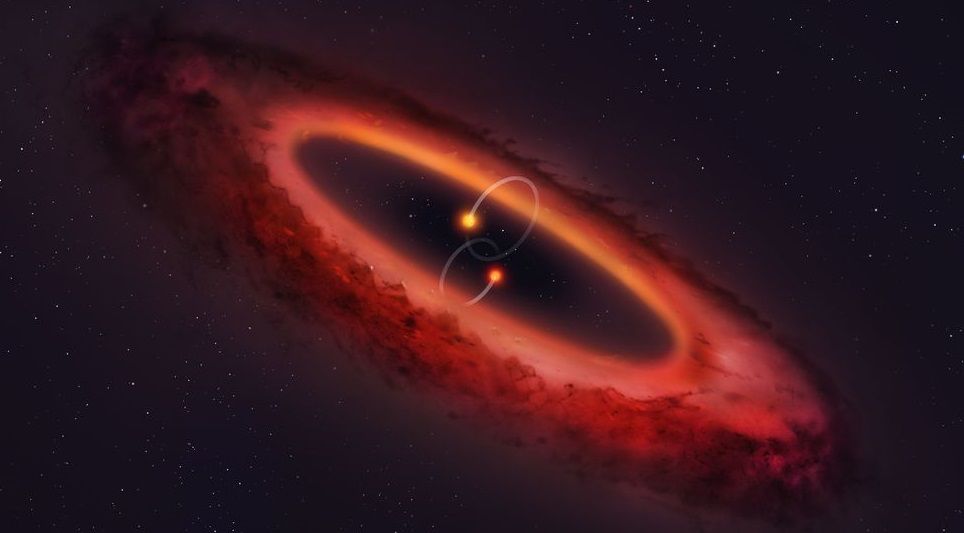
Researchers have discovered a highly unusual vertically-oriented protoplanetary disk orbiting around a four-star system.
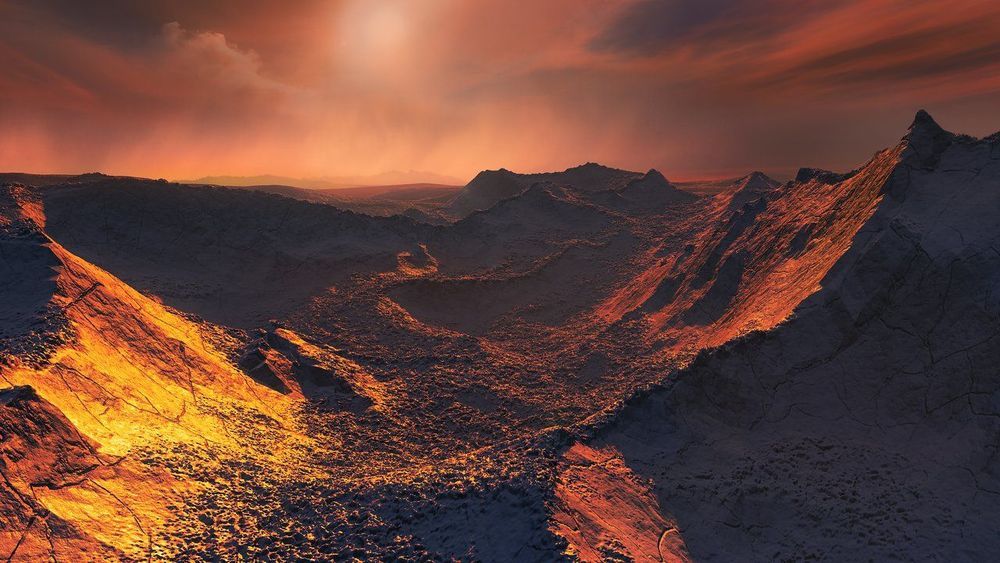


In 2018, scientists announced the discovery of a extrasolar planet orbiting Barnard’s star, an M-type (red dwarf) that is just 6 light years away. Using the Radial Velocity method, the research team responsible for the discovery determined that this exoplanet (Barnard’s Star b) was at least 3.2 times as massive as Earth and experienced average surface temperatures of about −170 °C (−274 °F) – making it both a “Super-Earth” and “ice planet”.
Based on these findings, it was a foregone conclusion that Barnard b would be hostile to life as we know it. But according to new study by a team of researchers from Villanova University and the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC), it is possible – assuming the planet has a hot iron/nickel core and experiences enhanced geothermal activity – that this giant iceball of a planet could actually support life.
The findings were shared at the 233rd meeting of the American Astronomy Society (AAS), which took place from January 6th to 10th in Seattle, Washington. The presentation, titled “X-Ray, UV, Optical Irradiances and Age of Barnard’s Star’s New Super Earth Planet – ‘Can Life Find a Way’ on such a Cold Planet”, was delivered during a press conference on January 10th and concerned findings that appeared in a recent study.

“Hear from leaders across science, academia, and business as they share the latest research and scientific advancements, industry innovation, and their perspective on how these domains will evolve,” Amazon’s re: Mars site says. Speakers from Amazon, MIT, UC Berkeley, NASA and Harvard are on the docket.
Amazon announces a new re: Mars conference that will gather experts in machine learning, robotics, automation and space in Las Vegas.

In December, NASA released a report on looking for “technosignatures” which are indirect pieces of evidence for extra-terrestrial civilizations. It covers a bunch of different scenarios.
NASA’s final report from their Technosignature Workshop is now out and addresses all the ways in which humanity is looking for evidence of extra-terrestrial civilizations.
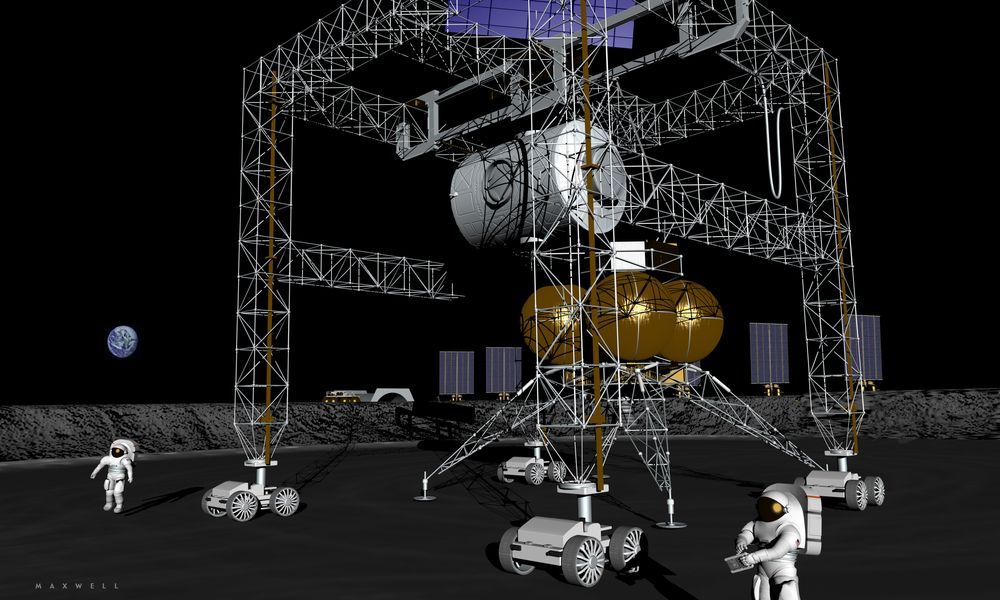

A Lunar Industrial Facility (LIF). Yes, a Lunar Industrial Facility. Science fiction you might say. Impossible you retort. Too expensive even if it could be done might be your rejoinder. We don’t have the technology, could be another rhetorical dismissal. These are all responses those who do not live and breath this every day may have, but these are reactionary responses that do not reflect where we are in the closing years of the second decade of the twenty first century. In this missive, which is a companion to a space policy paper released Monday August 1, 2017, is written to show that indeed a lunar industrial facility is possible, we do have the technology, and no it will not be too expensive. Furthermore, it enables something that though it would seem to be science fiction, isn’t, which is a shipyard in lunar orbit for the construction of humanities first truly interplanetary space vehicles, as well as providing the materials for very large Earth orbiting space platforms for science and commerce.
Why do we need interplanetary vehicles? We have over 9.1 billion reasons, for that is the number of humans who will be on the Earth in 2050, only 33 years from now. The greatest fear is that with only a single planet’s resources, we cannot provide for this number in any reasonable manner. This underpins most of the rhetoric today regarding resource conservation and how to confront other global problems. This is a self defeating philosophy. Rather than rationing poverty, it should be our common goal to help create a world where all of our fellow planetary citizens can live in a society that continues to progress, materially as well as morally. Our science knows beyond any shadow of a doubt now that resources many orders of magnitude greater than what are available from the Earth, exist in the solar system around us.
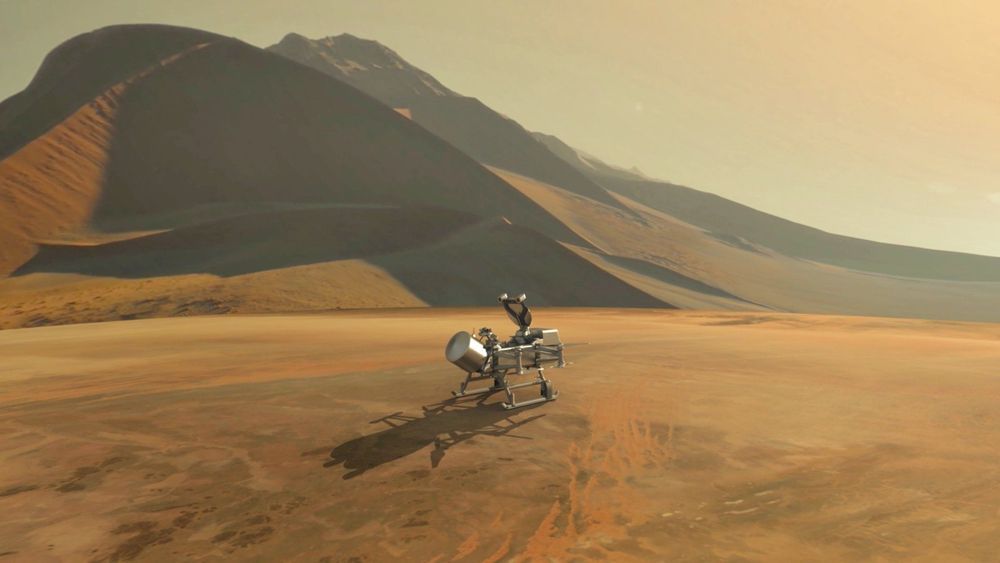




The spacecraft that have peered through the yellowish haze surrounding Saturn’s moon Titan discovered a strange, yet strangely familiar world where life could theoretically take root. Now, scientists want to return — this time buoyed by Earth’s fascination with drone technology.
That’s precisely what a team of scientists working on a proposed mission called Dragonfly want to do: combine terrestrial drone technology and instruments honed by Mars exploration to investigate the complex chemical reactions taking place on Saturn’s largest moon. Later this year, NASA will need to decide between that mission and another finalist proposal, which would collect a sample from a comet.
“At first blush, I think a lot of people think [Dragonfly] sounds like the literal meaning of incredible,” Melissa Trainer, a deputy principal investigator with the mission, told Space.com. “Not only is this an incredibly exciting concept with amazing, compelling science, but also, it is doable — it’s feasible from an engineering standpoint.” [Landing on Titan: Pictures from Huygens Probe on Saturn Moon].