Nanosized robots capable of crawling around on a person’s brain or underneath the skin may sound like a nightmare to some, but researchers suggest the mini machines could serve medical purposes such as gathering data on the brain or the spinal column.
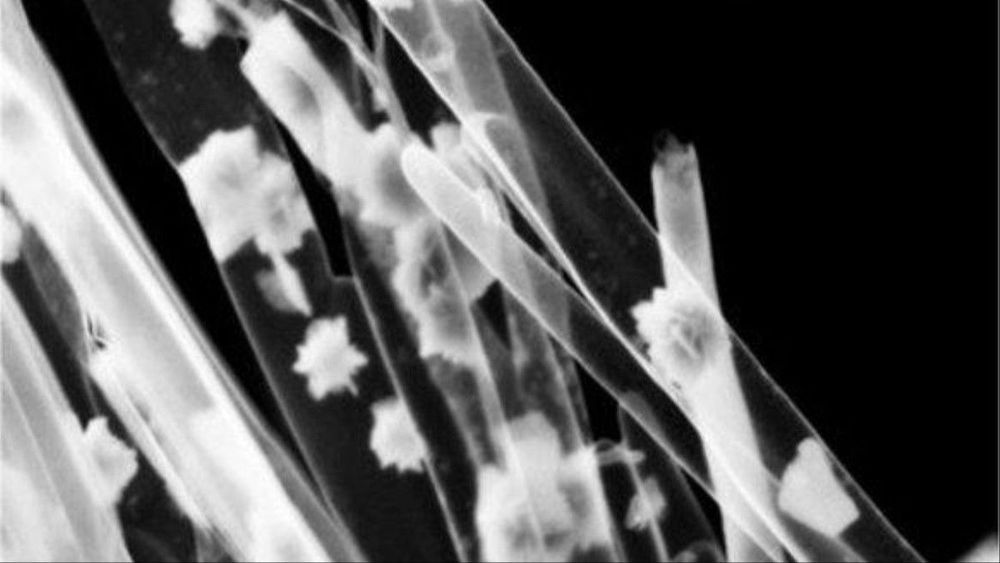
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and Cornell University recently announced they have built nanosized, solar-powered robots made from silicon. One million such robots can fit on a 4-inch silicon wafer. “These robots are built massively in parallel, so I don’t build just one robot, I build a million robots, which is awesome,” declares Marc Miskin, an assistant professor of electrical and systems engineering at the University of Pennsylvania.
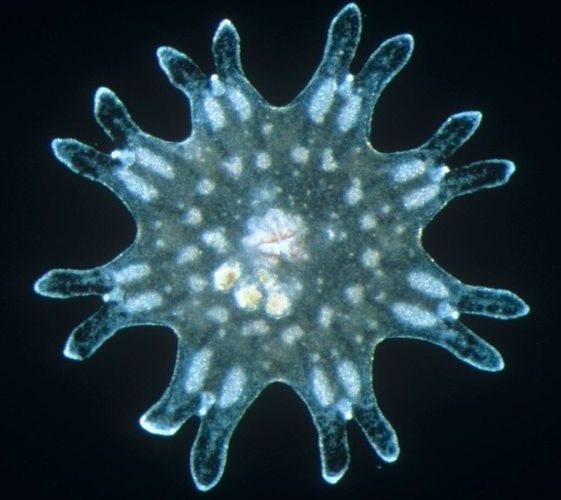
The microscopic machines can carry up to 30 times their own weight, travel at about the speed of biological cells, survive temperatures up to 400 degrees, live unscathed in battery acid or other harsh chemicals, and can be injected with a hypodermic needle.