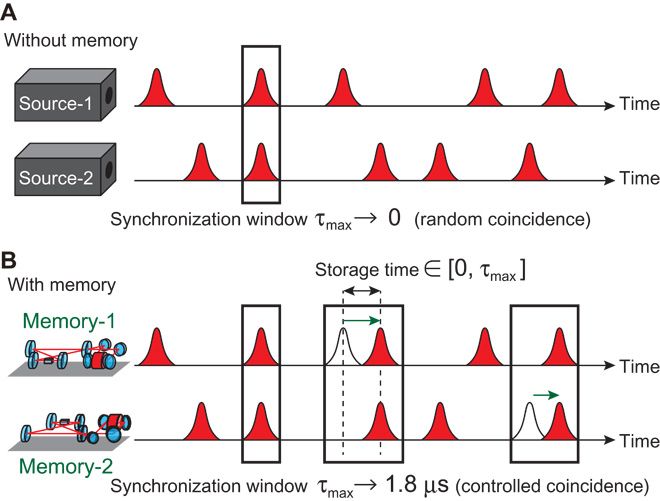
Wonderful! We’re well on our way of making QC more available on many devices in the near future.
Creating quantum computers which some people believe will be the next generation of computers, with the ability to outperform machines based on conventional technology—depends upon harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics, or the physics that governs the behavior of particles at the subatomic scale. Entanglement—a concept that Albert Einstein once called “spooky action at a distance”—is integral to quantum computing, as it allows two physically separated particles to store and exchange information.
Stevan Nadj-Perge, assistant professor of applied physics and materials science, is interested in creating a device that could harness the power of entangled particles within a usable technology. However, one barrier to the development of quantum computing is decoherence, or the tendency of outside noise to destroy the quantum properties of a quantum computing device and ruin its ability to store information.
Nadj-Perge, who is originally from Serbia, received his undergraduate degree from Belgrade University and his PhD from Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. He received a Marie Curie Fellowship in 2011, and joined the Caltech Division of Engineering and Applied Science in January after completing postdoctoral appointments at Princeton and Delft.