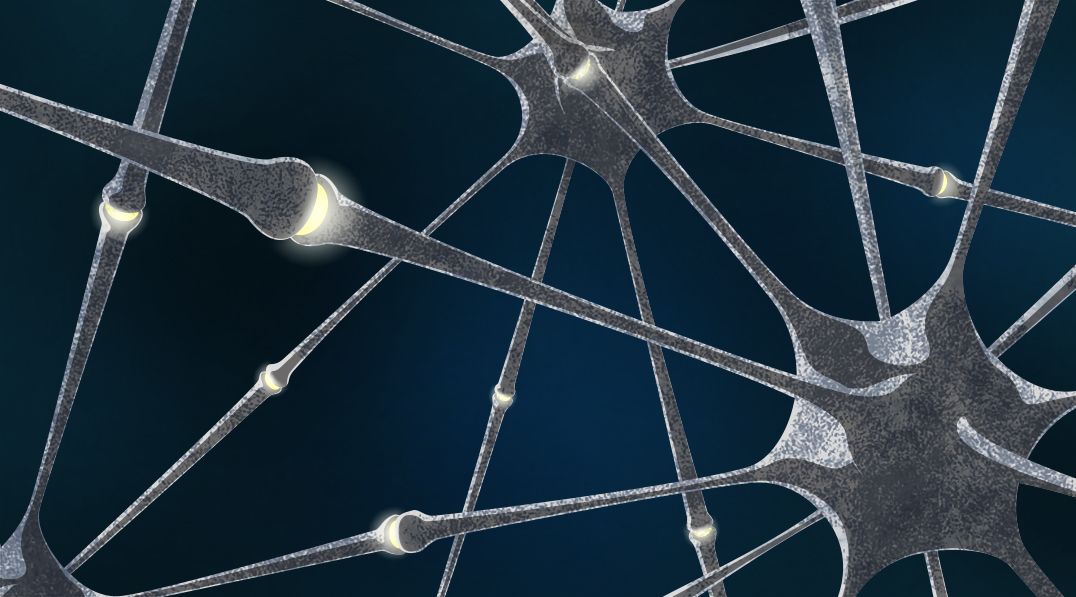
Russian scientists have managed to make nanoscale hafnium oxide-based memristors showcase synaptic properties.



I too believe AI could be bigger in the future once the under pinning technology and infrastructure moves to Quantum Technology so that hacking is under control and performance is where it needs to be.
When Mark Zuckerberg thinks about the future, he sees a world that’s dominated by mobile devices and virtual reality, but when Google CEO Sundar Pichai thinks about the future, all he sees is artificial intelligence. He suggested as much during Alphabet’s quarterly earnings call on Thursday, saying that mobile devices and virtual reality will dominate the immediate future, but that they’ll eventually be surpassed in importance by artificial intelligence. However, he didn’t go into detail about what this future will look like.
Artificial intelligence is nothing new at Google, but today we learned just how big a role top boss Sundar Pichai sees AI playing in our future. Answering an analyst query on Google-parent company Alphabet’s Q1 2016 earnings call about how the company is leading innovation, rather than simply adapting to changes in technology, Pichai talked about his role in projecting where Alphabet is going in the next 10 years. He gave a shout out to VR as the hot new platform, and then wrapped up his comments by saying: “In the long run, I think we will evolve in computing from a mobile-first world to an AI-first world.” Earlier in the call he cited Google’s DeepMind AlphaGo super computer defeating a human champion as an extraordinary achievement. He also said the company is investing in AI and machine learning, areas that are taking off and beginning to bear real-world benefits.
I almost snickered at this article because many of us have been highlighting many of the issues with AI. I am glad to see someone else also speaking up with the bigger issue with AI which is poor security due to the existing net infrastructure.
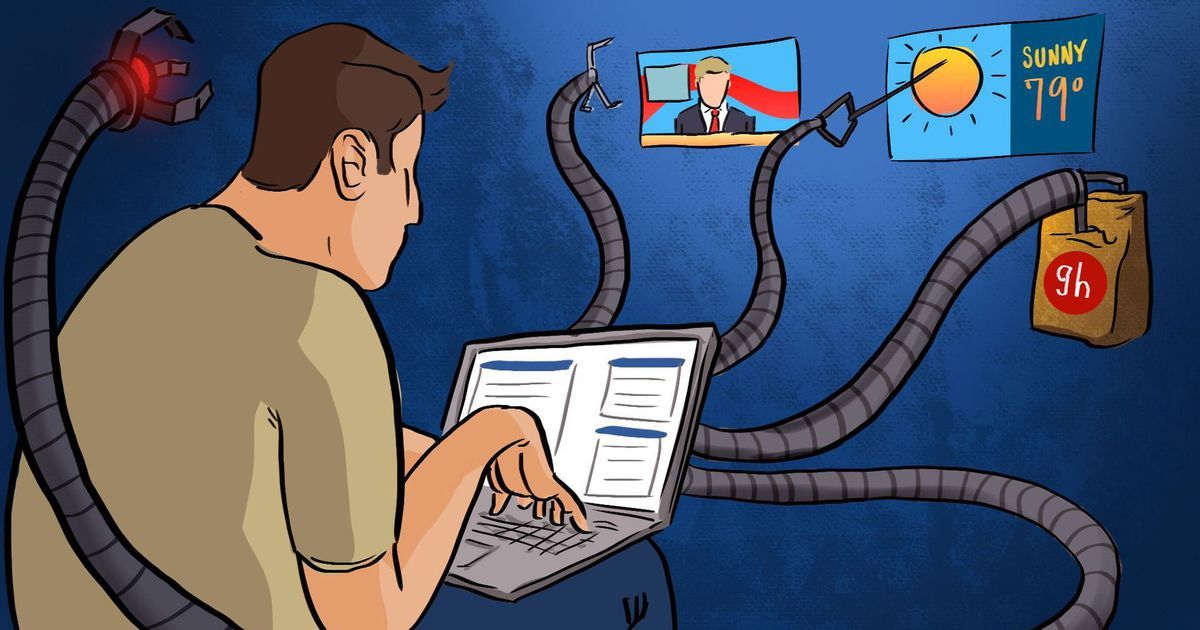
Facebook and others are all working on simplifying users’ lives with bots, but these novel interactive programs change the game in terms of security.
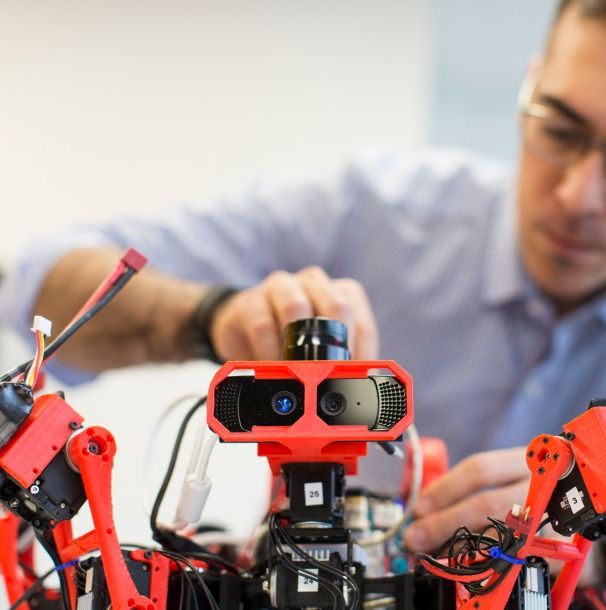

Good luck convincing business and consumers to buy your autonomous spider-bot.
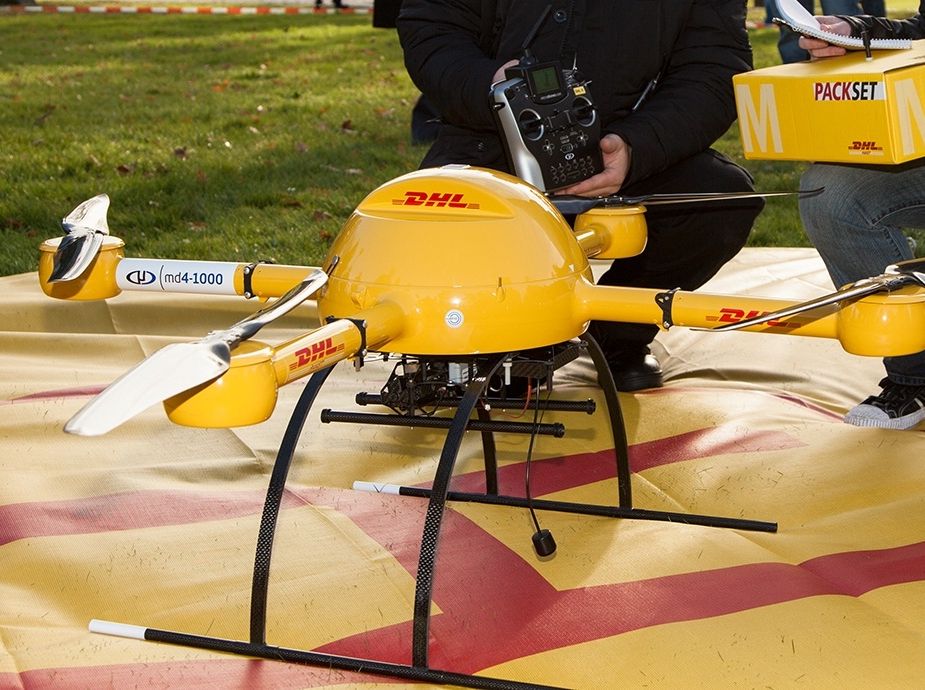
There are a number of major tech-driven companies that are researching 3D printing technology at a rapid rate, but very few invest as much as time and money into additive manufacturing as Siemens does. Whether they’re building their own €21.4 million metal 3D printing facility or helping 3D printing startups with their endeavors, the global engineering company is betting big within the 3D printing industry. Now, a research team from Siemens Corporate Technology’s Princeton campus has just revealed their latest innovation, the development of autonomous mobile 3D printing devices, which are being called spider-bots.
These unique printing devices, which look like spider-like robots, were almost entirely designed and manufactured by the Siemens Corporate Technology research team. They’re engineered with an extruder similar to the type used with FDM printing, and are able to print in polylactic acid (PLA). The spider-bots are equipped with an onboard camera and a laser scanner as well, which enables them to become aware of the surrounding environment during the print job. Software-wise, they’re all programmed with a modified version of Siemens’ NX PLM software, which is their product development, engineering, and manufacturing software solution. In the near-future, the Siemens research team hopes to utilize these spider-bots within the automotive and aerospace industries.
Every year, the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program puts out the call to the general public, hoping to find better or entirely new aerospace architectures, systems, or mission ideas. As part of the Space Technology Mission Directorate, this program has been in operation since 1998, serving as a high-level entry point to entrepreneurs, innovators and researchers who want to contribute to human space exploration.
This year, thirteen concepts were chosen for Phase I of the NIAC program, ranging from reprogrammed microorganisms for Mars, a two-dimensional spacecraft that could de-orbit space debris, an analog rover for extreme environments, a robot that turn asteroids into spacecraft, and a next-generation exoplanet hunter. These proposals were awarded $100,000 each for a nine month period to assess the feasibility of their concept.
Of the thirteen proposals, four came from NASA’s own Jet Propulsion Laboratory, with the remainder coming either from other NASA bodies, private research institutions, universities and aerospace companies from around the country. Taken as a whole, these ideas serve to illustrate of the kinds of missions NASA intends to purse in the coming years, as well as the cutting-edge technology they hope to leverage to make them happen.

It may sound like sci-fi. But millions and millions of dollars are pouring into projects to mine asteroids and the moon. And with a space gold rush comes space pirates.
With trillions of dollars worth of minerals lying just under the moon’s surface or spinning around the solar system inside asteroids, space mining is big business.
Well, big potential business. No one has dug nickel out of an asteroid or scooped any tantalum from the lunar dust—at least not for profit. Before space miners can get drilling, they need to invent specialized industrial robots, set up orbital outposts and—arguably most importantly—convince investors, workers, and prospective buyers that space minerals are worth the cost and effort of mining them.


Bots are only as good as their under pinning legacy infrastructure/ networks. Glad to see this article and someone speaking again for investors outside SV.
Bots hit the mark on every pattern Silicon Valley loves. But for investors and entrepreneurs — and executives outside of San Francisco trying to figure out what this bot business is all about — it’s worth taking a step back and looking at this frenzy with fresh eyes and a bigger picture.
Simple interactions between people — making a connection, following and messaging — when captured in a digital network of people who know each other already personally, professionally or by reputation, have created a handful of extremely valuable networks where three billion people today spend the majority of their time.
Facebook pages are like the once-vibrant amusement park that got knocked down for condos.