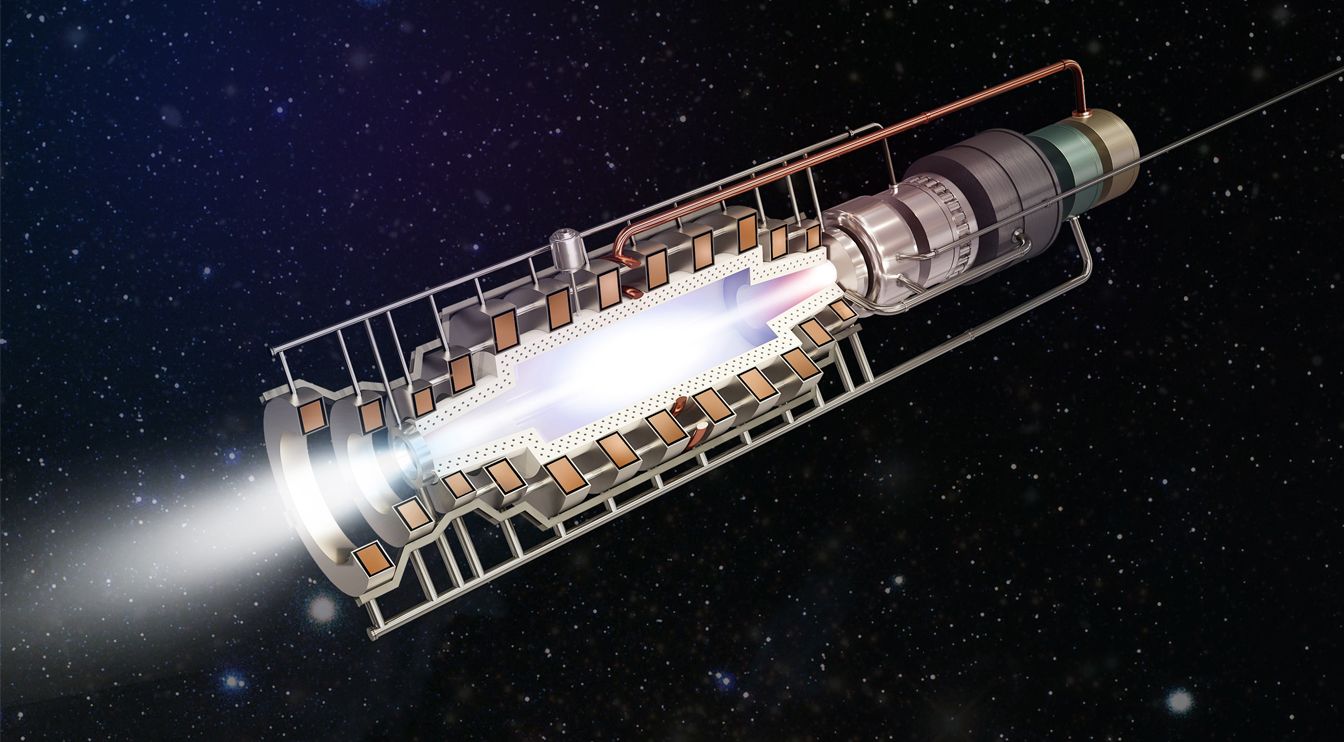
Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the sun, but closer to home scientists are trying to develop fusion reactors that could provide immense amounts of energy. These reactors are big and (currently) inefficient, but a NASA-funded startup called Princeton Satellite Systems is working on a small-scale fusion reactor that could power advanced fusion rockets. Suddenly, other planets and even other star systems could be in reach.
All the forms of rocket propulsion we currently have involve accelerating propellant out of a nozzle. Then, physics takes over and the vessel moves in the opposite direction. Most spacecraft use chemical propulsion, which provides a large amount of thrust over a relatively short period of time. Some missions have been equipped with ion drives, which use electrical currents to accelerate propellant. These engines are very efficient, but they have low thrust and require a lot of power. A fusion rocket might offer the best mix of capabilities.
Current nuclear reactors use fission to generate energy; large atomic nuclei are broken apart and some of that mass is transformed into energy. Fusion is the opposite. Small atomic nuclei are fused together, causing some mass to be converted into energy. This is what powers stars, but we’ve had trouble producing the necessary temperatures and pressure on Earth to get net positive energy generation.