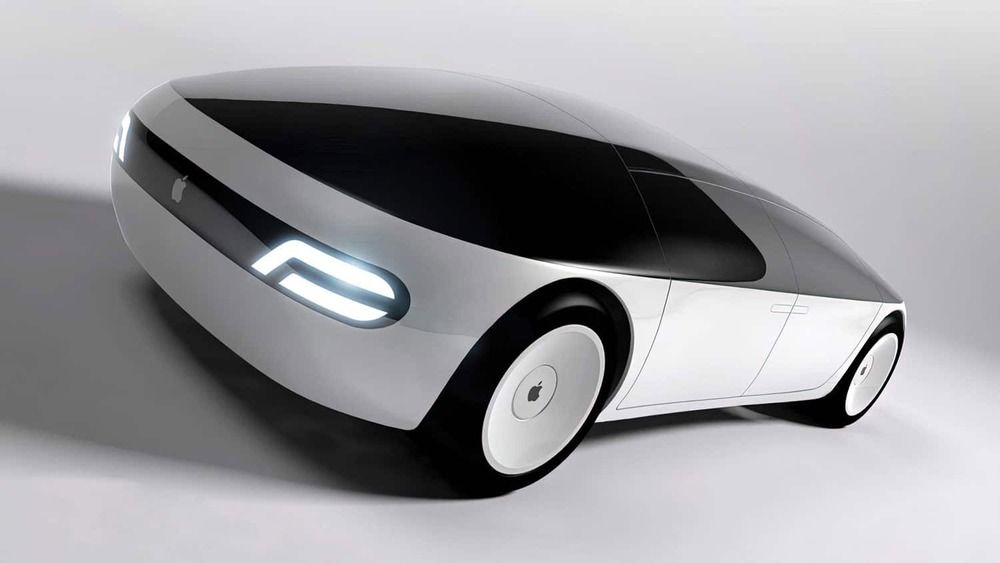
Apple’s first passenger car could include its own breakthrough battery technology.
Apple is actively working on various automotive projects that could ultimately lead to an “Apple Car” and is targeting 2024 to produce a passenger vehicle.


Honorable Mentions
One more scientific brilliance this year is the use of light in neuroscience and tissue engineering. One study, for example, used lasers to directly print a human ear-like structure under the skin of mice, without a single surgical cut. Another used light to incept smell in mice, artificially programming an entirely new, never-seen-in-nature perception of a scent directly into their brains. Yet another study combined lasers with virtual reality to dissect how our brains process space and navigation, “mentally transporting” a mouse to a virtual location linked to a reward. To cap it off, scientists found a new way to use light to control the brain through the skull without surgery—though as of now, you’ll still need gene therapy. Given the implications of unauthorized “mind control,” that’s probably less of a bug and more of a feature.
We’re nearing the frustratingly slow, but sure, dying gasp of Covid-19. The pandemic defined 2020, but science kept hustling along. I can’t wait to share what might come in the next year with you—may it be revolutionary, potentially terrifying, utterly bizarre or oddly heart-warming.
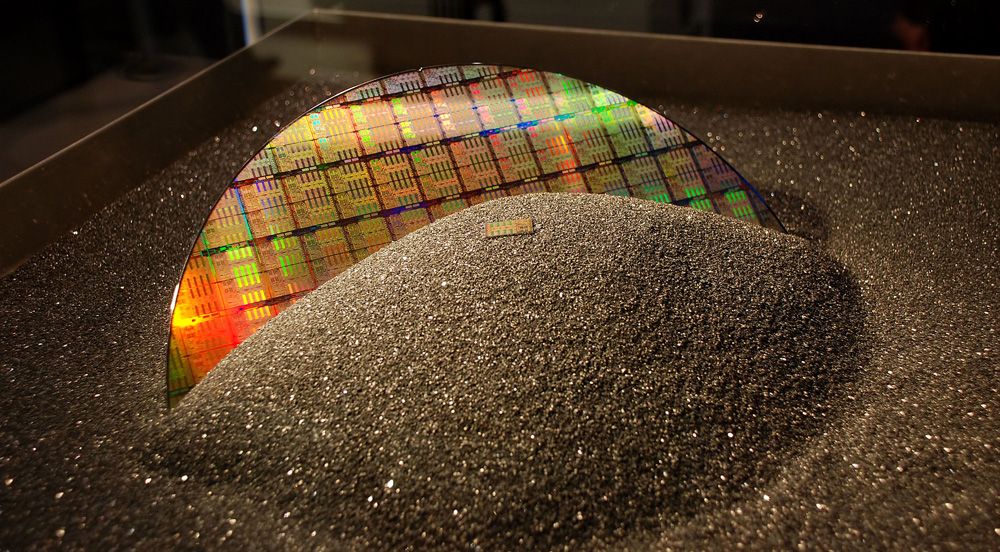
One of the ongoing questions these past few months has been why so many tech products have been so hard to buy. We’ve made repeated reference to known potential factors like COVID-19, economic disruptions, yield issues, and the impact of scalping bots, but there’s a new argument for what’s causing such general problems across so many markets: Insufficient investment in 200mm wafers.
Today, leading-edge silicon is invariably manufactured on 300mm wafers. Over the past few decades, manufacturers have introduced larger wafer sizes: 100mm, 150mm, 200mm, and 300mm have all been common standards at one time or another. In the PC enthusiast space, 300mm wafers have long been considered superior to 200mm wafers, because the larger wafer size reduces waste and typically improves the foundry’s output in terms of chips manufactured per day.
There aren’t that many commercial foundries still dedicated to 150mm or smaller wafer sizes, but a number of foundries still run 200mm fab lines. TSMC and Samsung both offer the node, as well as a number of second-tier foundries. GlobalFoundries has 200mm facilities, as do SMIC, UMC, TowerJazz, and SkyWater. A great many IoT and 5G chips are built on 200mm, as are some analog processors, MEMS devices, and RF solutions.

Even Apple wants to get into the automobile business it seems.
(Reuters) — Apple Inc is moving forward with self-driving car technology and is targeting 2024 to produce a passenger vehicle that could include its own breakthrough battery technology, people familiar with the matter told Reuters.
The iPhone maker’s automotive efforts, known as Project Titan, have proceeded unevenly since 2014 when it first started to design its own vehicle from scratch. At one point, Apple drew back the effort to focus on software and reassessed its goals. Doug Field, an Apple veteran who had worked at Tesla Inc, returned to oversee the project in 2018 and laid off 190 people from the team in 2019.
Since then, Apple has progressed enough that it now aims to build a vehicle for consumers, two people familiar with the effort said, asking not to be named because Apple’s plans are not public. Apple’s goal of building a personal vehicle for the mass market contrasts with rivals such as Alphabet Inc’s Waymo, which has built robo-taxis to carry passengers for a driverless ride-hailing service.
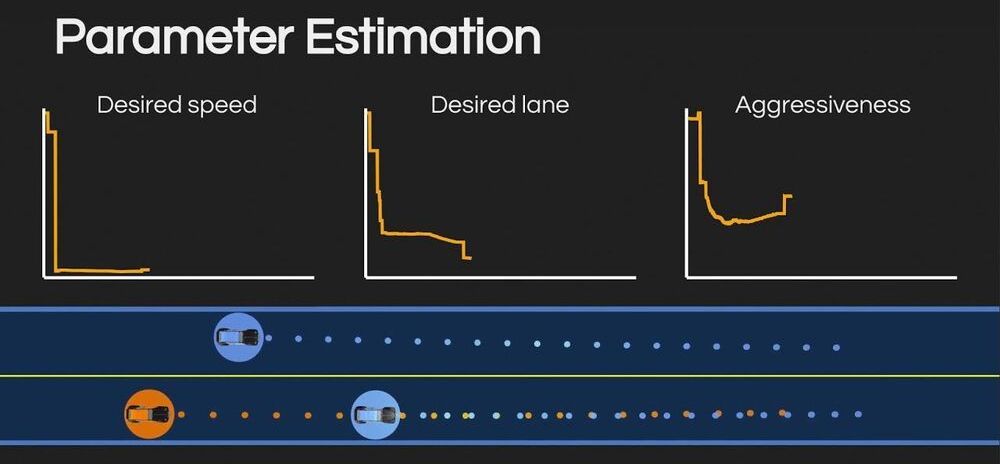
While many self-driving vehicles have achieved remarkable performance in simulations or initial trials, when tested on real streets, they are often unable to adapt their trajectories or movements based on those of other vehicles or agents in their surroundings. This is particularly true in situations that require a certain degree of negotiation, for instance, at intersections or on streets with multiple lanes.
Researchers at Stanford University recently created LUCIDGames, a computational technique that can predict and plan adaptive trajectories for autonomous vehicles. This technique, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, integrates an algorithm based on game theory and an estimation method.
“Following advancements in self-driving technology that took place over the past few years, we have observed that some driving maneuvers, such as turning left at an unprotected intersection, changing lanes or merging onto a crowded highway, can still be challenging for self-driving cars, while humans can execute them quite easily,” Simon Le Cleac’h, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “We believe that these interactions involve a significant part of negotiation between the self-driving vehicle and the cars in its surroundings.”

A team of scientists at Freie Universität Berlin has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) method for calculating the ground state of the Schrödinger equation in quantum chemistry. The goal of quantum chemistry is to predict chemical and physical properties of molecules based solely on the arrangement of their atoms in space, avoiding the need for resource-intensive and time-consuming laboratory experiments. In principle, this can be achieved by solving the Schrödinger equation, but in practice this is extremely difficult.
Up to now, it has been impossible to find an exact solution for arbitrary molecules that can be efficiently computed. But the team at Freie Universität has developed a deep learning method that can achieve an unprecedented combination of accuracy and computational efficiency. AI has transformed many technological and scientific areas, from computer vision to materials science. “We believe that our approach may significantly impact the future of quantum chemistry,” says Professor Frank Noé, who led the team effort. The results were published in the reputed journal Nature Chemistry.
Central to both quantum chemistry and the Schrödinger equation is the wave function —a mathematical object that completely specifies the behavior of the electrons in a molecule. The wave function is a high-dimensional entity, and it is therefore extremely difficult to capture all the nuances that encode how the individual electrons affect each other. Many methods of quantum chemistry in fact give up on expressing the wave function altogether, instead attempting only to determine the energy of a given molecule. This however requires approximations to be made, limiting the prediction quality of such methods.

The 60-year-old sub is preparing to take its deepest plunge yet. But in the age of autonomous machines, why are humans exploring the ocean floor at all?

Eighty-one years ago, our world-class research center in California’s Silicon Valley was born. Ground broke on Ames Research Center on Dec. 20, 1939. It was the second aeronautical laboratory established by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics to perform fundamental research on all things flight. From its very beginnings, Ames was a place for innovation. Tests performed in its wind tunnels transformed military aircraft during World War II and paved the way for air travel at supersonic speeds. In the 1950s and ‘60s, its researchers looked to the stars and came up with new designs and materials for spacecraft that would make human spaceflight a reality. Fast-forward to the present, and the center contributes to virtually every major agency mission through its expertise in spacecraft entry systems, robotics, aeronautics, supercomputing, and so much more! Here are things to know about Ames.
The Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover is the latest lunar exploration mission led by Ames. Launching in 2023, the mobile robot will search for water ice inside craters and other places at the Moon’s South Pole. Its survey will help pave the way for astronaut missions to the lunar surface beginning in 2024 as part of the Artemis program.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com/.
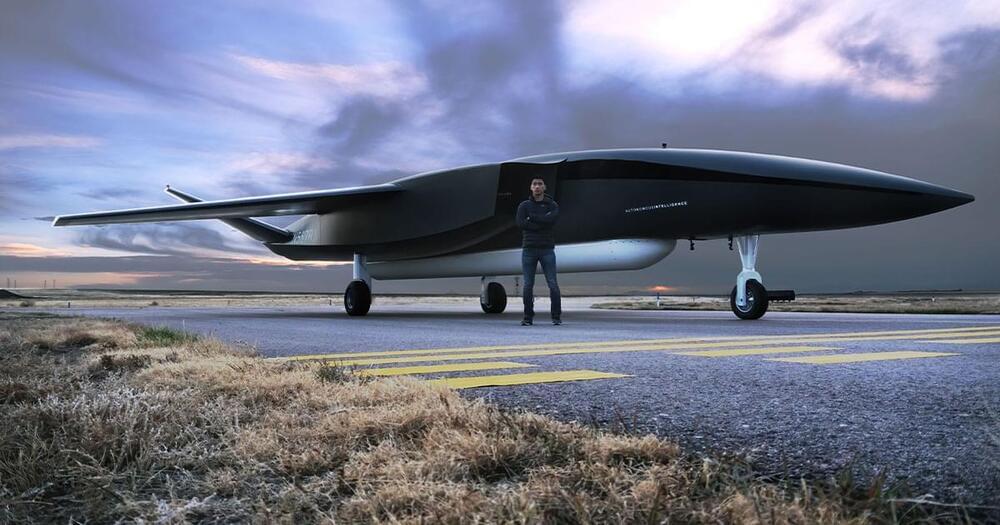

Go big or go home. This Alabama-based start-up just unveiled the biggest drone in the world — and it looks sublime. The massive drone, called the Ravn X, is designed to launch small satellites into orbit while airborne.
Aevum — the space startup — has worked mainly in the background, until yesterday when they unveiled their gigantic autonomous drone.
They built the high-altitude aircraft and launch vehicle to ferry satellites to orbit and improve space access — similar goals to space-tech leaders like Virgin Orbit, Rocket Lab, and SpaceX. But if you want to get ahead of the competition and can’t be the first, why not be the biggest?
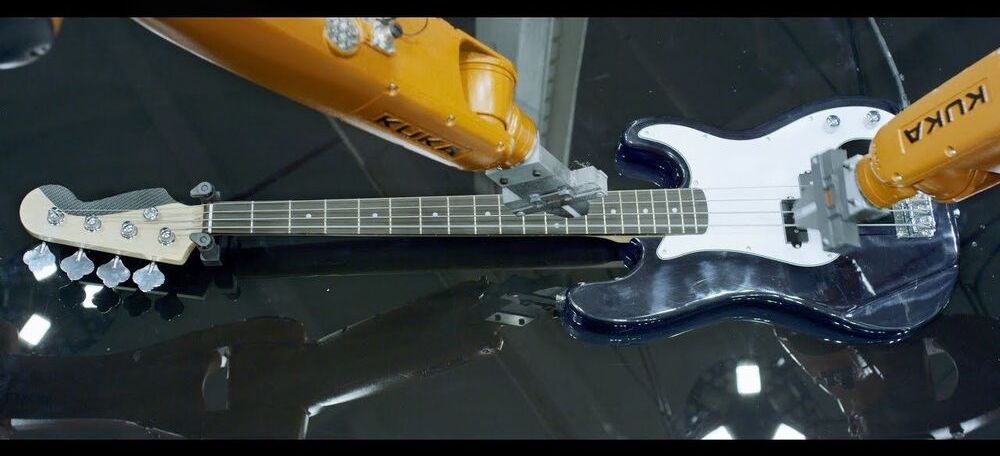

https://music.youtube.com/watch?v=bAdqazixuRY&list=RDAMVMbAdqazixuRY
► Album & 4k Video: http://NigelStanford.com/y/a-/Automatica.
► Spotify: http://NigelStanford.com/y/Spotify.
Subscribe and like to see more Robot videos, as I release them for my album Automatica.
Robots rock, they were fun to work with. My favorite is the robotic drummer. More work to be done, and maybe I could play with them live. Stay tuned smile Thank you to Kuka, Sennheiser and Roland.