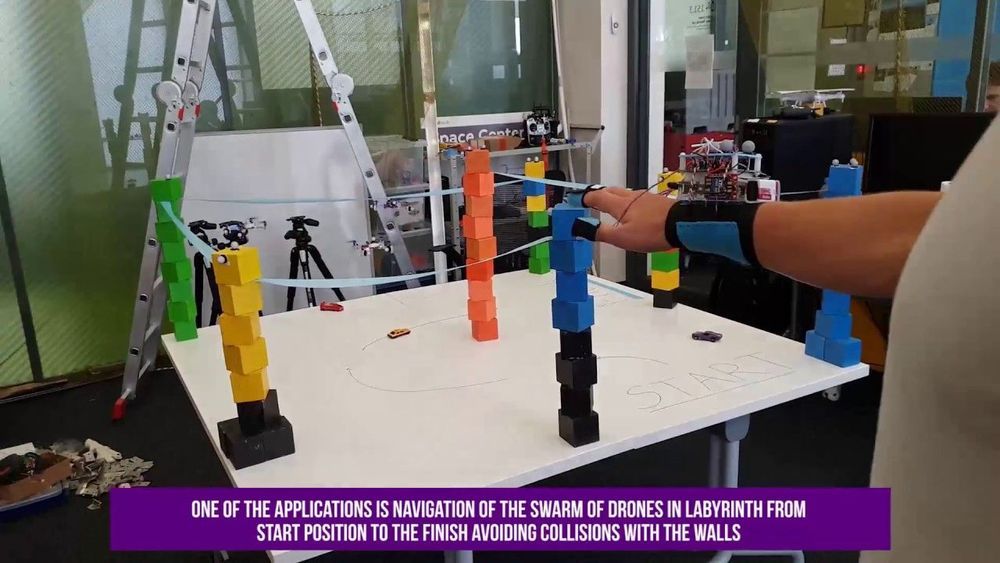
Researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech) in Russia have recently introduced a new strategy to enhance interactions between humans and robotic swarms, called SwarmTouch. This strategy, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, allows a human operator to communicate with a swarm of nano-quadrotor drones and guide their formation, while receiving tactile feedback in the form of vibrations.
“We are working in the field of swarm of drones and my previous research in the field of haptics was very helpful in introducing a new frontier of tactile human-swarm interactions,” Dzmitry Tsetserukou, Professor at Skoltech and head of Intelligent Space Robotics laboratory, told TechXplore. “During our experiments with the swarm, however, we understood that current interfaces are too unfriendly and difficult to operate.”
While conducting research investigating strategies for human-swarm interaction, Tsetserukou and his colleagues realised that there are currently no available interfaces that allow human operators to easily deploy a swarm of robots and control its movements in real time. At the moment, most swarms simply follow predefined trajectories, which have been set out by researchers before the robots start operating.