Smart phone apps provide nearly instantaneous navigation on Earth; the Deep Space Atomic Clock could do the same for future robotic and human explorers.
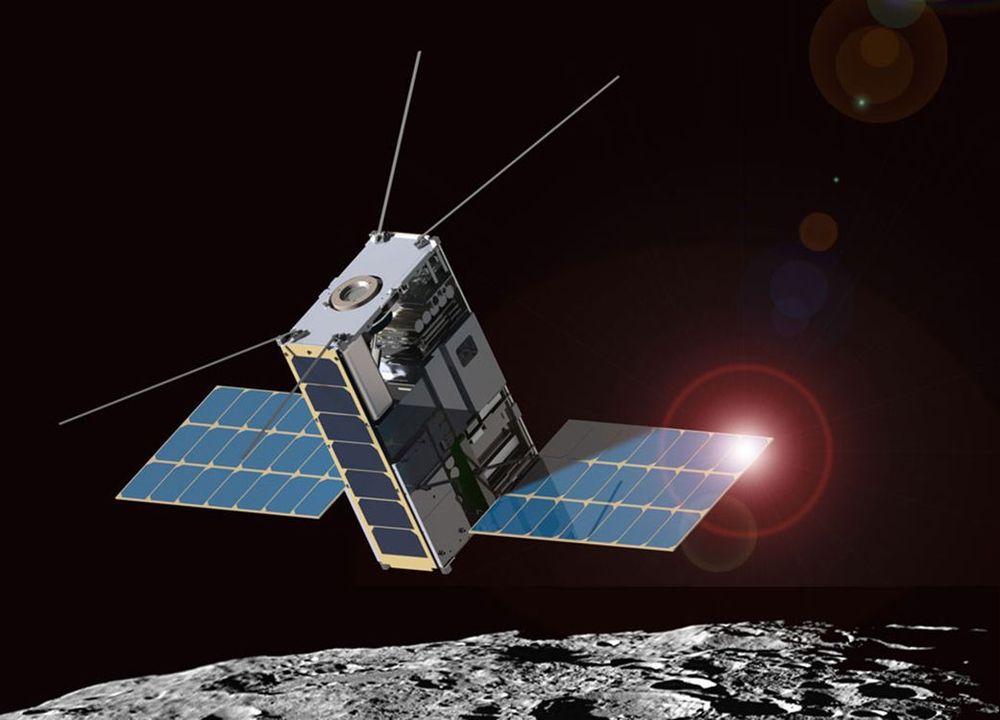
As the time when NASA will begin sending humans back to the Moon draws closer, crewed trips to Mars are an enticing next step. But future space explorers will need new tools when traveling to such distant destinations. The Deep Space Atomic Clock mission is testing a new navigation technology that could be used by both human and robotic explorers making their way around the Red Planet and other deep space destinations.
In less than a year of operations, the mission has passed its primary goal to become one of the most stable clocks to ever fly in space; it is now at least 10 times more stable than atomic clocks flown on GPS satellites. In order to keep testing the system, NASA has extended the mission through August 2021. The team will use the additional mission time to continue to improve the clock’s stability, with a goal of becoming 50 times more stable than GPS atomic clocks.