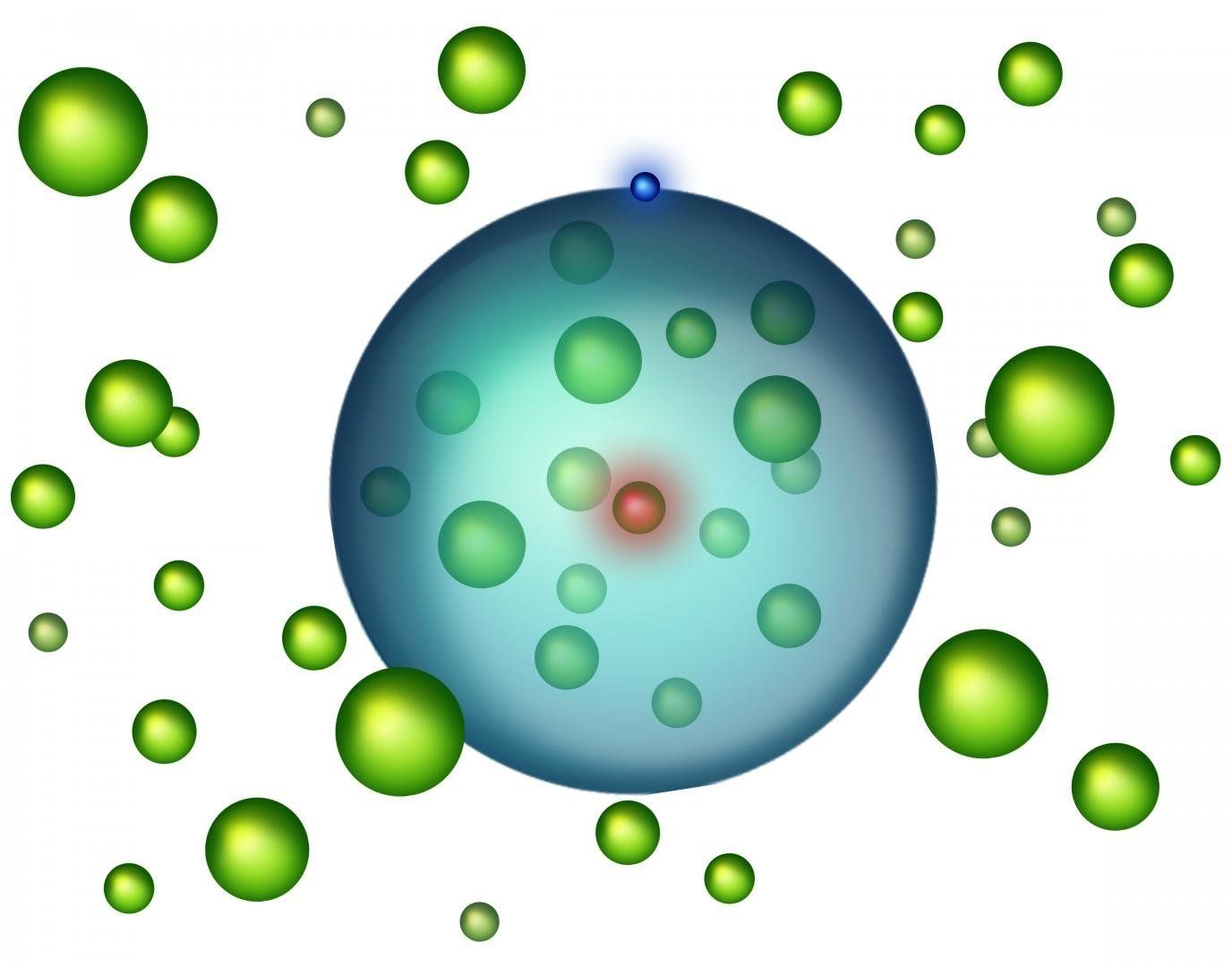
What is inside an atom between the nucleus and the electron? Usually there is nothing, but why could there not be other particles too? If the electron orbits the nucleus at a great distance, there is plenty of space in between for other atoms. A “giant atom” could be created, filled with ordinary atoms. All these atoms form a weak bond, creating a new, exotic state of matter at cold temperatures, referred to as Rydberg polarons.
A team of researchers has now presented this state of matter in the journal Physical Review Letters. The theoretical work was done at TU Wien (Vienna) and Harvard University, the experiment was performed at Rice University in Houston (Texas).
Two special fields of atomic physics, which can only be studied in extreme conditions, have been combined in this research project: Bose-Einstein condensates and Rydberg atoms. A Bose-Einstein condensate is a state of matter created by atoms at ultracold temperatures, close to absolute zero. Rydberg atoms are those in which one single electron is lifted into a highly excited state and orbits the nucleus at a very large distance.