Miniaturization has enabled technology like smartphones, health watches, medical probes and nano-satellites, all unthinkable a couple decades ago. Just imagine that in the course of 60 years, the transistor has shrunk from the size of your palm to 14 nanometers in dimension, 1000 times smaller than the diameter of a hair.
Miniaturization has pushed technology to a new era of optical circuitry. But in parallel, it has also triggered new challenges and obstacles, for example, controlling and guiding light at the nanometer scale. Researchers are looking for techniques to confine light into extremely tiny spaces, millions of times smaller than current ones. Studies had earlier found that metals can compress light below the wavelength-scale (diffraction limit).
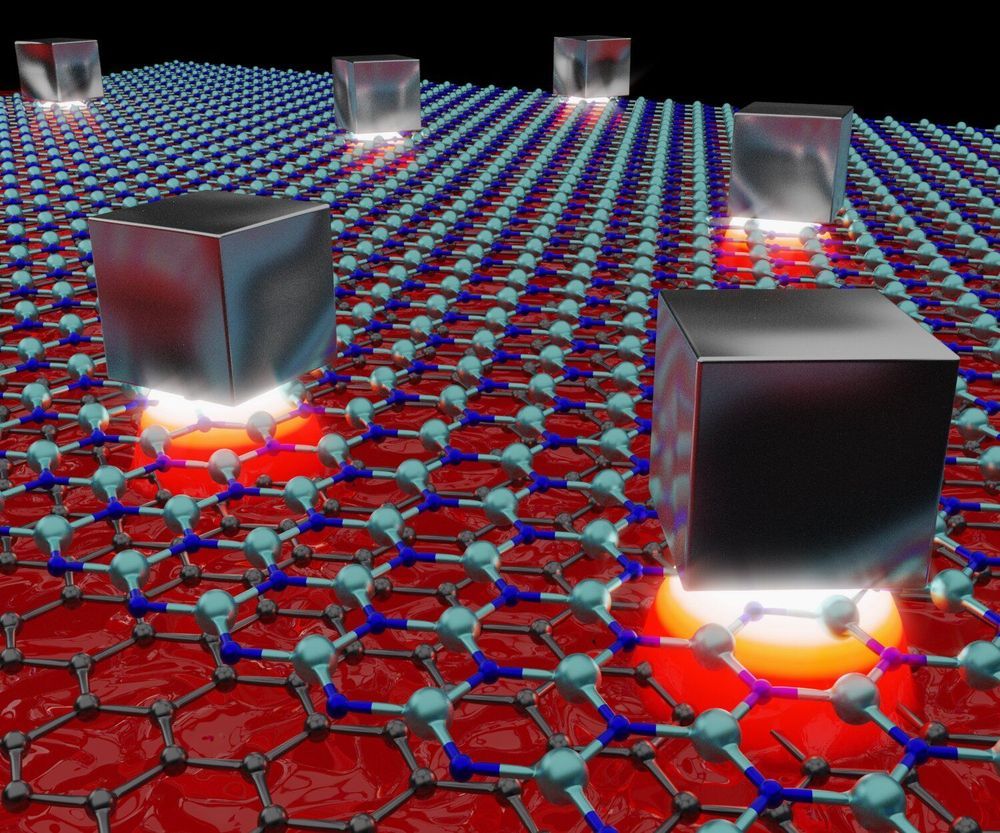
In that aspect, graphene, a material composed from a single layer of carbon atoms, which exhibits exceptional optical and electrical properties, is capable of guiding light in the form of plasmons, which are oscillations of electrons that strongly interact with light. These graphene plasmons have a natural ability to confine light to very small spaces. However, until now, it was only possible to confine these plasmons in one direction, while the actual ability of light to interact with small particles like atoms and molecules resides in the volume into which it can be compressed. This type of confinement in all three dimensions is commonly regarded as an optical cavity.