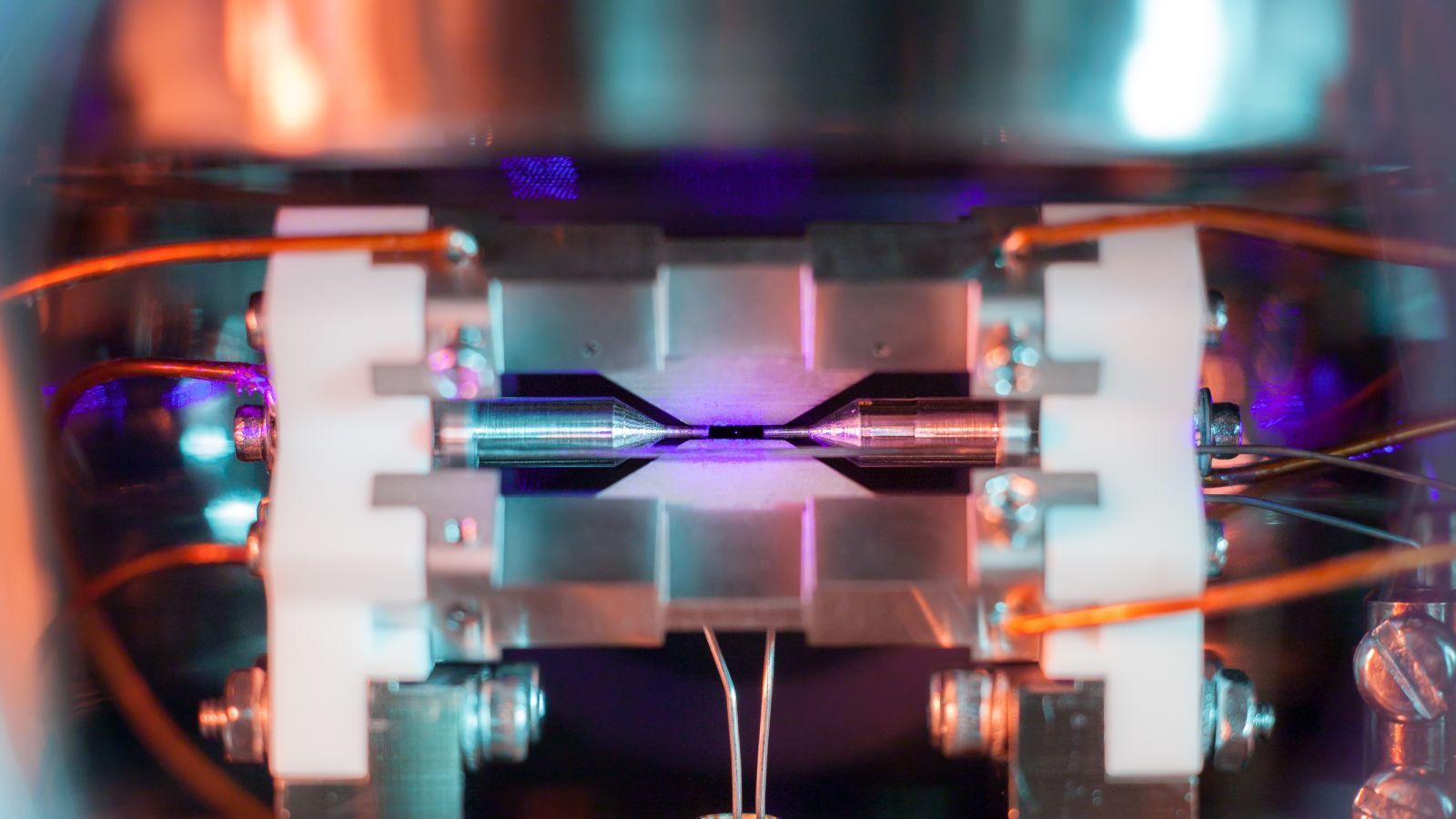
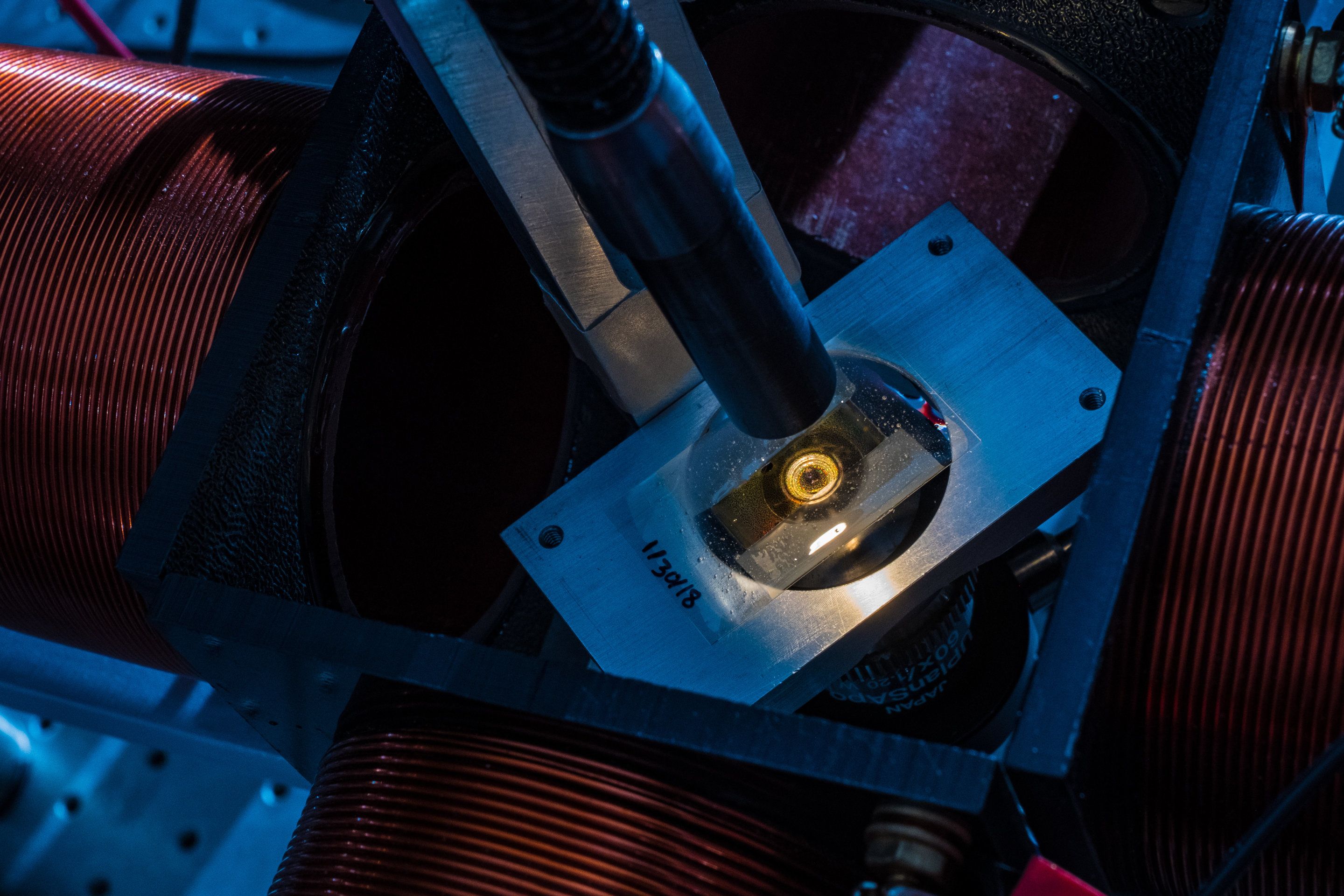
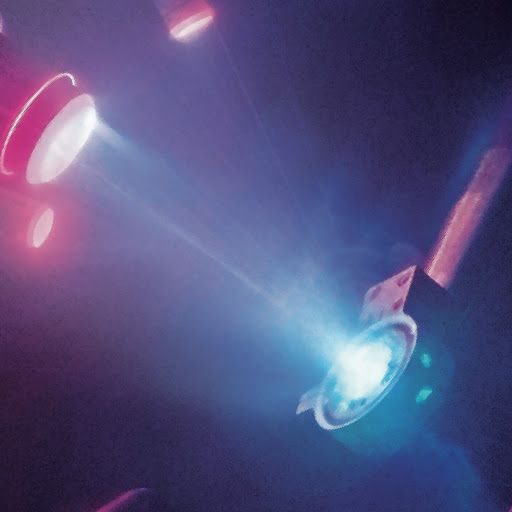
Zoom in close on the center of the picture above, and you can spot something you perhaps never thought you’d be able to see: a single atom. Here is a close-up if, you’re having trouble:
This strontium atom is emitting light after being excited by a laser, and it’s the winner of the UK’s Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) photography award. The EPSRC announced the winners of its fifth annual contest yesterday. Winning photographer David Nadlinger, graduate student at the University of Oxford, was just excited to be able to show off his research.
“It’s exciting to find a picture that resonates with other people that shows what I spend my days and nights working on,” Nadlinger told me. The best part, to him, was “the opportunity to excite people about my research, more than winning a competition.”
Read more