Summary: NIH researchers have identified a specific type of sensory neurons which become activated as a result of pulling a single hair.
Source: NIH.
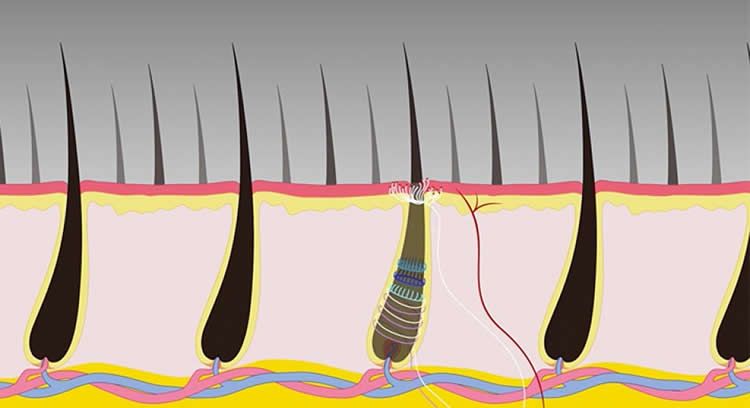
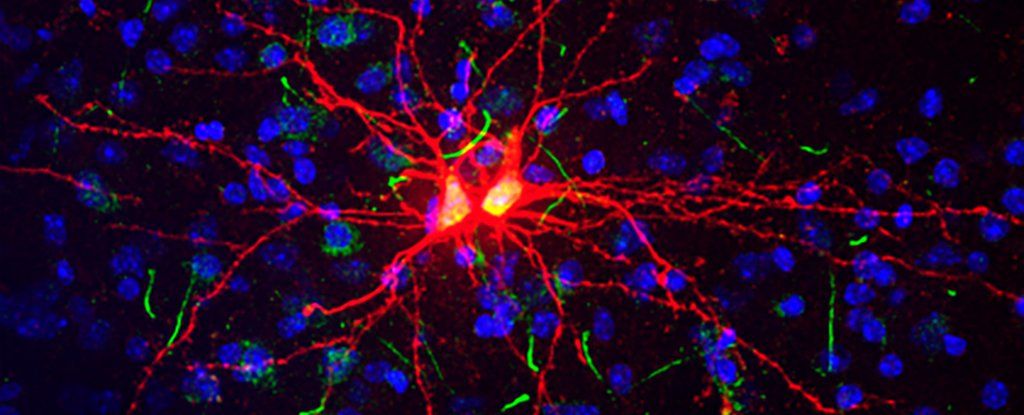
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health have identified a class of sensory neurons (nerve cells that electrically send and receive messages between the body and brain) that can be activated by stimuli as precise as the pulling of a single hair. Understanding basic mechanisms underlying these different types of responses will be an important step toward the rational design of new approaches to pain therapy. The findings were published in the journal Neuron.