Before the pandemic, the lab of Stanford University biochemist Peter S. Kim focused on developing vaccines for HIV, Ebola and pandemic influenza. But, within days of closing their campus lab space as part of COVID-19 precautions, they turned their attention to a vaccine for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Although the coronavirus was outside the lab’s specific area of expertise, they and their collaborators have managed to construct and test a promising vaccine candidate.
“Our goal is to make a single-shot vaccine that does not require a cold-chain for storage or transport. If we’re successful at doing it well, it should be cheap too,” said Kim, who is the Virginia and D. K. Ludwig Professor of Biochemistry. “The target population for our vaccine is low-and middle-income countries.”
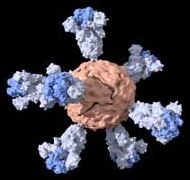
Their vaccine, detailed in a paper published in ACS Central Science (“A Single Immunization with Spike-Functionalized Ferritin Vaccines Elicits Neutralizing Antibody Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice”), contains nanoparticles studded with the same proteins that comprise the virus’s distinctive surface spikes.