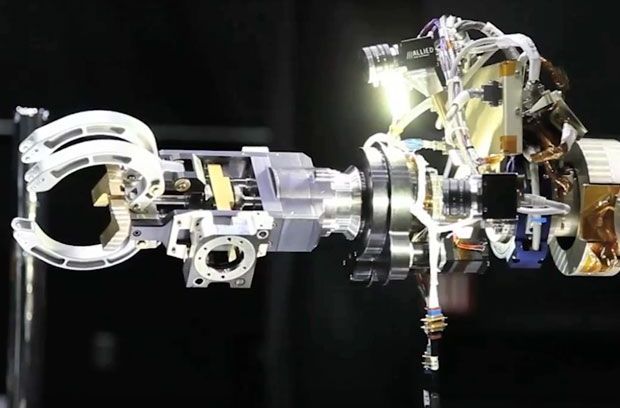
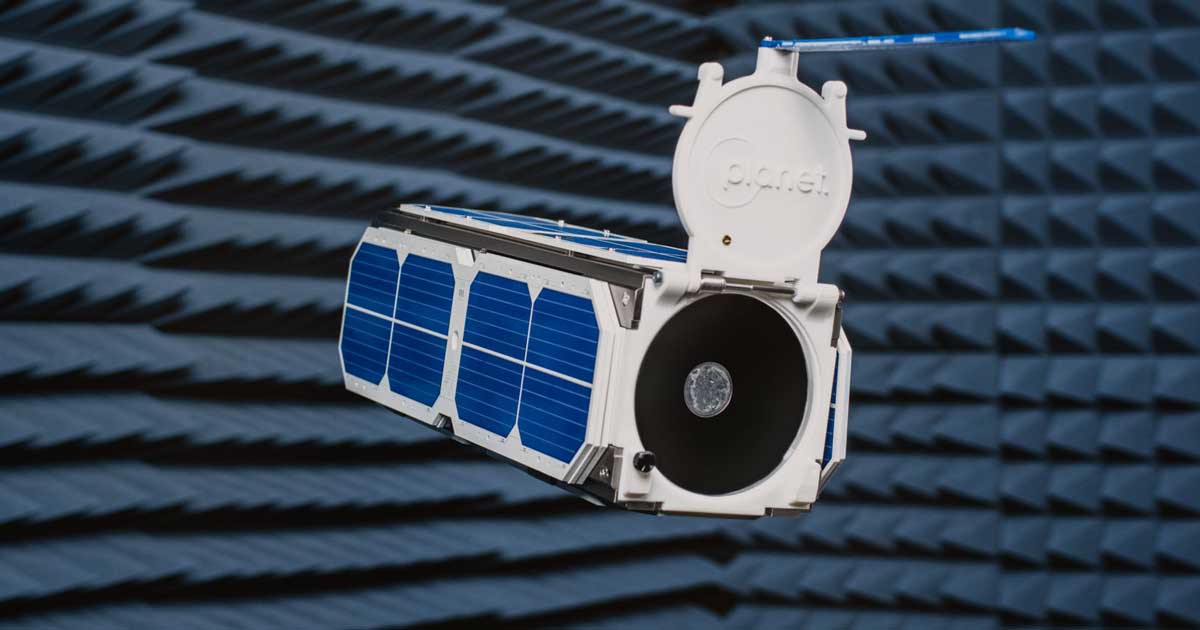
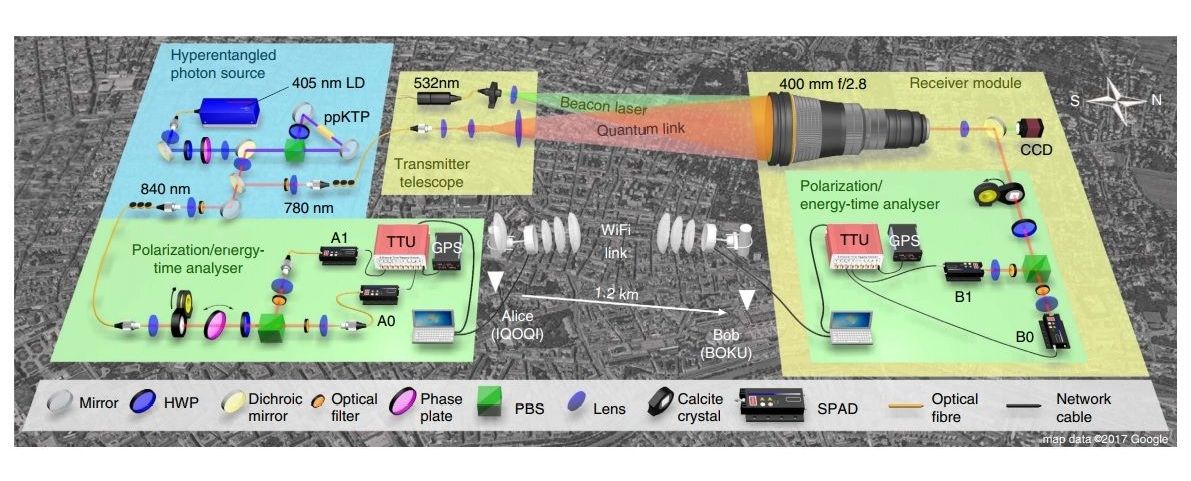
Let’s say you are the program manager of a very large, complex system. Perhaps it’s an aircraft, or a building, or a communications network. Your system is valued at over US $500 million. Could you imagine being told that you won’t ever be able to maintain it? That once it’s operational, it will never be inspected, repaired, or upgraded with new hardware?
Welcome to the world of satellite building. After a satellite is launched, it is on a one-way journey to disrepair and obsolescence, and there is little anyone can do to alter that path. Faults (which are called anomalies in the space business) can only be diagnosed remotely, using data and inferential reasoning. Software fixes and upgrades may be possible, but the nuts and bolts remain untouched. The upshot: Even if a satellite is operating well, it could lose its state-of-the-art status just a few years into a typical 15-year lifetime.
If governments and private companies could actively repair and revitalize their satellites in geosynchronous orbit—and move them to new orbits as needed—they could extend the lifespans of their investments and substantially defer the cost of building and launching replacements.