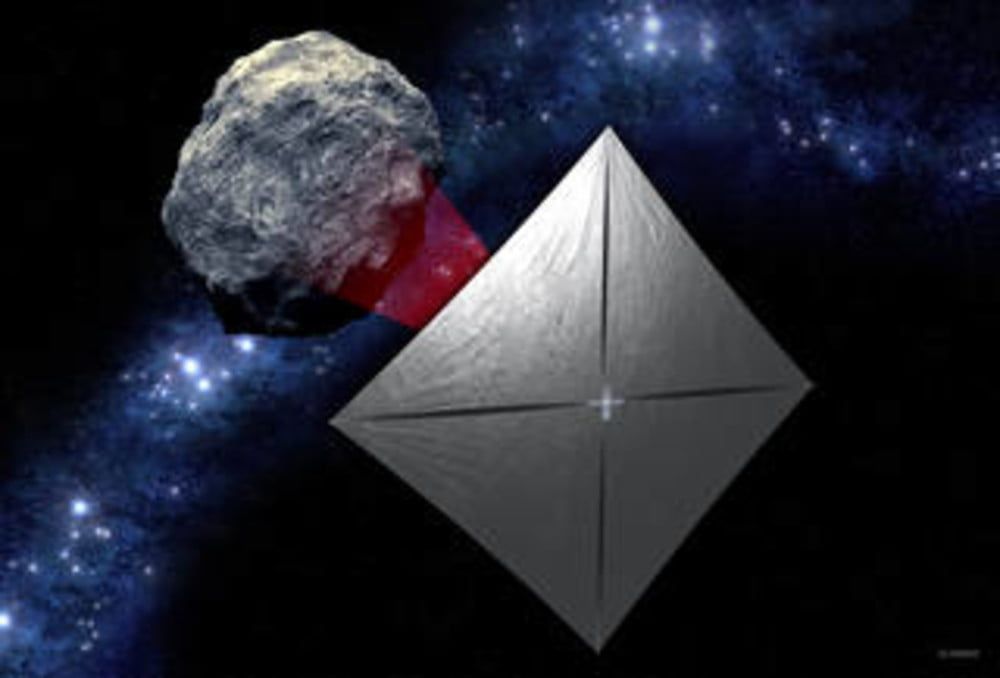
Following the success in 2019 of Bill Nye and the Planetary Society’s solar sail craft LightSail 2, NASA plans to launch its own solar sail project to investigate near-Earth asteroids.
The Near-Earth Asteroid Scout (NEA Scout) is a small satellite around the size of a shoebox that will sail through space powered by sunlight. The hardware will consist of a stainless steel boom structure across which a thin, aluminum-coated plastic sail will be stretched. The total area covered by the sail is around that of a racquetball court, and as photons from the sun bounce off the shiny surface, they will propel the craft forward.
As wacky as this idea sounds — it was made famous by, among others, science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke — it has been shown to work in low-Earth orbit by the LightSail project. Now NASA will take this one step further by deploying a solar sail in deep space.