Machine learning is part of every tech company’s pitch to consumers, but what does it mean for Apple? At WWWDC 2020, the company showed that it’s all about delivering small conveniences through iOS, the Apple Watch, HomeKit, and more.
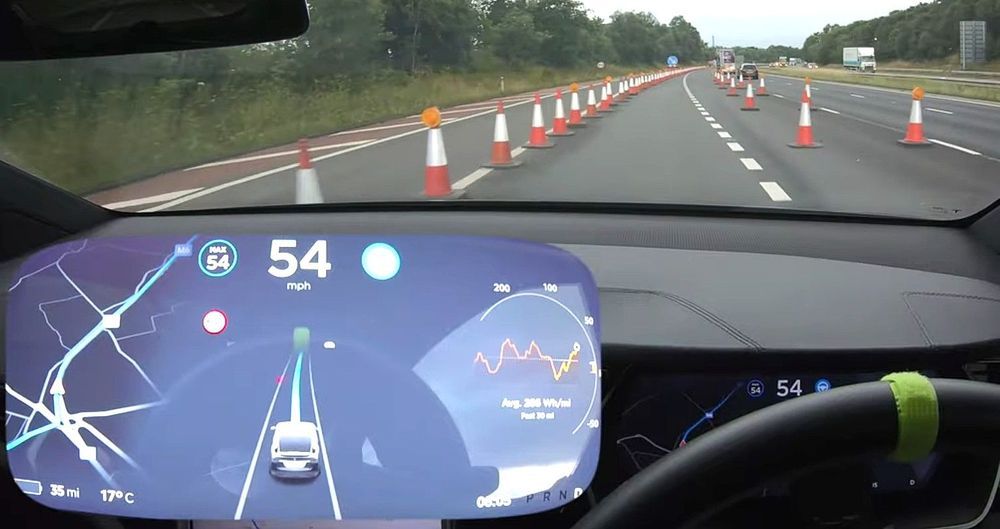



Tesla’s Full Self-Driving suite continues to improve with a recent video showing a Model 3 safely shifting away from a makeshift lane of construction cones while using Navigate on Autopilot.
Tesla owner-enthusiast Jeremy Greenlee was traveling through a highway construction zone in his Model 3. The zone contained a makeshift lane to the vehicle’s left that was made up of construction cones.
In an attempt to avoid the possibility of any collision with the cones from taking place, the vehicle utilized the driver-assist system and automatically shifted one lane to the right. This maneuver successfully removed any risk of coming into contact with the dense construction cones that were to the left of the car, which could have caused hundreds of dollars in cosmetic damage to the vehicle.

The article is providing an answer to the following questions that are relevant to the study of intelligence:
What is “understanding”?
How can we tell whether a system has it or not? https://bit.ly/3fynqYu
#AI #MechineLearning #neuroscience #consciousness #philosophy #technology #cognition #intelligence


A collective of more than 1,000 researchers, academics and experts in artificial intelligence are speaking out against soon-to-be-published research that claims to use neural networks to “predict criminality.” At the time of writing, more than 50 employees working on AI at companies like Facebook, Google and Microsoft had signed on to an open letter opposing the research and imploring its publisher to reconsider.
The controversial research is set to be highlighted in an upcoming book series by Springer, the publisher of Nature. Its authors make the alarming claim that their automated facial recognition software can predict if a person will become a criminal, citing the utility of such work in law enforcement applications for predictive policing.
“By automating the identification of potential threats without bias, our aim is to produce tools for crime prevention, law enforcement, and military applications that are less impacted by implicit biases and emotional responses,” Harrisburg University professor and co-author Nathaniel J.S. Ashby said.

A startup recently emerging from stealth is aiming to automate much of the process for feature development with the goal of making data scientists more self-reliant.
Circa 2010
Updated at 18:30 EST to correct timeline of prediction to 2030 from 2020 Reverse-engineering the human brain so we can simulate it using computers may be just two decades away, says Ray Kurzweil, artificial intelligence expert and author of the best-selling book The Singularity is Near. It would be the first step toward creating machines \[…\].
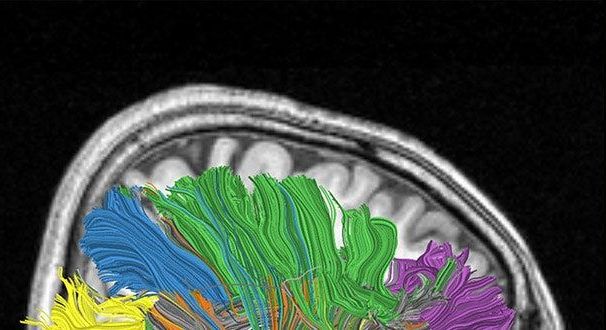
To create artificial general intelligence, we need to study the brain.

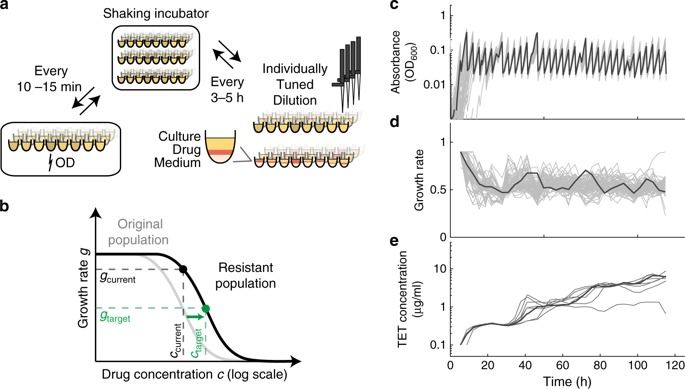
Genetic perturbations that affect bacterial resistance to antibiotics have been characterized genome-wide, but how do such perturbations interact with subsequent evolutionary adaptation to the drug? Here, we show that strong epistasis between resistance mutations and systematically identified genes can be exploited to control spontaneous resistance evolution. We evolved hundreds of Escherichia coli K-12 mutant populations in parallel, using a robotic platform that tightly controls population size and selection pressure. We find a global diminishing-returns epistasis pattern: strains that are initially more sensitive generally undergo larger resistance gains. However, some gene deletion strains deviate from this general trend and curtail the evolvability of resistance, including deletions of genes for membrane transport, LPS biosynthesis, and chaperones. Deletions of efflux pump genes force evolution on inferior mutational paths, not explored in the wild type, and some of these essentially block resistance evolution. This effect is due to strong negative epistasis with resistance mutations. The identified genes and cellular functions provide potential targets for development of adjuvants that may block spontaneous resistance evolution when combined with antibiotics.