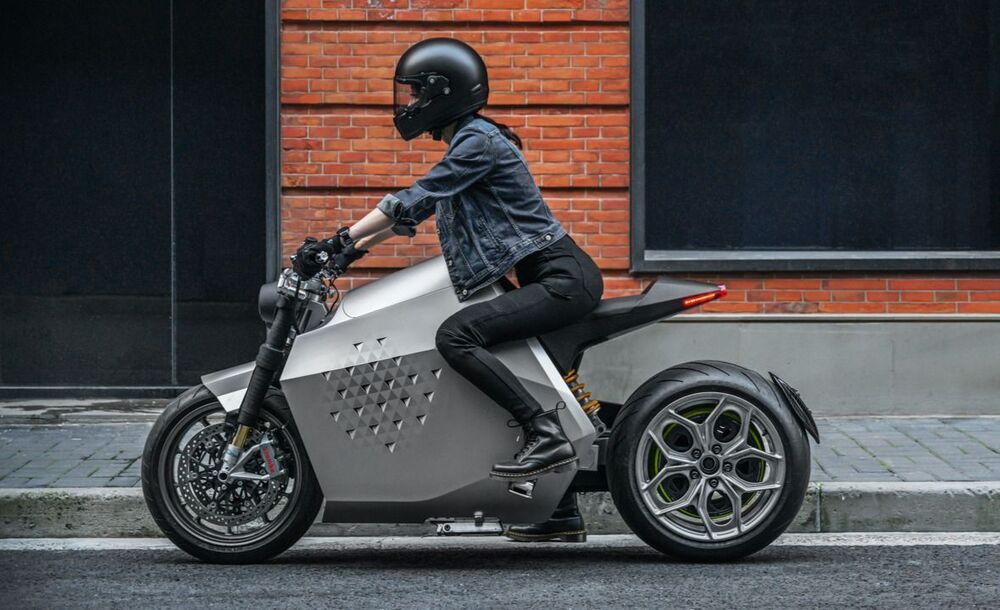
Beijing’s Da Vinci Dynamics has launched its DC100, a high-performance electric streetbike with an impressive 250-mile (400 km) NEDC range, and some wacky “robotic” tricks, including the alleged ability to self-balance and follow you around.
We’ve got ourselves a bit of a kitchen sinker here; Da Vinci has thrown all sorts of features at this one. But even some of the basic specs are a tad elusive. For starters, while it makes a peak of 135 horsepower, putting it very much in the “fast electric” category, the company says it runs “a smart control system that seamlessly integrates multiple different motors.” Who the what now? Multiple motors? A separate press release then states it’s actually 137 horsepower, running through a hub motor.
Peak torque is listed at a ludicrous 850 Nm (627 lb-ft), but then hub motors often have wild torque specs; witness the outrageous Verge TS, with a hub motor that doesn’t even need a middle in it to break 1000 Nm (738 lb-ft). The DC100 will sprint from 0–100 km/h in somewhere between 3–4 seconds, so crazy torque or no crazy torque, a well-ridden gixxer will still see it off at the lights.