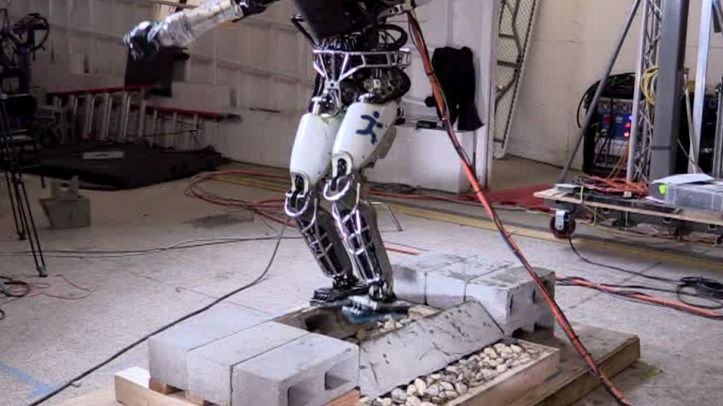
Researchers are also working on making sure that if and when the robot does take a tumble, it falls safely and doesn’t fracture its… er, circuit boards.




That’s the bad news.
The good news is that mental health professionals have smarter tools than ever before, with artificial intelligence-related technology coming to the forefront to help diagnose patients, often with much greater accuracy than humans.
A new study published in the journal Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, for example, showed that machine learning is up to 93 percent accurate in identifying a suicidal person. The research, led by John Pestian, a professor at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, involved 379 teenage patients from three area hospitals.

In Brief
Senator Ted Cruz opened up last Wednesday’s hearing by the US Senate Subcommittee on Space, Science, and Competitiveness with a description of the changing landscape of technology: “Whether we recognize it or not, artificial intelligence is already seeping into our daily lives.”
Senator Cruz explained that scientists are predicting how investments in AI will increase by more than 300 percent in the next few years, which means AI will have a more prominent role in society. With that in mind, the subcommittee’s hearing focused on the impact AI has in various sectors of US society, and how to best ensure US leadership in AI development.

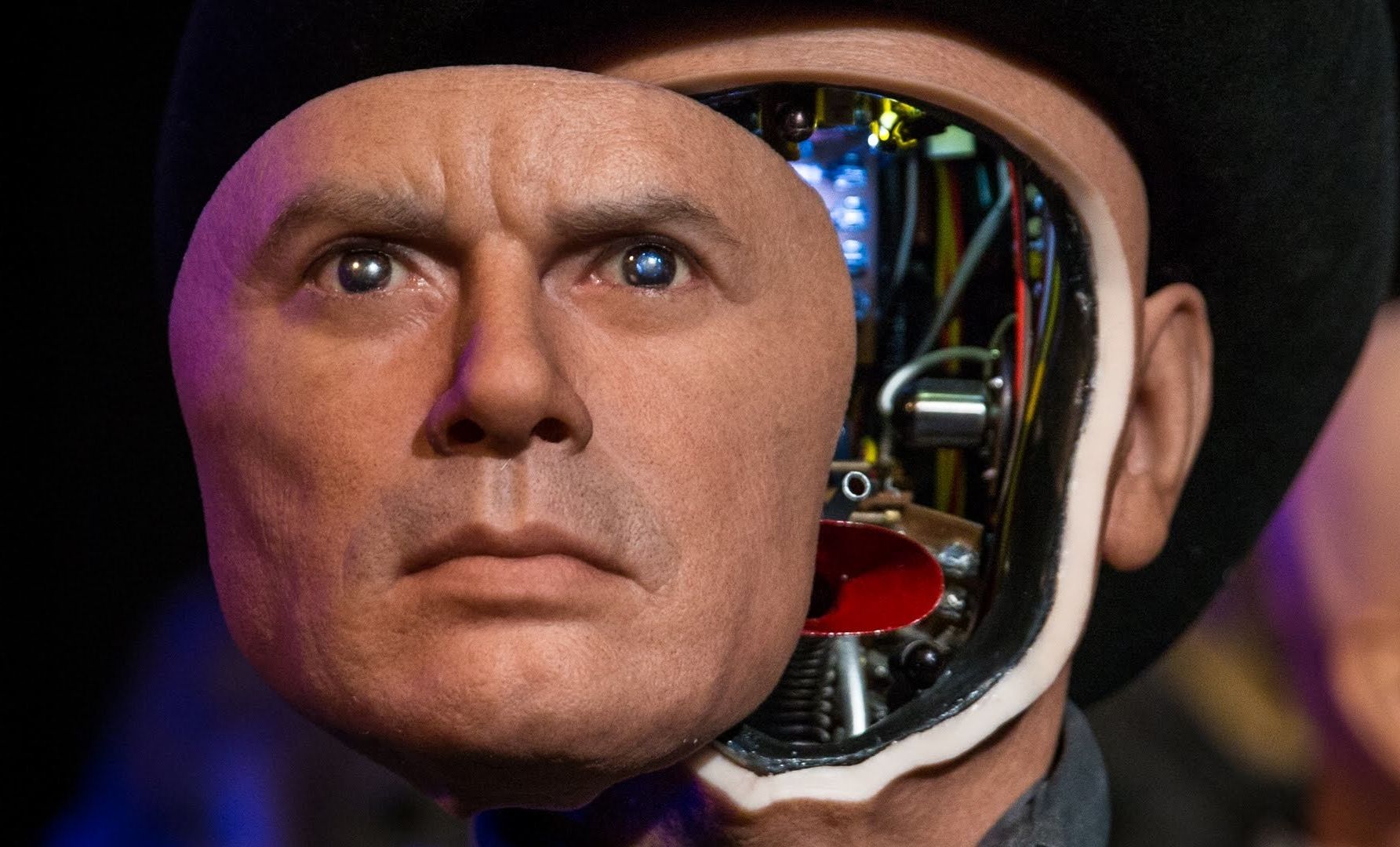
The goal of roboticists has long been to make A.I. as efficient as the human brain, and researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology just brought them one step closer.
In a recent paper, published in the journal Biology, scientists were able to successfully train a neural network to recognize faces at different angles by feeding it a set of different orientations for several face templates. Although this only initially gave the neural network the ability to roughly reach invariance — the ability to process data regardless of form — over time, the network taught itself to achieve full “mirror symmetry. Through mathematical algorithms, the neural network was able to mimic the human brain’s ability to understand objects are the same despite orientation or rotation.


AI (someday once things are more secured) is going to drastically reduce our cost of government. At least the VA believes AI is going to make them better at treating folks; my guess it’s a mix of cost saving potential via automation and improving diagnosis.
Flow Health and the VA are building a medical knowledge graph with deep learning to inform medical decision-making and train AI to personalize care plans.
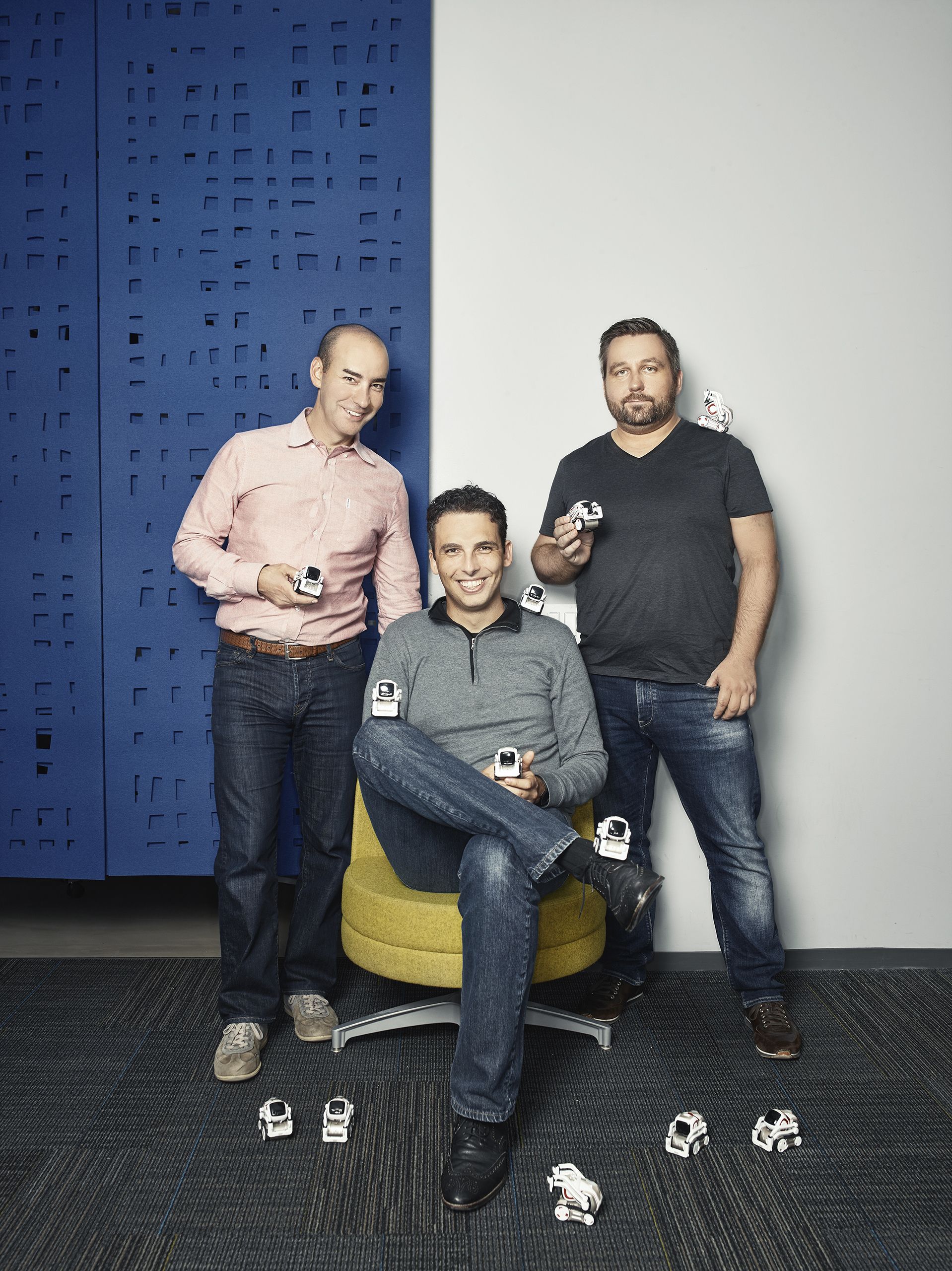

The first thing I learned about Cozmo is that it doesn’t like to stay put very long. Roused from slumber, the little robot’s face illuminates, and it begins zooming around the table in front of me. A moment later, it notices I’m watching and turns to greet me, saying my name with a computerized chirp.
Cozmo, which came out on Oct. 17, is the latest toy from six-year-old San Francisco startup Anki. It’s also an attempt to bring the burgeoning fields of robotics and artificial intelligence to consumers. While companies large and small work on both, applications tend to be in high-end computing, defense and government. Anki is betting toys will give the technologies a foothold at home. And Gartner predicts sales of such smart toys will grow, globally, from 8 million units this year to 421 million by 2020.
Toymakers have been cramming circuit boards and wireless chips into their products for years. Mattel and Hasbro, for example, sell high-tech versions of classics Barbie and Furby. But toys like Cozmo differ in the way they interact with the people and objects around them, changing their behavior over time as their software “learns.” Right out of the box, cameras and sensors allow Cozmo to recognize individuals, avoid falls or bumping into obstacles and play simple games like keep-away. But Anki says it will evolve; in December it will be able to recognize pets and learn new words. “Every input trigger, no matter what happens to him, will influence his future behavior,” says Hanns Tappeiner, Anki’s president.

Here is the bottom line: the companies that launches QC devices, network infrastructures (platforms, IaaS, SaaS, etc.) will win as everyone knows those billions invested by tech in AI will finally have the ROI that they need to show to their shareholders at the end of the day. When you have consumers and businesses too scared to use your products thanks to the Dark Web, etc. QC is your only way out of this mess.
Without QC infrastructure; means you’re AI investment is limited and you will not see the real ROI potential that you could have. And, synbio technology such as cell circuitry used to eradicate cancer and other illness or disabilities, connected humans, etc. will not have the level of adoption and performance we need to make this area impactful and life changing for so many. Personally, I look forward to a day when hospitals, going to the doctor, etc. are things of the past.
Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ: MSFT) can come up with its own scalable operational quantum computer by 2025. This could lead to quantum jump in MSFT stock in long term.

Technological unemployment speeding up, and the elite types as always trying to get the poor and middle class to go at each others throats, rather than address the elephant charging at both of them, that robots and AI are coming for all the jobs in under 10 years now.
Other states are also learning the same basic economic lesson: Customers have a limit to what they will pay for service. Voters in Washington, Colorado, Maine and Arizona voted to raise minimum wages on Election Day, convinced of the policy’s merits after millions of dollars were spent by union advocates. In the immediate aftermath, family-owned restaurants, coffee shops and even childcare providers have struggled to absorb the coming cost increase—with parents paying the cost through steeper childcare bills, and employees paying the cost through reduced shift hours or none at all.
The out-of-state labor groups who funded these initiatives aren’t shedding tears over the consequences. Like their Soviet-era predecessors who foolishly thought they could centrally manage prices and business operations to fit an idealistic worldview, economic reality keeps ruining the model of all gain and no pain. This brings me to my last correct prediction, which is that the Fight for $15 was always more a creation of the left-wing Service Employees International Union (SEIU) rather than a legitimate grassroots effort. Reuters reported last year that, based on federal filings, the SEIU had spent anywhere from $24 million to $50 million on the its Fight for $15 campaign, and the number has surely increased since then.
This money has bought the union a lot of protesters and media coverage. You can expect more of it on November 29. But the real faces of the Fight for $15 are the young people and small business owners who have had their futures compromised. Those faces are not happy ones.