Driverless cars need superhuman senses. And for the most part they seem to have them, in the form of lidar, radar, ultrasound, near-infrared, and other sensors. But regular cameras, often forgotten about in favor of more exotic technologies, are incredibly important given they’re used to collect data that’s used to, say, read the messages on road signs. So Sony’s new image sensor is designed to give regular camera vision a boost, too.
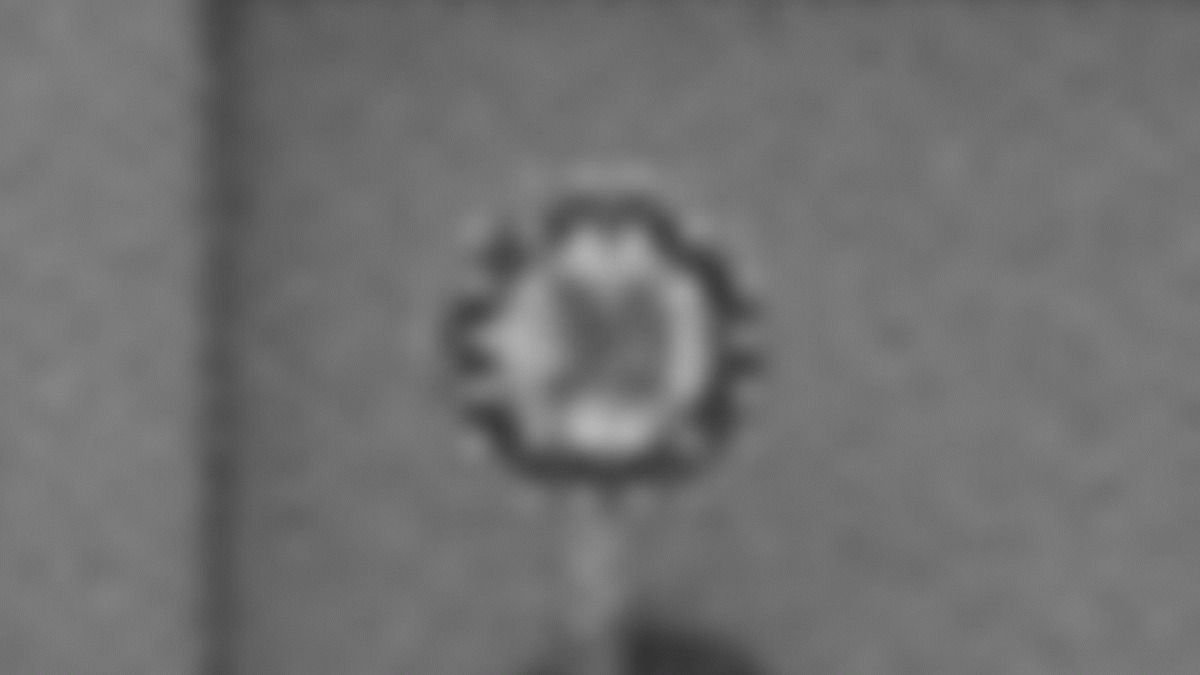
The new $90 IMX324 has an effective resolution of only 7.42 megapixels, which sounds small compared to your smartphone camera. But with about three times the vertical resolution of most car camera sensors, it packs a punch. It can see road signs from 160 meters away, has low-light sensitivity that allows it to see pedestrians in dark situations, and offers a trick that captures dark sections at high sensitivity but bright sections at high resolution in order to max out image recognition. The image above shows how much sharper the new tech than its predecessor from the same distance.
Don’t expect a beefed-up camera to eliminate the need for other sensors, though: even with strong low-light performance, cameras don’t work well in the dark, and they can’t offer the precise ranging abilities of other sensors. That means lidar and radar will remain crucial complements to humble optical cameras, however fancy they get.
Read more