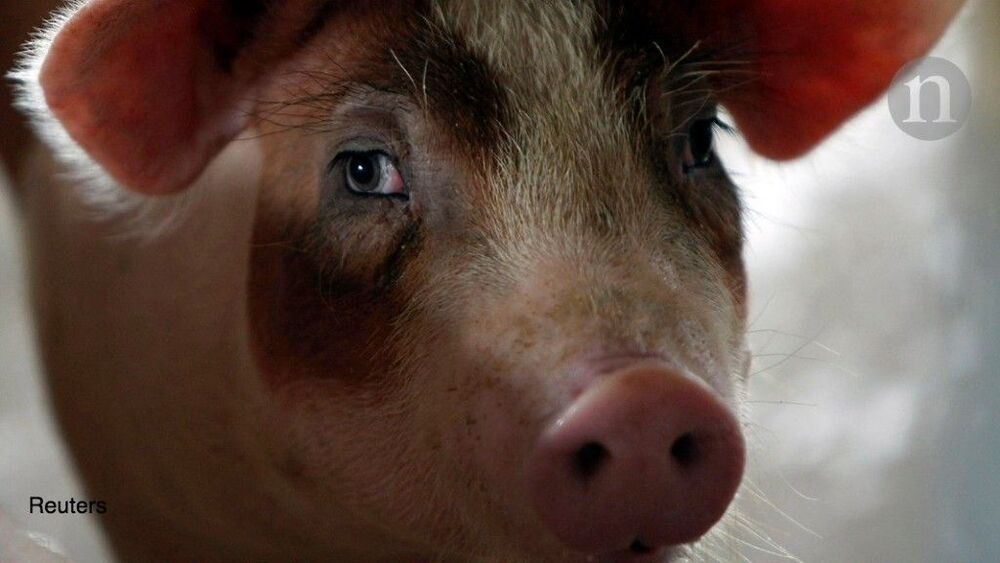
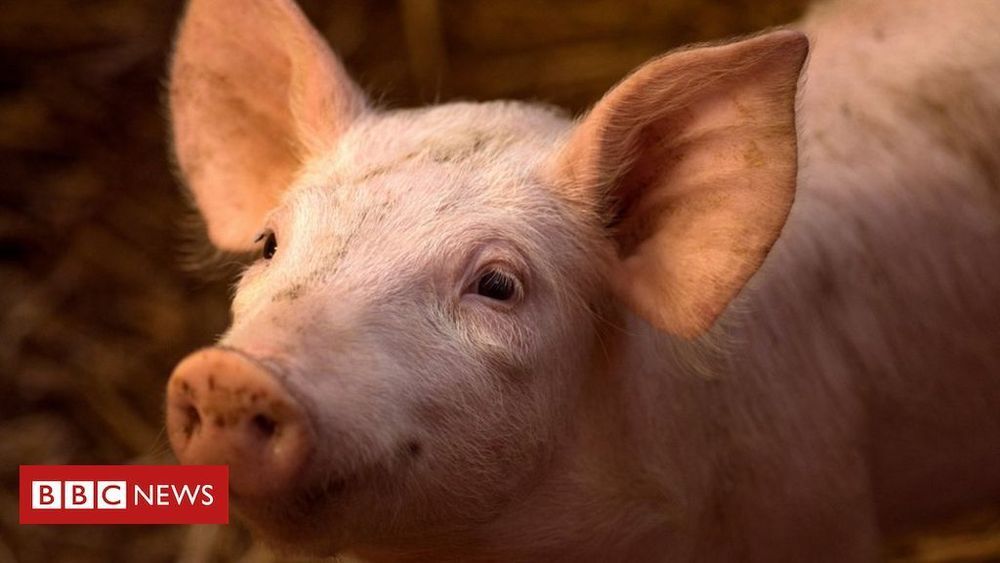
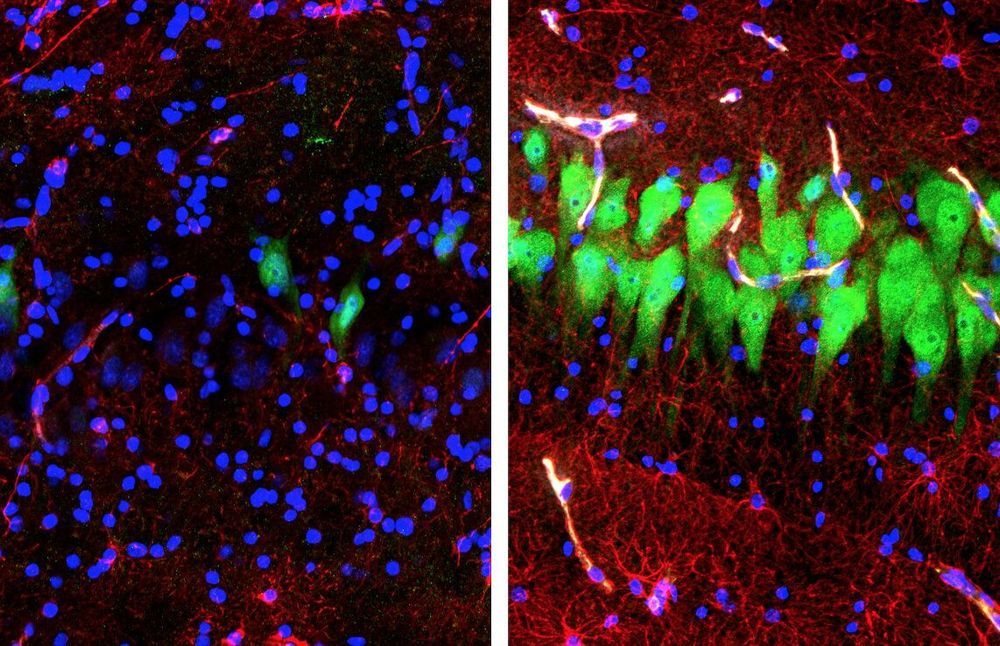
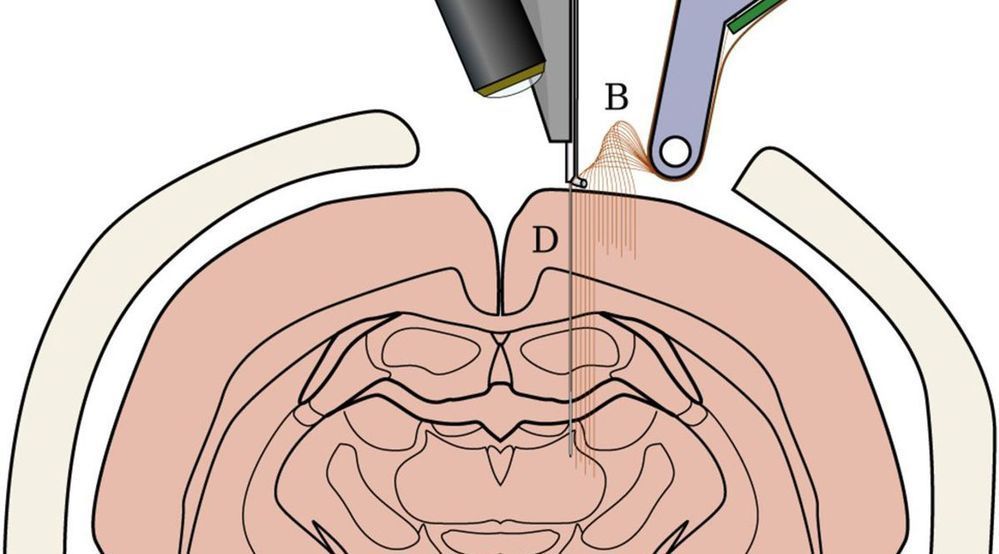
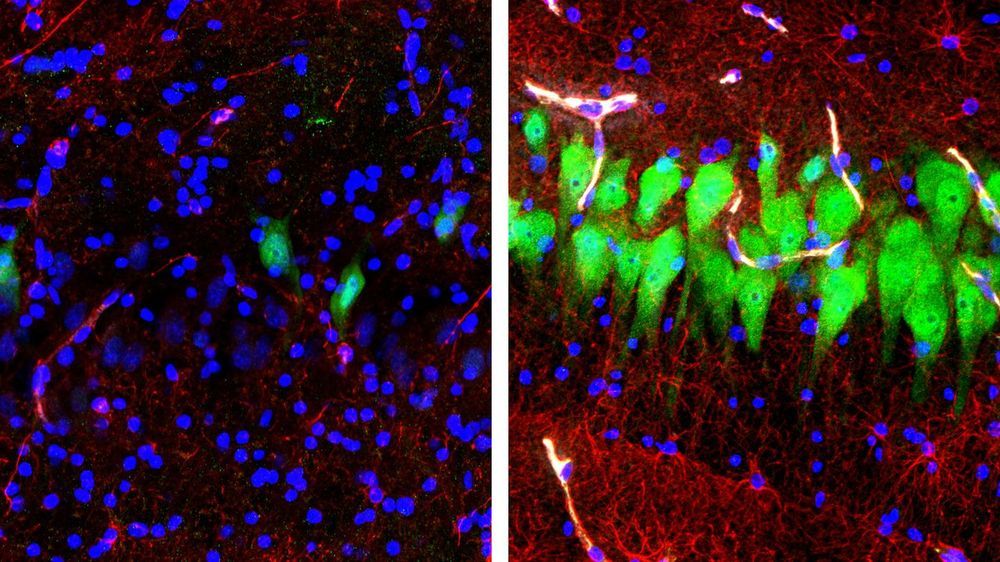
Circulation and cellular activity were restored in a pig’s brain four hours after its death, a finding that challenges long-held assumptions about the timing and irreversible nature of the cessation of some brain functions after death, Yale scientists report April 18 in the journal Nature.
The brain of a postmortem pig obtained from a meatpacking plant was isolated and circulated with a specially designed chemical solution. Many basic cellular functions, once thought to cease seconds or minutes after oxygen and blood flow cease, were observed, the scientists report.
“The intact brain of a large mammal retains a previously underappreciated capacity for restoration of circulation and certain molecular and cellular activities multiple hours after circulatory arrest,” said senior author Nenad Sestan, professor of neuroscience, comparative medicine, genetics, and psychiatry.