The key appears to be lateralization, meaning the specialization of different sides of the brain for different functions.
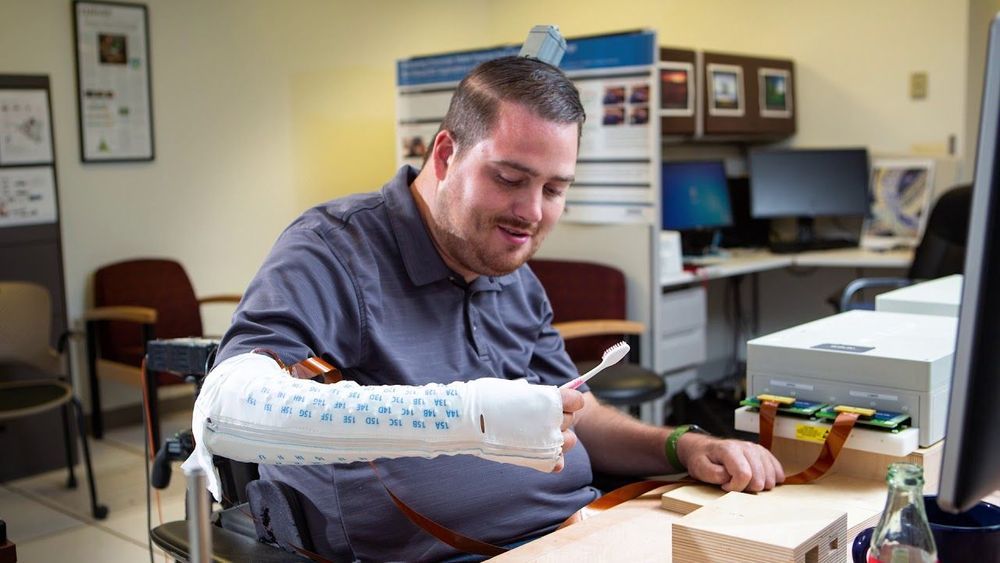



Paralysis used to mean a life sentence of immobility with no way out—until now.
Back in 2010, Ian Burkhart suffered a devastating injury that would leave him mostly paralyzed. Even though he was still able to move his shoulders and elbows, he had lost sensation in his hands. That was until Patrick Ganzer at Battelle Memorial Institute fast-forwarded biotech into the future by developing a brain implant that would turn Burkhart’s life around. When the implant connects to a specialized brain-computer interface, it does something that has never been done before and has restored both movement and touch in his right hand.
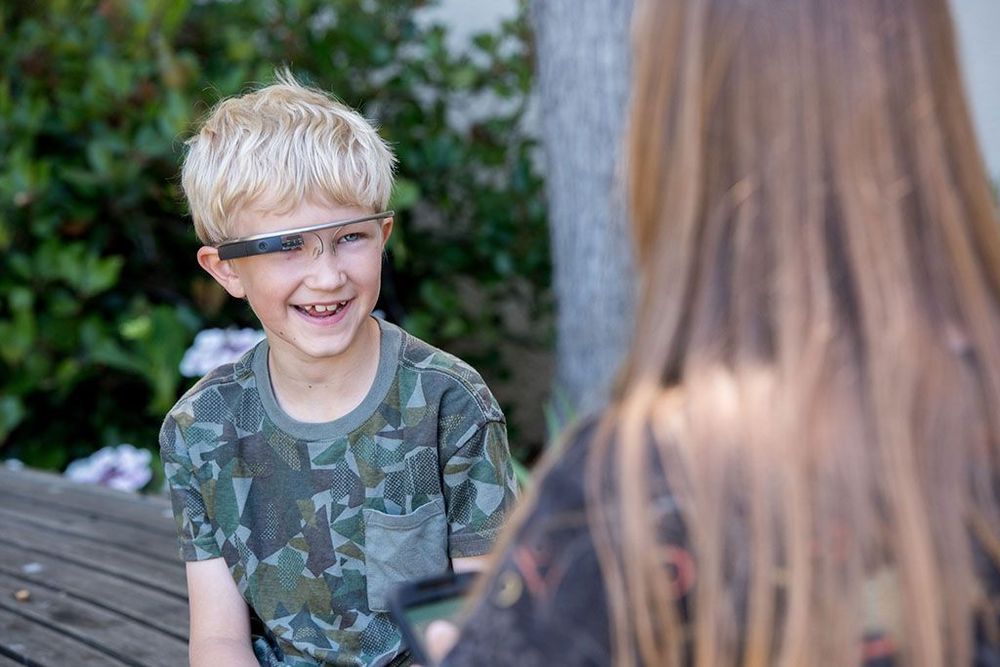

Children with autism were able to improve their social skills by using a smartphone app paired with Google Glass to help them understand the emotions conveyed in people’s facial expressions, according to a pilot study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Prior to participating in the study, Alex, 9, found it overwhelming to look people in the eye. Gentle encouragement from his mother, Donji Cullenbine, hadn’t helped. “I would smile and say things like, ‘You looked at me three times today!’ But it didn’t really move the bar,” she said. Using Google Glass transformed how Alex felt about looking at faces, Cullenbine said. “It was a game environment in which he wanted to win — he wanted to guess right.”
The therapy, described in findings published online Aug. 2 in npj Digital Medicine, uses a Stanford-designed app that provides real-time cues about other people’s facial expressions to a child wearing Google Glass. The device, which was linked with a smartphone through a local wireless network, consists of a glasses-like frame equipped with a camera to record the wearer’s field of view, as well as a small screen and a speaker to give the wearer visual and audio information. As the child interacts with others, the app identifies and names their emotions through the Google Glass speaker or screen. After one to three months of regular use, parents reported that children with autism made more eye contact and related better to others.
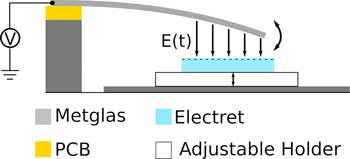
Electrical signals measurements such as the ECG (electrocardiogram) can show how the human brain or heart works. Next to electrical signals magnetic signals also reveal something about the activity of these organs. They could be measured with little effort and without skin contact. But the especially weak signals require highly sensitive sensors.
Scientists from the Collaboraive research Center 1261 “Magnetoelectric Sensors” at Kiel University have now developed a new concept for cantilever sensors, with the future aim of measuring these low frequencies of heart and brain activity.
The extremely small, energy-efficient sensors are particularly well-suited for medical applications or mobile microelectronics. This is made possible by the use of electrets. Such material is permanently electrically charged, and is also used in microphones for hearing aids or mobile phones.

I’ve been shocked sometimes when I walk in and see the patients. Most of the ones I’ve intubated are young — 30s, 40s, 50s. These are people who walked into the ER because they were coughing a day or two ago, or sometimes hours ago. By the time I come into the room, they are in severe respiratory distress. Their oxygen level might be 70 or 80 percent instead of 100, which is alarming. They are taking 40 breaths a minute when they should be taking 12 or 14. They have no oxygen reserves. They are pale and exhausted. It puts them in a mental fog, and sometimes they don’t hear me when I introduce myself. Some are panicky and gasping. Others are mumbling or incoherent. Last week, one patient was crying and asking to use my phone so they could call family and say goodbye, but their oxygen levels were dropping, and we didn’t have time, and I couldn’t risk bringing my phone in and contaminating it with virus, and the whole thing was impossible. I kept apologizing. I just —. I don’t know. I have to find a way to hold it together in order to do this job. I tear up sometimes, and if I do, it can fog up my face shield.
“It’s a powerless feeling, watching someone die”: An anesthesiologist on the frontline of coronavirus outbreak.

If you found this article informative please like and follow our Facebook page for the latest in neuroscience news: https://m.facebook.com/story.php?story_fbid=572929550002060&id=383136302314720
MORGANTOWN, W.Va. – The West Virginia University Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute today announced a new study published in partnership with Weill Cornell Medical Center that demonstrates the successful opening of the blood brain barrier in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex using focused ultrasound to treat six patients with early onset Alzheimer’s disease.
This first-in-the-world study has been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal. The effort is part of a Phase II clinical trial, sponsored by INSIGHTEC, which developed the technology and manufactures the focused ultrasound device, Exablate Neuro.
“The blood brain barrier has long presented a challenge in treating the most pressing neurological disorders,” Ali Rezai, M.D., executive chair of the WVU Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute, said. “The ability to non-invasively and reversibly open the blood brain barrier in deep brain areas such as the hippocampus, offers a new potential in developing treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.”
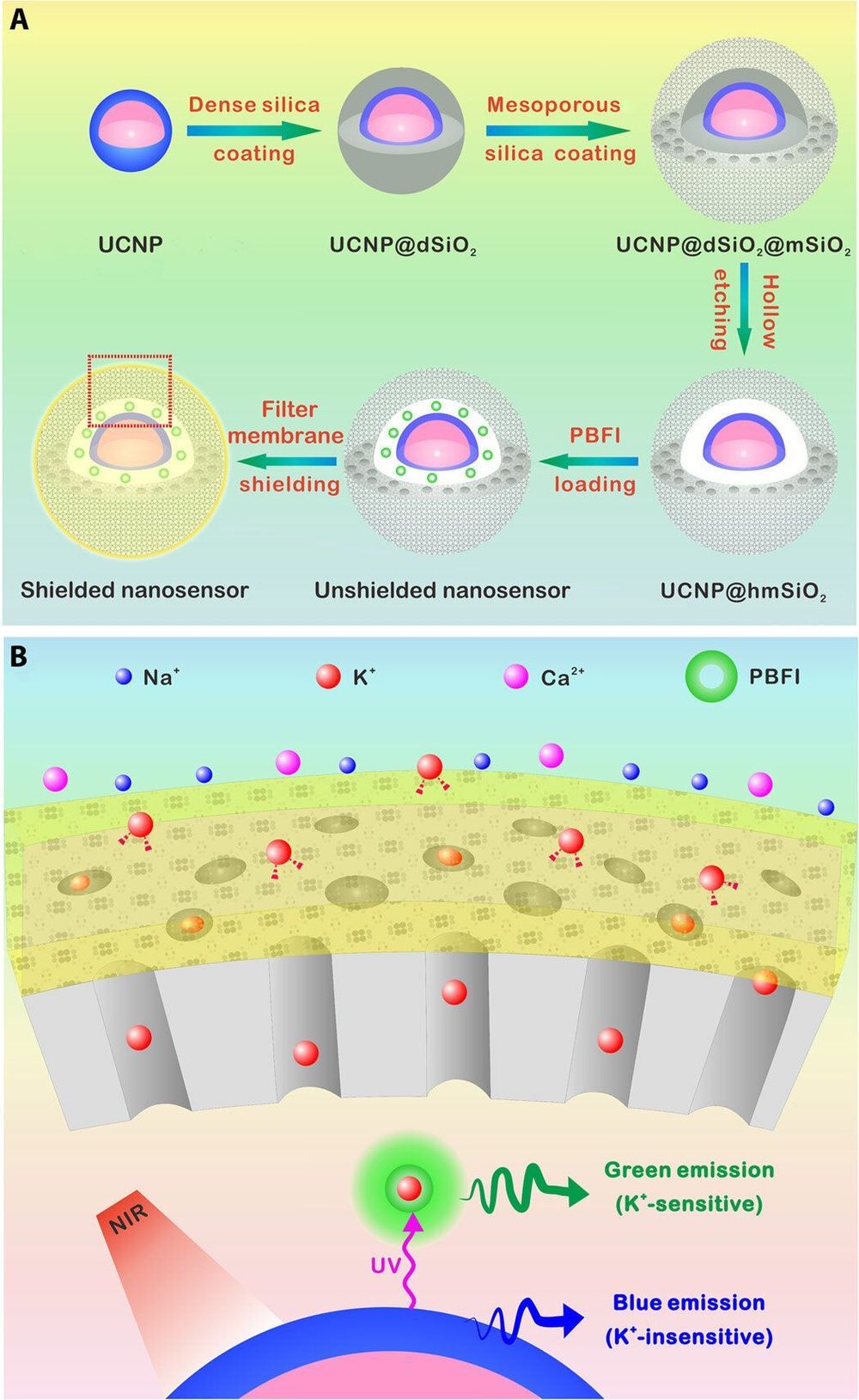
Researchers have developed a number of potassium ion (K+) probes to detect fluctuating K+ concentrations during a variety of biological processes. However, such probes are not sensitive enough to detect physiological fluctuations in living animals and it is not easy to monitor deep tissues with short-wavelength excitations that are in use so far. In a new report, Jianan Liu and a team of researchers in neuroscience, chemistry, and molecular engineering in China, describe a highly sensitive and selective nanosensor for near infrared (NIR) K+ ion imaging in living cells and animals. The team constructed the nanosensor by encapsulating upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and a commercial potassium ion indicator in the hollow cavity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and coated them with a K+ selective filter membrane. The membrane adsorbed K+ from the medium and filtered away any interfering cations. In its mechanism of action, UCNPs converted NIR to ultraviolet (UV) light to excite the potassium ion indicator and detect fluctuating potassium ion concentrations in cultured cells and in animal models of disease including mice and zebrafish larvae. The results are now published on Science Advances.
The most abundant intracellular cation potassium (K+) is extremely crucial in a variety of biological processes including neural transmission, heartbeat, muscle contraction and kidney function. Variations in the intracellular or extracellular K+ concentration (referred herein as [K+]) suggest abnormal physiological functions including heart dysfunction, cancer, and diabetes. As a result, researchers are keen to develop effective strategies to monitor the dynamics of [K+] fluctuations, specifically with direct optical imaging.
Most existing probes are not sensitive to K+ detection under physiological conditions and cannot differentiate fluctuations between [K+] and the accompanying sodium ion ([Na+]) during transmembrane transport in the Na+/K+ pumps. While fluorescence lifetime imaging can distinguish K+ and Na+ in water solution, the method requires specialized instruments. Most K+ sensors are also activated with short wavelength light including ultraviolet (UV) or visible light—leading to significant scattering and limited penetration depth when examining living tissues. In contrast, the proposed near-infrared (NIR) imaging technique will offer unique advantages during deep tissue imaging as a plausible alternative.
Does anyone remember this from July 2019? 🤔.
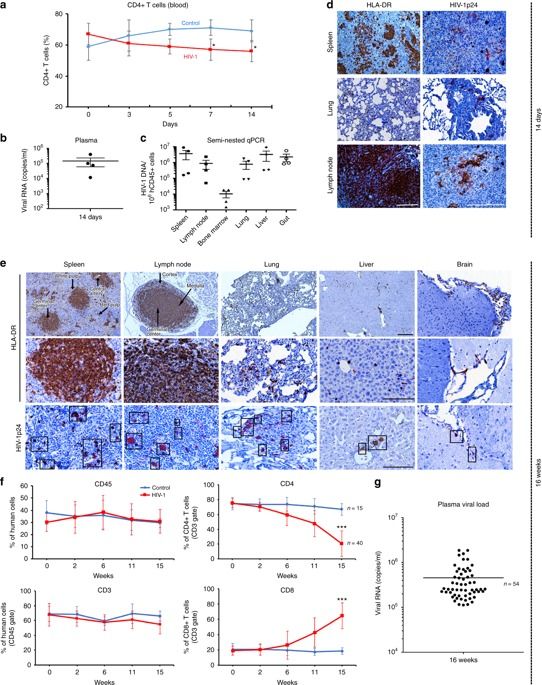
Elimination of HIV-1 requires clearance and removal of integrated proviral DNA from infected cells and tissues. Here, sequential long-acting slow-effective release antiviral therapy (LASER ART) and CRISPR-Cas9 demonstrate viral clearance in latent infectious reservoirs in HIV-1 infected humanized mice. HIV-1 subgenomic DNA fragments, spanning the long terminal repeats and the Gag gene, are excised in vivo, resulting in elimination of integrated proviral DNA; virus is not detected in blood, lymphoid tissue, bone marrow and brain by nested and digital-droplet PCR as well as RNAscope tests. No CRISPR-Cas9 mediated off-target effects are detected. Adoptive transfer of human immunocytes from dual treated, virus-free animals to uninfected humanized mice fails to produce infectious progeny virus. In contrast, HIV-1 is readily detected following sole LASER ART or CRISPR-Cas9 treatment. These data provide proof-of-concept that permanent viral elimination is possible.
Stephen Wolfram is a cult figure in programming and mathematics. He is the brains behind Wolfram Alpha, a website that tries to answer questions by using algorithms to sift through a massive database of information. He is also responsible for Mathematica, a computer system used by scientists the world over.
Last week, Wolfram launched a new venture: the Wolfram Physics Project, an ambitious attempt to develop a new physics of our Universe.
The new physics, he declares, is computational. The guiding idea is that everything can be boiled down to the application of simple rules to fundamental building blocks.

Researchers have confirmed that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve cognitive function in the brain. A research group of Professor Seung-Hee Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST found that the application of neuropeptide somatostatin improves visual processing and cognitive behaviors by reducing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the cortex.
This study, reported at Science Advances on April 22nd, sheds a new light on the therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. According to a recent study in Korea, one in ten seniors over 65 is experiencing dementia-related symptoms in their daily lives such as memory loss, cognitive decline, and motion function disorders. Professor Lee believes that somatostatin treatment can be directly applied to the recovery of cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Professor Lee started this study noting the fact that the level of somatostatin expression was dramatically decreased in the cerebral cortex and cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients.