Arsenal including electromagnetic railguns and microwave weapons aims to neutralize web of satellites that give US its main strategic edge.



It costs $80k to send a Nano- Satellite into space! To send the materials to build a lunar base is going to be expensive!
This week it was announced that NASA found a forgotten satellite in Lunar Orbit, which got me thinking about an idea to recycle existing Space Junk in the construction of an International Lunar Base with cost savings. We could use a modified version of my Google Deepmind NEO tracker to source the Space Junk and the ideas listed below to capture and redirect the Space Junk.
https://github.com/Agilebrett/AI-Deepmind-vs-Near-Earth-Objects

Several companies will collectively be launching about 20,000 satellites over the next few years. SpaceX, OneWeb, Telesat, O3b Networks and Theia Holdings — all told the FCC they have plans to field constellations of V-band satellites in non-geosynchronous orbits to provide communications services in the United States and elsewhere. So far the V-band spectrum of interest, which sits directly above Ka-band from about 37 GHz to the low 50 GHz range, has not been heavily employed for commercial communications services.
* SpaceX, for example, proposes a “VLEO,” or V-band low-Earth orbit (LEO) constellation of 7,518 satellites to follow the operator’s initially proposed 4,425 satellites that would function in Ka- and Ku-band.
* Boeing has a proposed global network of about 3000 satellites.

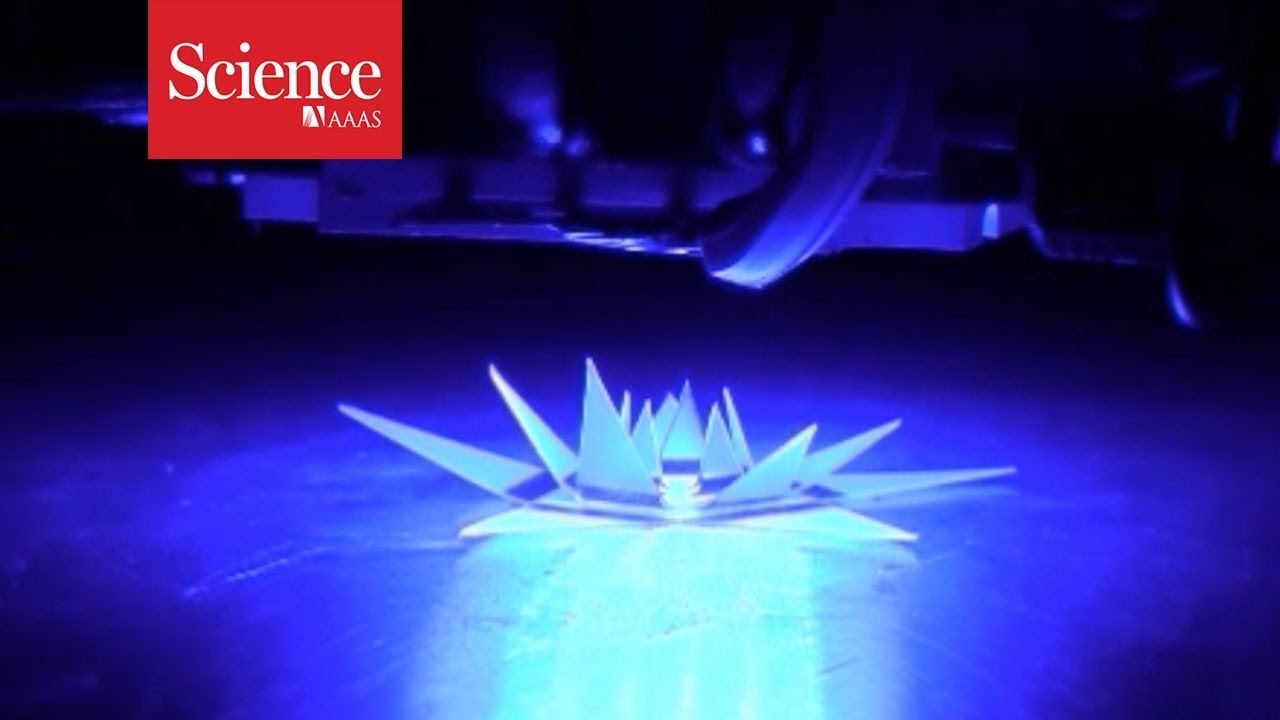
Inspired by origami, North Carolina State University researchers have found a way to remotely control the order in which a two-dimensional (2-D) sheet folds itself into a three-dimensional (3D) structure.
“A longstanding challenge in the field has been finding a way to control the sequence in which a 2-D sheet will fold itself into a 3D object,” says Michael Dickey, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and co-corresponding author of a paper describing the work. “And as anyone who has done origami — or folded their laundry—can tell you, the order in which you make the folds can be extremely important.”
“The sequence of folding is important in life as well as in technology,” says co-corresponding author Jan Genzer, the S. Frank and Doris Culberson Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State. “On small length scales, sequential folding via molecular machinery enables DNA to pack efficiently into chromosomes and assists proteins to adopt a functional conformation. On large length scales, sequential folding via motors helps solar panels in satellites and space shuttles unfold in space. The advance of the current work is to induce materials to fold sequentially using only light.”


This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
Enhancing situational awareness is a vital mission also in space. The US Department of Defense’s Strategic Command Joint Space Operations Center got Sky and Space’s signature on an agreement ahead of the company’s planned launch of 200 nano-satellites into space, as space junk continues to be a big issue.
The agreement provides for Sky and Space to receive “space situational awareness services” from the US Department of Defence so the company’s nano-satellites will be able to avoid objects like space junk and other satellites.

China’s State Council, the country’s chief administrative authority, recently published a White Paper on its space policies. It not only lifted a veil of secrecy that shielded Beijing’s space policies, but also outlined the country’s recent achievements and offered a five-year outlook on future activities.
Since its first satellite launch in 1970, China has become a major player in the space domain. However, it was only in 2003 that China became the third country to independently send people into space.
Beijing has placed significant resources into narrowing the capability gap that has separated it from other leading nations in this area. It took only eight years from its entry into manned spaceflight, in 2003, to the launch of the first prototype component of its space station, the Tiangong-1.

Electronic circuits are found in almost everything from smartphones to spacecraft and are useful in a variety of computational problems from simple addition to determining the trajectories of interplanetary satellites. At Caltech, a group of researchers led by Assistant Professor of Bioengineering Lulu Qian is working to create circuits using not the usual silicon transistors but strands of DNA.
The Qian group has made the technology of DNA circuits accessible to even novice researchers—including undergraduate students—using a software tool they developed called the Seesaw Compiler. Now, they have experimentally demonstrated that the tool can be used to quickly design DNA circuits that can then be built out of cheap “unpurified” DNA strands, following a systematic wet-lab procedure devised by Qian and colleagues.
A paper describing the work appears in the February 23 issue of Nature Communications.