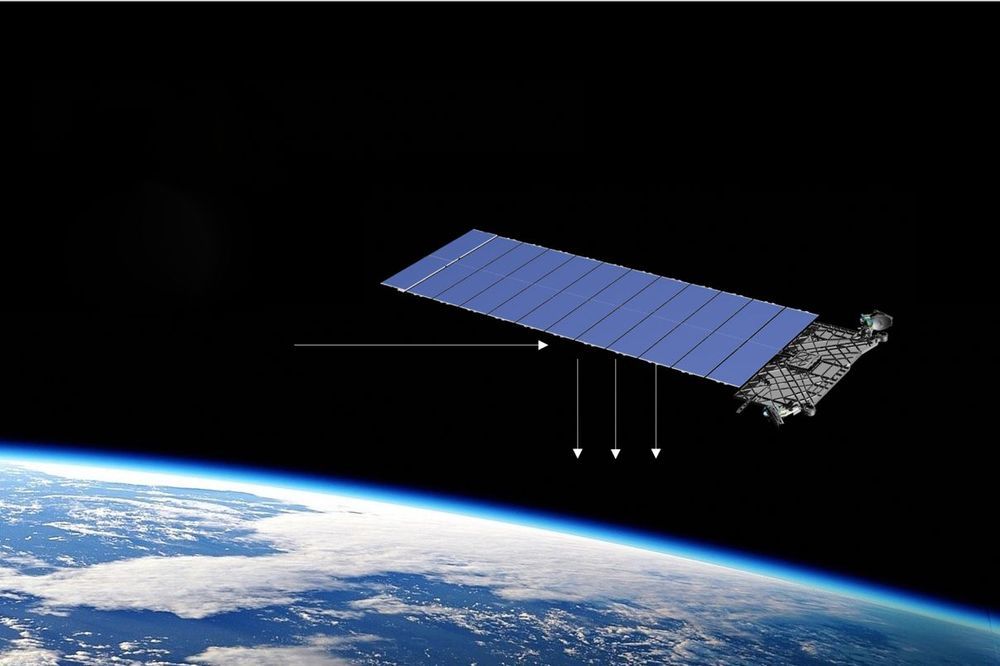
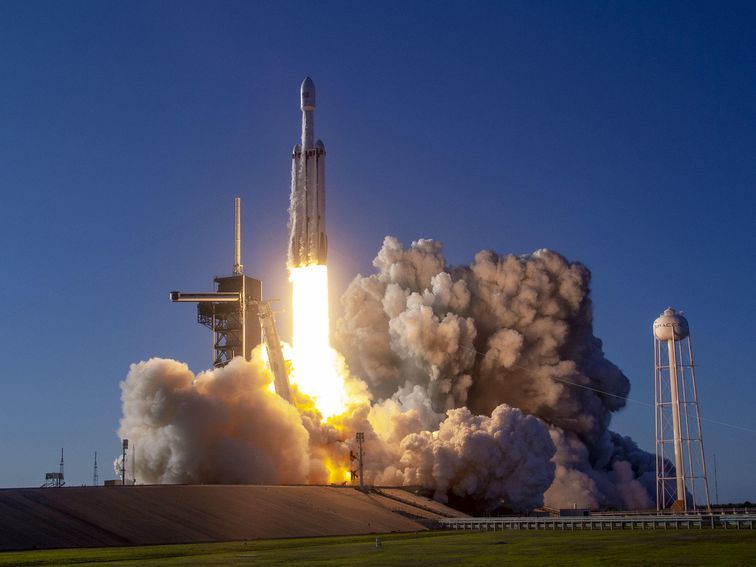
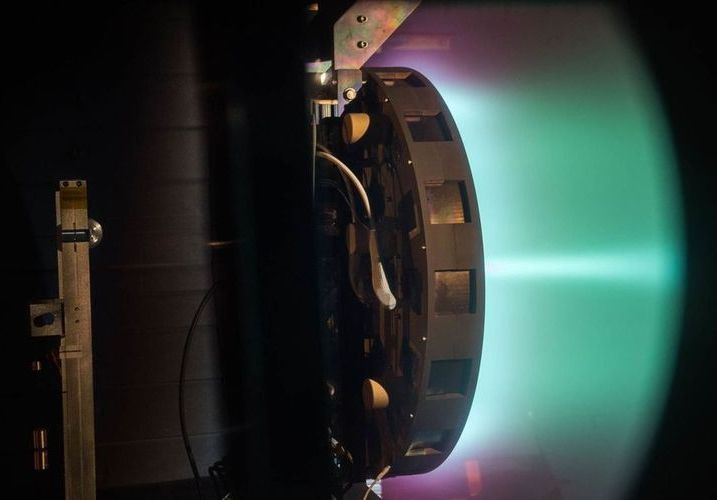
These propulsion systems already help satellites stay in position and spacecraft explore the solar system. Now engineers want to build a bigger one that could take us to Mars.
Category: satellites
SpaceX has announced that it will mount a sun visor on each of its Starlink satellites and have them perform controlled maneuvers, to make them less visible to members of the astronomy community making detailed observations of the night sky. SpaceX has already launched over 400 satellites to bolster a constellation that could one day provide global broadband internet access.
The proliferation of satellite technology and the increasing affordability of reaching low-Earth orbit (LEO) has led many – particularly those in the science community – to raise concerns about the impact that space traffic may have on the night sky. This issue has only grown more contentious with the advent of the megaconstellation, which is the term used to describe vast swarms of satellites working as a network as they fly choreographed orbits through LEO space.
SpaceX’s Starlink megaconstellation is well underway to becoming a reality, and could one day provide high-speed, low latency satellite-based broadband on a global scale.
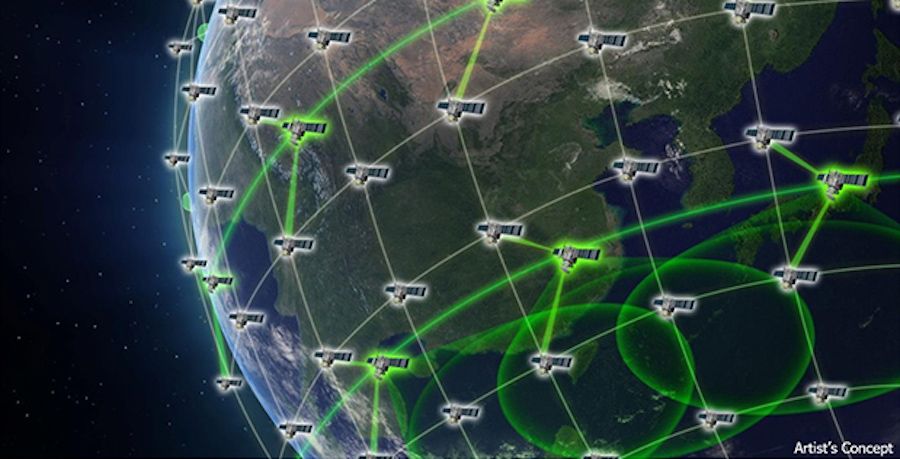
SEAKR Engineering, Inc. has been awarded as the prime contractor for Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Pit Boss contract to further expand its contractual work supporting the Blackjack program. The award for Phase I Option II is part of a three-phase effort seeking on-orbit demonstration of full processing capability in a multi-satellite constellation. SEAKR was first awarded a DARPA Pit Boss contract in October 2019.
DARPA’s Blackjack program focuses on integrating commercial satellite technologies into a constellation of military satellites. As sole prime, SEAKR will continue developing it’s Pit Boss solution to support the Blackjack program’s mission as a next generation on-board processor.
SEAKR said the solution will leverage off-the-shelf electronics adapted through design implementation to function reliably in space. The company said this award validates its program success in seeking on-orbit demonstration of state-of-the-art processing capability incorporating autonomous operations, Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning techniques, and bridged terrestrial and on-orbit technologies.
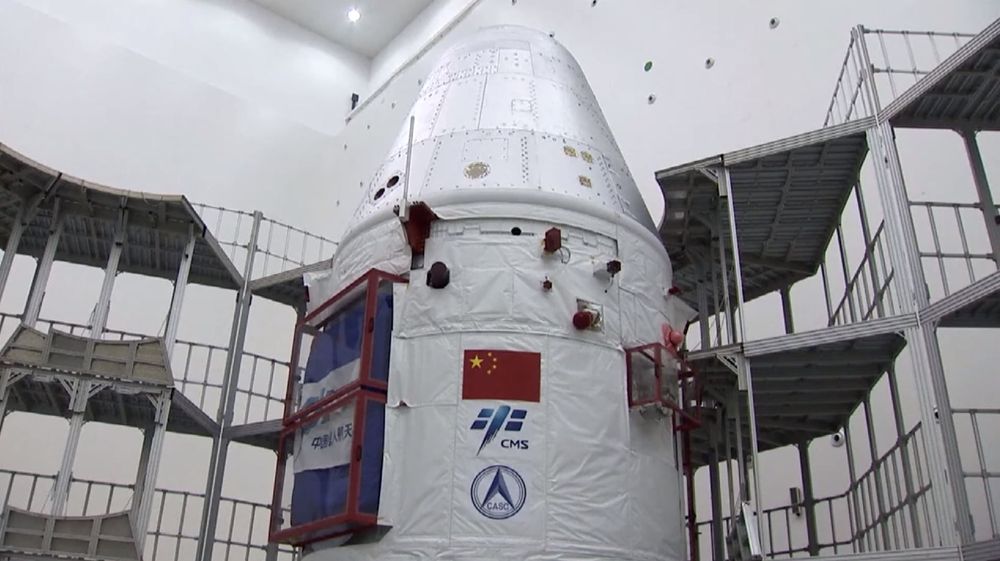
HELSINKI — China rolled out a Long March 5B launcher Wednesday for a mission to prove space station launch capabilities and test a new spacecraft for deep space human spaceflight.
Images of the Long March 5B shared on Chinese social media indicated that the rollout at Wenchang Satellite Launch Center was completed early April 29.
Launch from the coastal Wenchang launch site can now be expected around May 5. However, an official announcement has not yet been made.
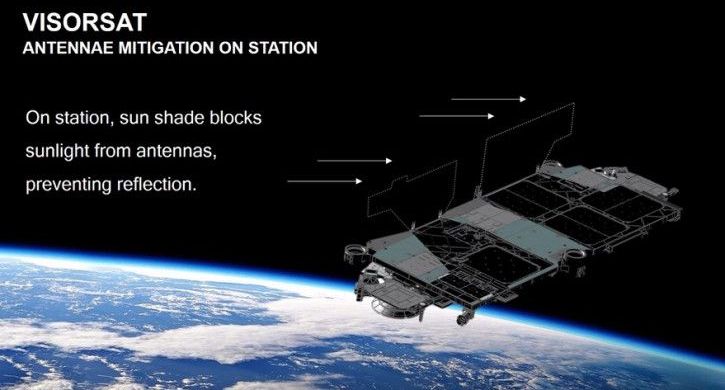
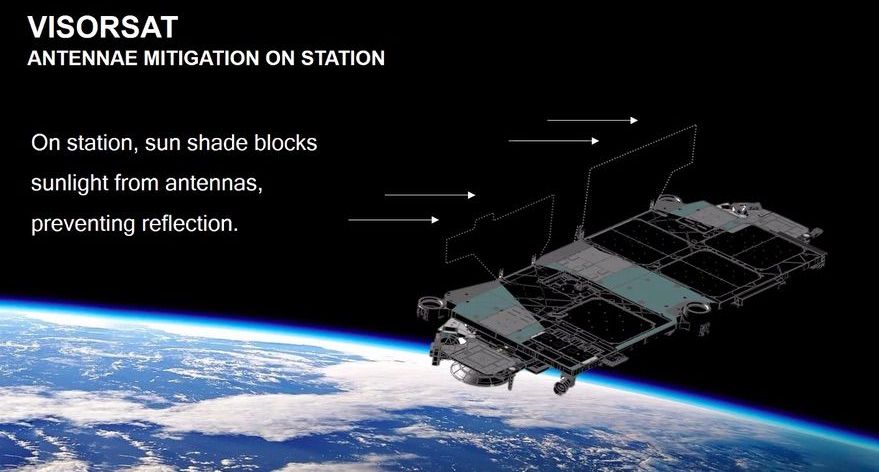
During a virtual conference briefing this week, SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk provided more details about a new plan that his company has to mitigate the impact of their Starlink satellite constellation on night sky observation. Musk first revealed on Twitter the intent to build a “sun visor” to lower their visibility, but we didn’t know much about how it would work or how it compared to the test dark paint job that SpaceX tried previously.
As reported by Space News, SpaceX’s new “VisorSat” approach will essentially use sun visors to block inbound sunlight from hitting the reflective antennas on the spacecraft, stopping them from reflecting said light back to Earth, which is why they appear as bright lights in the night sky.
This new hardware addition to future Starlink satellites will supplement other measures, including making use of a new method for changing the orientation of the satellites as they raise into their target orbits after launch, which is a period during which they’re especially visible. The overall goal, according to Musk, is to “make the satellites invisible to the naked eye within a week, and to minimize the impact on astronomy,” with a specific focus on ensuring that whatever impact the constellation does have doesn’t impeded the ability of scientists and researchers to make new discoveries.
Iran has apparently lofted its first military satellite into orbit, ending a series of setbacks for the nation’s space program.
A two-stage Qassed rocket lifted off from the Markazi Desert in central Iran on Wednesday (April 22) and successfully delivered a military reconnaissance satellite called Nour to orbit, Al-Jazeera reported. The rocket could be seen successfully launching into soace in this video from Iran’s Tasnim News Agency and PressTV.
Musk also tries to assure scientists his Starlink satellites won’t ruin the sky as many fear, and says he’d like to help send more observatories into orbit.
WASHINGTON — SpaceX Chief Executive Elon Musk said April 27 that he hopes to test a new way to reduce the brightness of the company’s Starlink satellites on the next launch for the broadband megaconstellation.
In a briefing to a committee working on the next astrophysics decadal survey, Musk said the experimental “VisorSat,” along with a new approach for orienting Starlink satellites as they raise their orbits, should address concerns raised by astronomers that the Starlink constellation could interfere with their observations.
“Our objectives, generally, are to make the satellites invisible to the naked eye within a week, and to minimize the impact on astronomy, especially so that we do not saturate observatory detectors and inhibit discoveries,” Musk said.
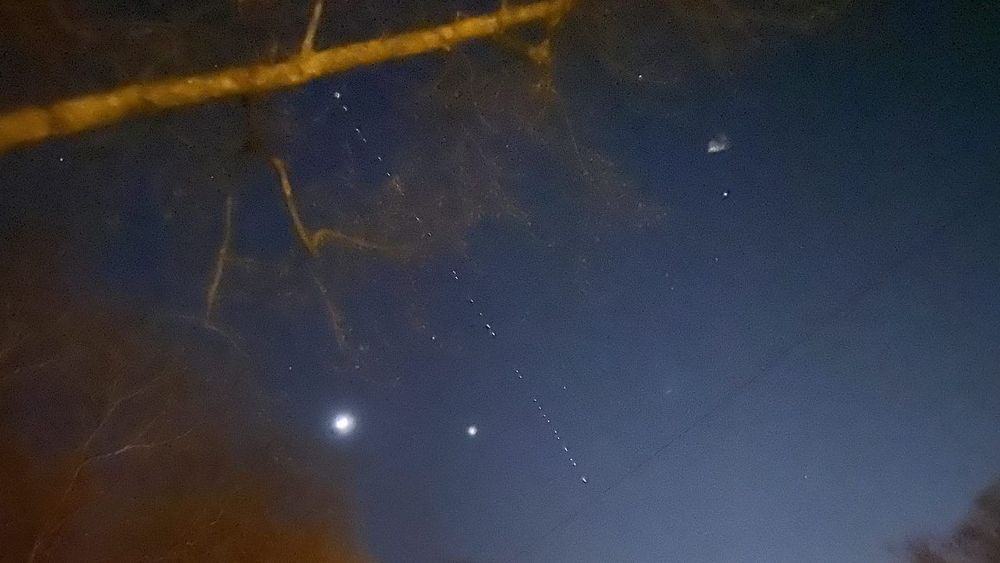
We’re getting many calls and emails from WGN viewers who say they spotted a strange string of lights crossing the night sky on Sunday.
No, it’s not planes flying in formation or a meteor shower. It’s actually a satellite string that’s part of SpaceX’s “Starlink” project. You can read more about it below.
While much of the world economy stands still, SpaceX is running full speed ahead.
WASHINGTON — The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency awarded Lockheed Martin a $5.8 million contract for satellite integration work for the Blackjack program, the company announced April 24.
Blackjack is a project to deploy a constellation of 20 satellites in low Earth orbit by 2022 and demonstrate that a LEO system can provide global high-speed communications.
Lockheed Martin will define and manage interfaces between Blackjack’s satellite buses, payloads and the so-called Pit Boss autonomous data processor. The work will be performed at the company’s satellite manufacturing plant in Sunnyvale, California.