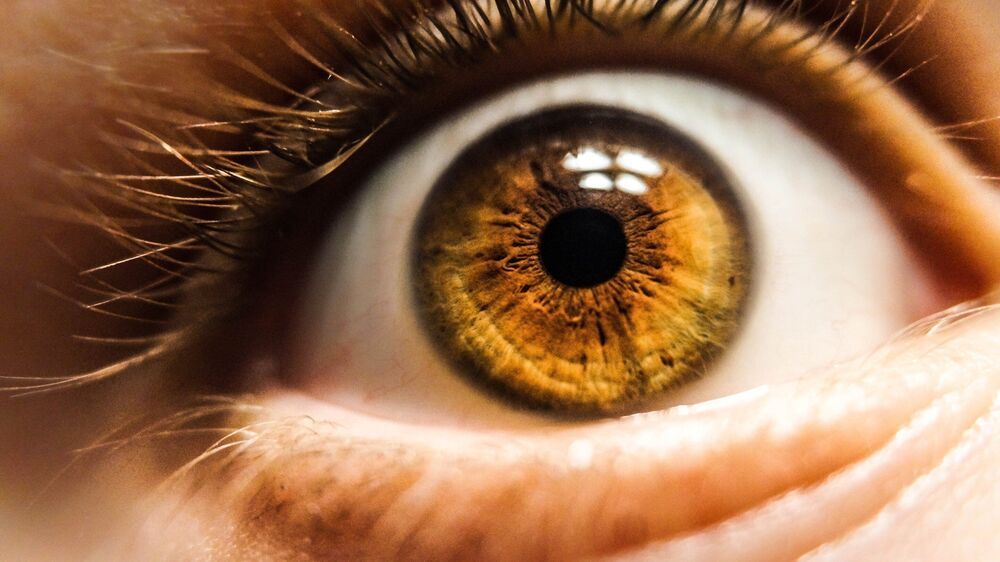
Researchers at Oregon State University are making key advances with a new type of optical sensor that more closely mimics the human eye’s ability to perceive changes in its visual field.
The sensor is a major breakthrough for fields such as image recognition, robotics and artificial intelligence. Findings by OSU College of Engineering researcher John Labram and graduate student Cinthya Trujillo Herrera were published today in Applied Physics Letters.
Previous attempts to build a human-eye type of device, called a retinomorphic sensor, have relied on software or complex hardware, said Labram, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science. But the new sensor’s operation is part of its fundamental design, using ultrathin layers of perovskite semiconductors—widely studied in recent years for their solar energy potential—that change from strong electrical insulators to strong conductors when placed in light.