Change is coming; will you be ready?
I remember many decades ago when folks were trying to learn a new OS that changed businesses, governments/ educational institutions, and households around the world. That OS was called Windows; and hearing the stories as well as watching people try to use a PC and a mouse was interesting then.
Now, the world will again go through a large scale metamorphosis again when more and more QC is evolved and made available over the next 5 to 7 years in the technology mainstream. Change is often necessary and often can be good as well.
You might ask yourself, “What is quantum computing, and how do I get involved?”
Before we begin to explain quantum computing, a brief glimpse of the past is essential to understand how quantum computing came to be.
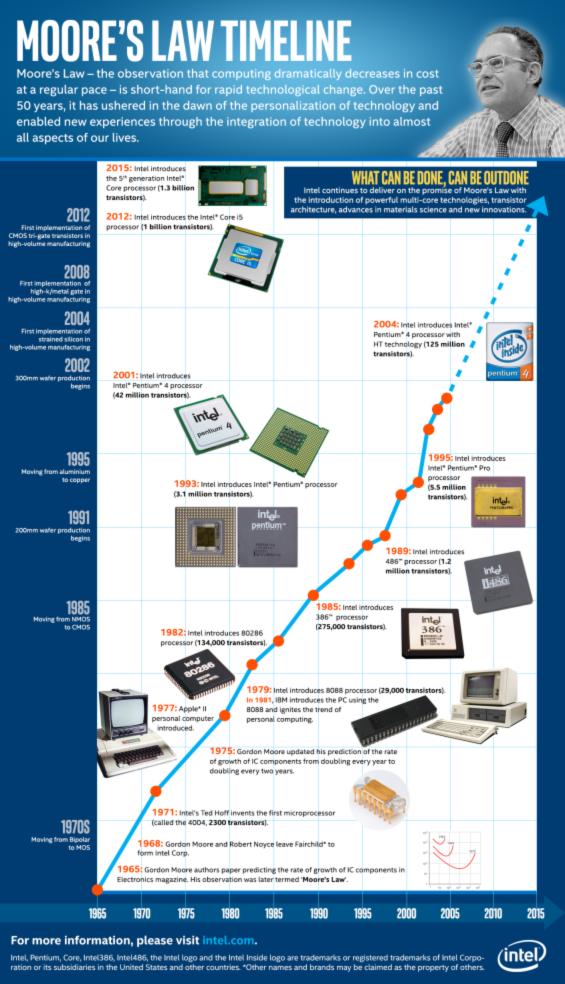
From our very first laptop to the laptops we have today, it is clear that technology is exponentially advancing faster than our expectations. Phones and computers get thinner and faster, but why? Thanks to the effects of Moore’s Law, which states that the number of transistors in a dense circuit will double approximately every two years, the amount of “stuff” needed to be put on a board is more densely packed.
Read more