Machine is so far able to identify eight common crimes such as fraud, gambling, dangerous driving and ‘picking quarrels’, researchers say.



In news that definitely doesn’t sound like a dystopian nightmare, researchers in China have developed a machine that can charge people with crimes using artificial intelligence.
The scientists claim the technology can decide on charges with more than 97 per cent accuracy, based on verbal descriptions of the case. The machine was built as a time-saving device and tested by the Shanghai Pudong People’s Procuratorate, the country’s busiest district prosecution office.
Trained using more than 17,000 cases dating from 2015 to 2020, it can run on a desktop computer and decides whether to press a charge by analysing hundreds of “traits” obtained from a human-generated case description, South China Morning Post reports.

Emerging technologies including AI, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), 5G, and blockchain (and related digital currencies) have all progressed on their own merits and timeline. Each has found a degree of application, though clearly AI has progressed the furthest. Each technology is maturing while overcoming challenges ranging from blockchain’s energy consumption to VR’s propensity for inducing nausea. They will likely converge in readiness over the next several years, underpinned by the now ubiquitous cloud computing for elasticity and scale. And in that convergence, the sum will be far greater than the parts. The catalyst for this convergence will be the metaverse — a connected network of always-on 3D virtual worlds.
The metaverse concept has wide-sweeping potential. On one level, it could be a 3D social media channel with messaging targeted perfectly to every user by AI. That’s the Meta (previously Facebook) vision. It also has the potential to be an all-encompassing platform for information, entertainment, and work.
There will be multiple metaverses, at least initially, with some tailored to specific interests such as gaming or sports. The key distinction between current technology and the metaverse is the immersive possibilities the metaverse offers, which is why Meta, Microsoft, Nvidia, and others are investing so heavily in it. It may also become the next version of the Internet.

As robotics is growing, tech enthusiasts are looking beyond the story of the evolution of robotics and learning deeply about what is robotics. This article deals with the robotics evolution.
A magnetic field can be used to switch nanolasers on and off, shows new research from Aalto University. The physics underlying this discovery paves the way for the development of optical signals that cannot be disturbed by external disruptions, leading to unprecedented robustness in signal processing.
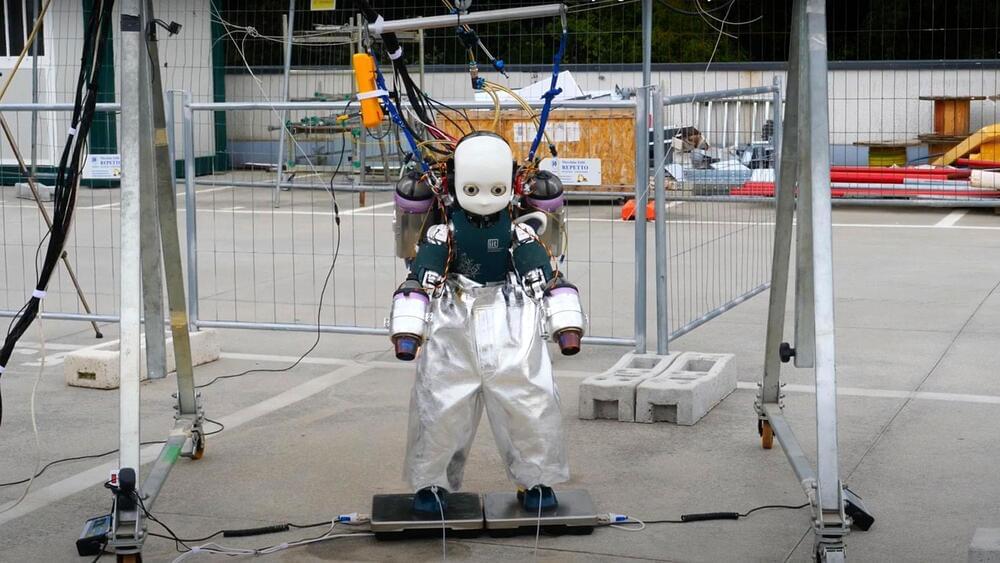

IRonCub is equipped with jet engines that will help make it fly.

Mars-sized object orbiting extremely closely to an M-dwarf star has been validated using the Penn State Habitable-zone Planet Finder (HPF). The planet, which was originally classified as a false positive in an automated search of data collected by the Kepler space telescope, is about half the size of Earth and is so close to its host star that it orbits in less than 10 hours. If it were orbiting a star the size of our sun it would be skimming the star’s corona—the aura of exceedingly hot plasma.
Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, along with solid, liquid, and gas. It is an ionized gas consisting of positive ions and free electrons. It was first described by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s.

The modern electric vehicle renaissance has been hampered from day one by the physical limitations imposed by the current state of battery technology. Inefficiencies in the form of heavy battery packs and low power densities have long limited not just the range and performance of EVs but the very forms they can take — there’s a reason Tesla started with a Roadster and not a Cybertruck. But steady advancements in power systems over the past few years — alongside skyrocketing demand for larger, electrified vehicles which cater to the US market — has led to a watershed moment in 2021: the emergence of EV pickups and SUVs.
Yes, we all know the Model X exists and Tesla “did it first” — spare me your tweets — however, the sheer number and variety of new, pure EV pickup and SUV models either ready to hit the showroom floor or in active development is staggering compared to just a few years ago. Let’s take a look at some of this year’s standouts.
GM is betting big on its proprietary Ultium battery technology, investing $35 billion in self-driving and EV technologies through 2025. The company has also announced that it intends to sell 30 EV models by the end of 2025 and EVs exclusively after 2035 with the 1,000 horsepower GMC Hummer EV serving as its vanguard offering.

The Neuro-Network.
𝐓𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐓𝐞𝐜𝐡 𝐅𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐔𝐓𝐒 𝐂𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐁𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐍𝐞𝐱𝐭 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝐢𝐧 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐑𝐨𝐛𝐨𝐭𝐬 𝐖𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐎𝐮𝐫 𝐁𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐬
𝙍𝙚𝙨𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙘𝙝𝙚𝙧𝙨 𝙖𝙩 𝙏𝙝𝙚 𝙐𝙣𝙞𝙫𝙚𝙧𝙨𝙞𝙩𝙮 𝙤𝙛 𝙏𝙚𝙘𝙝𝙣𝙤𝙡𝙤𝙜𝙮 𝙎𝙮𝙙𝙣𝙚𝙮 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙙𝙚𝙫𝙚𝙡𝙤𝙥𝙚𝙙 𝙖𝙣 𝙞𝙣𝙣𝙤𝙫𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 … See more.
This new biosensor developed by UTS researchers could be the next step in brain-controlled robotics, given its greater strength.
AutoML-Zero is unique because it uses simple mathematical concepts to generate algorithms “from scratch,” as the paper states. Then, it selects the best ones, and mutates them through a process that’s similar to Darwinian evolution.
AutoML-Zero first randomly generates 100 candidate algorithms, each of which then performs a task, like recognizing an image. The performance of these algorithms is compared to hand-designed algorithms.-Zero then selects the top-performing algorithm to be the “parent.”
“This parent is then copied and mutated to produce a child algorithm that is added to the population, while the oldest algorithm in the population is removed,” the paper states.