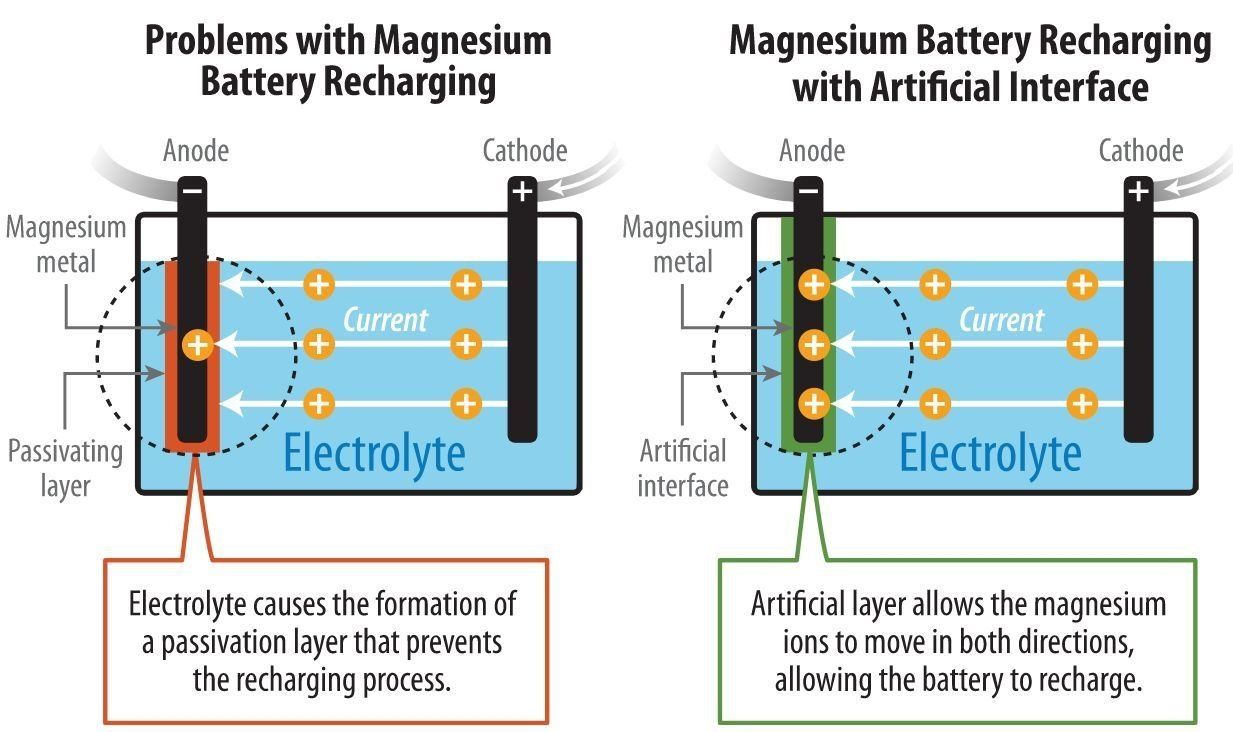
Making a giant leap in the ‘tiny’ field of nanoscience, a multi-institutional team of researchers is the first to create nanoscale particles composed of up to eight distinct elements generally known to be immiscible, or incapable of being mixed or blended together. The blending of multiple, unmixable elements into a unified, homogenous nanostructure, called a high entropy alloy nanoparticle, greatly expands the landscape of nanomaterials—and what we can do with them.
This research makes a significant advance on previous efforts that have typically produced nanoparticles limited to only three different elements and to structures that do not mix evenly. Essentially, it is extremely difficult to squeeze and blend different elements into individual particles at the nanoscale. The team, which includes lead researchers at University of Maryland, College Park (UMD)’s A. James Clark School of Engineering, published a peer-reviewed paper based on the research featured on the March 30 cover of Science.
“Imagine the elements that combine to make nanoparticles as Lego building blocks. If you have only one to three colors and sizes, then you are limited by what combinations you can use and what structures you can assemble,” explains Liangbing Hu, associate professor of materials science and engineering at UMD and one of the corresponding authors of the paper. “What our team has done is essentially enlarged the toy chest in nanoparticle synthesis; now, we are able to build nanomaterials with nearly all metallic and semiconductor elements.”
Read more