How do you separate carbon dioxide from carbon monoxide? One way, showcased by a new study from Kanazawa University, is to use a bowl of vanadium. More precisely, a hollow, spherical cluster of vanadate molecules can discriminate between CO and CO 2, allowing potential uses in CO 2 storage and capture.
At the molecular scale, small objects can fit inside larger ones, just like in the everyday world. The resulting arrangements, known as host-guest interactions, are stabilized by non-covalent forces like electrostatics and hydrogen bonds. Each host will happily take in certain molecules, while shutting out others, depending on the size of its entrance and how much interior space it can offer the guest.
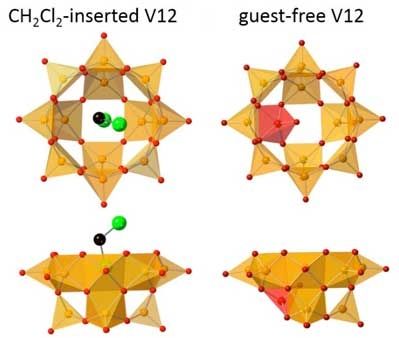
Anion structures of CH 2 Cl 2 (guest)-inserted V12 (left) and guest-free V12 are shown. Orange and red square pyramids represent VO 5 units with their bases directed to the center of the bowl, and the inverted VO 5 unit. Green and black spheres represent Cl and C, respectively. Hydrogen atoms of CH 2 Cl 2 are omitted for clarity. (Image: Kanazawa University)