Category: neuroscience

Brain adapts after rare dementia attacks language center
People with a rare kind of dementia that initially attacks the language center of the brain end up recruiting other areas of the brain to decipher sentences, according to a new study.
The study is one of the first to show that people with a neurodegenerative disease can call upon intact areas of the brain for help. People who have had strokes or traumatic brain injuries sometimes use additional regions of the brain to accomplish tasks that were handled by the now-injured part.
“We were able to identify regions of the brain that allowed the patients to compensate for the dying of neurons in the brain,” says first author Aneta Kielar, an assistant professor of speech, language, and hearing sciences and of cognitive science at the University of Arizona.

Video Gaming as a Geroprotective Strategy
Contrary to certain sensationalist articles declaring that video games are harmful, there is, in fact, growing evidence that playing video games may have a positive effect on cognitive health, particularly in older people [1].
Today, we will be taking a look at the scientific evidence to see if brain training or hitting your favorite video game titles could help keep you healthy as you age.
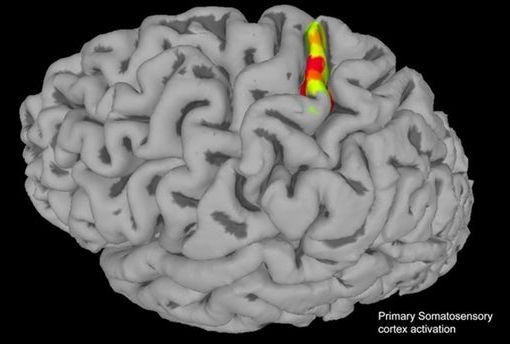
Brain implants put paralyzed man back in touch with himself
Researchers at Caltech have induced a range of sensations in the arm of a paralyzed man. The breakthrough comes courtesy of electrodes implanted in the brain, which stimulated the neurons to produce different feelings depending on the type of electrical signals. The team says the research could eventually lead to advanced prosthetic limbs that allow users to feel realistic sensations through them.
Plenty of exciting research is being conducted to help paralyzed people regain control of and feeling in their limbs. The NeuroLife system has helped a quadriplegic man move his arms again using just his thoughts, allowing him to perform a number of actions. Electrical nerve stimulation, both with and without electrode implants, has helped several people voluntarily move their legs again, often for the first time in years.
In this new study, Caltech researchers implanted two tiny arrays of electrodes into the somatosensory cortex, the small region of the brain responsible for the body’s sensations of movement or position, as well as cutaneous sensations such as touch, pressure and vibration.

Your Mind Is Not Limited to Your Brain, Scientists Say
Have you ever questioned someone’s state of mind or reminded someone that it pays to be mindful? Maybe you’ve told someone that they needed to be more open-minded? Or perhaps you’ve felt like you need to find some peace of mind for yourself.
But have you ever wondered what exactly a mind is?
If you try, it’s quite difficult to define the concept. It is the center and stronghold of your being, the basis of your consciousness and without it can you even be considered to be truly alive? I have wondered many times about what and where it is.
Alzheimer’s gene neutralised in human brain cells for the first time
S cientists have claimed an important breakthrough in the battle against Alzheimer’s after neutralising the most significant gene responsible for the disease for the first time.
A team in California successfully identified the protein associated with the high-risk apoE4 gene and then manage to prevent it damaging human neuron cells.
The study could open the door to a potential new drug capable of halting the disease, however the researchers have urged caution because so far their compound has only been tried on collections of cells in a laboratory.