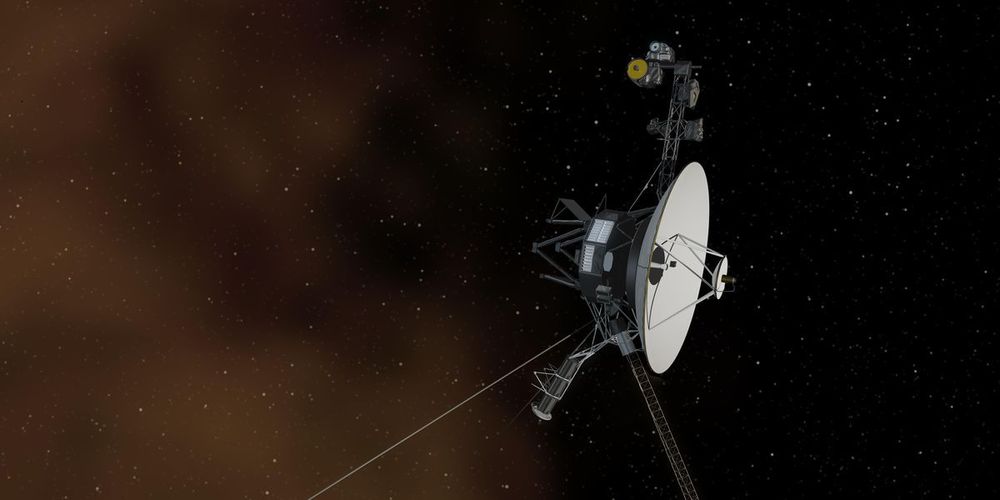
A long-simmering crisis for deep space missions ends before it could become a problem.
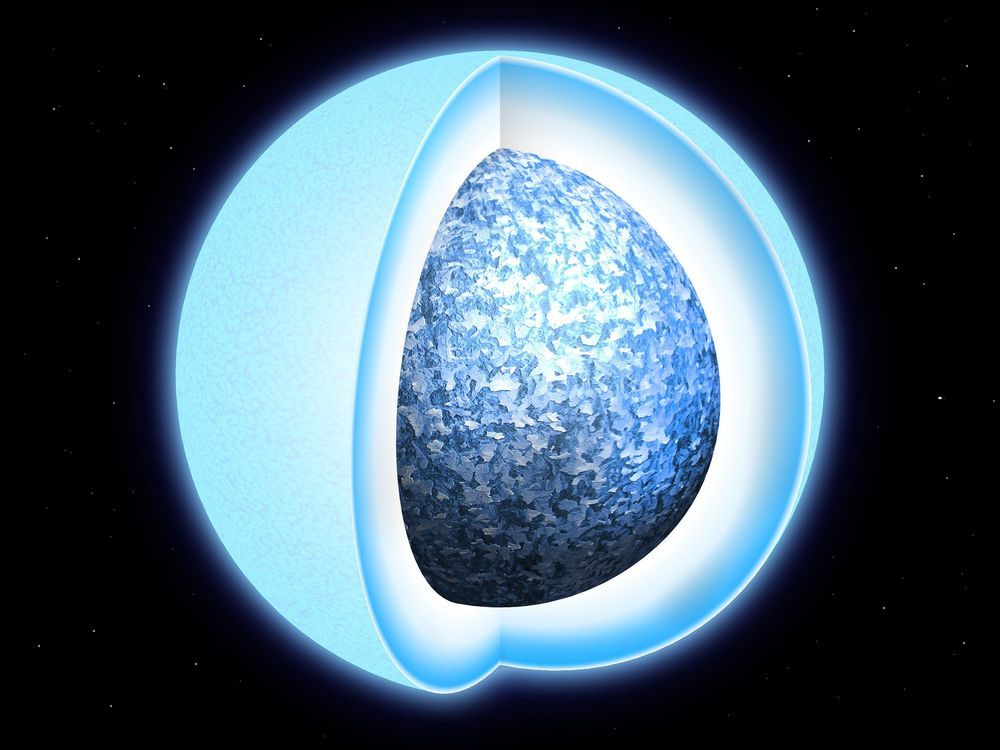



The first direct evidence of white dwarf stars solidifying into crystals has been discovered by astronomers at the University of Warwick, and our skies are filled with them.
Observations have revealed that dead remnants of stars like our Sun, called white dwarfs, have a core of solid oxygen and carbon due to a phase transition during their lifecycle similar to water turning into ice but at much higher temperatures. This could make them potentially billions of years older than previously thought.
The discovery, led by Dr. Pier-Emmanuel Tremblay from the University of Warwick’s Department of Physics, has been published in Nature and is largely based on observations taken with the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite.
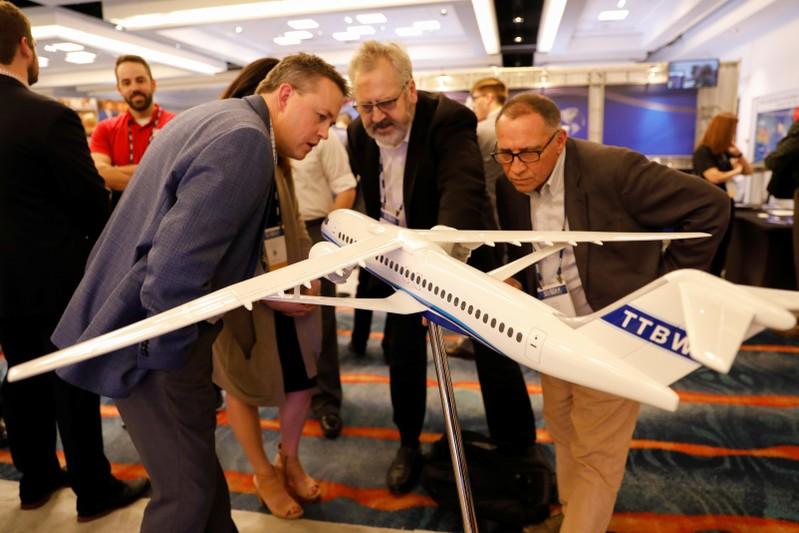

SAN DIEGO (Reuters) — Boeing Co unveiled a speedier and higher-flying version of a concept plane on Tuesday aimed at sharply reducing fuel use thanks to its elongated ultra-light wings.
The so-called Transonic Truss-Braced Wing aircraft boasts a 170-foot (52 meter) wingspan that sits atop the fuselage and is braced from underneath by a truss in a design reminiscent of biplanes from the early years of aviation.
The world’s largest planemaker and U.S. space agency NASA have been studying the concept plane for nearly a decade as part of the Subsonic Ultra Green Aircraft Research program. Boeing unveiled a reconfigured model or prototype and artist’s rendering at an aerospace conference in San Diego.

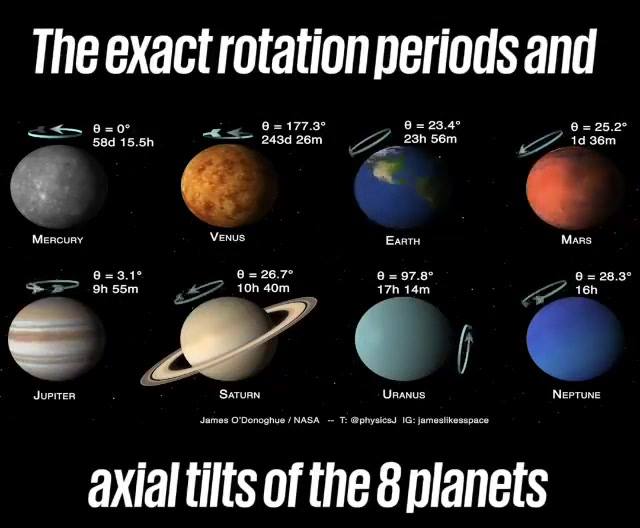
Its spin axis is tilted by a whopping 98 degrees.
Venus takes 243 Earth days to rotate once on its axis – the slowest rotation of any planet – and its rotation is retrograde to its orbital path. Combined with its orbital period, this means that a single solar day on Venus (the time between one sunup to the next) is 117 Earth days.
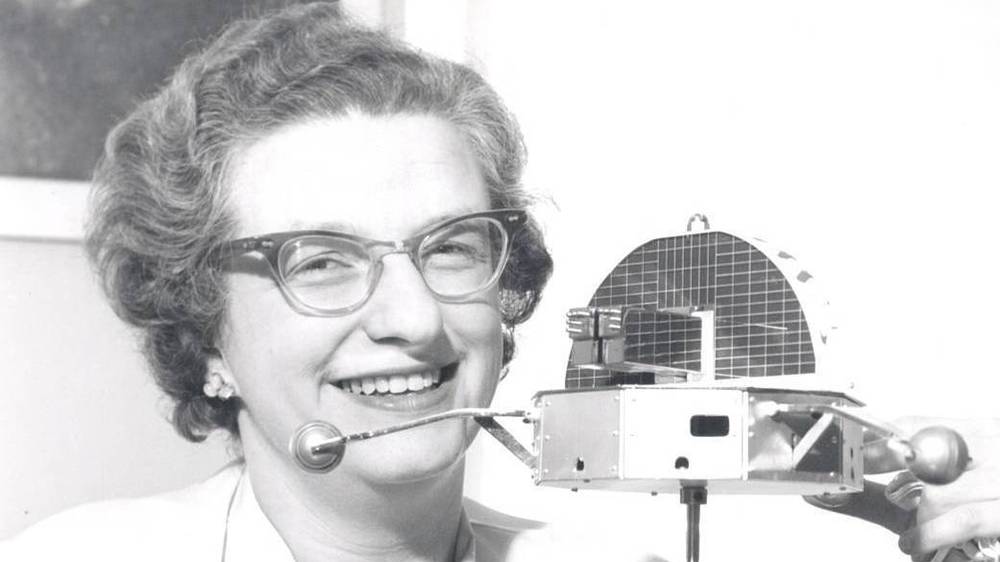

When Nancy Grace Roman was a child, her favorite object to draw was the moon.
Her mother used to take her on walks under the nighttime sky and show her constellations, or point out the colorful swirls of the aurora. Roman loved to look up at the stars and imagine.
Eventually, her passion for stargazing blossomed into a career as a renowned astronomer. Roman was one of the first female executives at NASA, where she served as the agency’s first chief of astronomy.

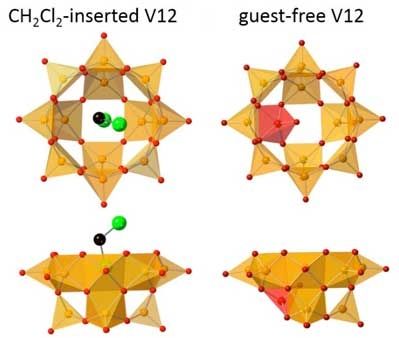
How do you separate carbon dioxide from carbon monoxide? One way, showcased by a new study from Kanazawa University, is to use a bowl of vanadium. More precisely, a hollow, spherical cluster of vanadate molecules can discriminate between CO and CO 2, allowing potential uses in CO 2 storage and capture.
At the molecular scale, small objects can fit inside larger ones, just like in the everyday world. The resulting arrangements, known as host-guest interactions, are stabilized by non-covalent forces like electrostatics and hydrogen bonds. Each host will happily take in certain molecules, while shutting out others, depending on the size of its entrance and how much interior space it can offer the guest.
Anion structures of CH 2 Cl 2 (guest)-inserted V12 (left) and guest-free V12 are shown. Orange and red square pyramids represent VO 5 units with their bases directed to the center of the bowl, and the inverted VO 5 unit. Green and black spheres represent Cl and C, respectively. Hydrogen atoms of CH 2 Cl 2 are omitted for clarity. (Image: Kanazawa University)
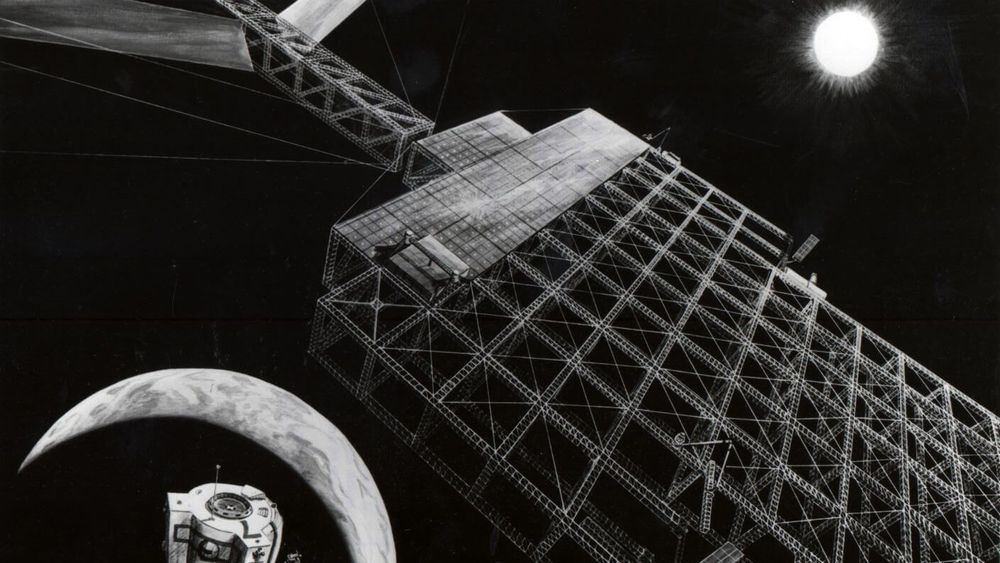


Over seven decades ago in 1941, Isaac Asimov wrote a short story, “Reason” (PDF), in which energy captured from the sun was transmitted via microwave beams to nearby planets from a space station. Flash forward to today, scientists are looking to make that very science fiction dream a reality for Earth.
There has been tremendous research on space-based solar power (SBSP) or space solar power (SSP) since the mid 20th century. Here is a great timeline of the various international studies and projects related to SBSP.
With SBSP, we could solve our energy and greenhouse gas emission problems with little environmental impact. Professor Sergio Pellegrino of CalTech recently said an SBSP system would receive eight times more energy than Earth does. With SBSP’s continuous massive energy output capability and the fact that our sun is slated to exist for another 10 billion years, we can safely assume we will not run out of this energy source anytime soon.