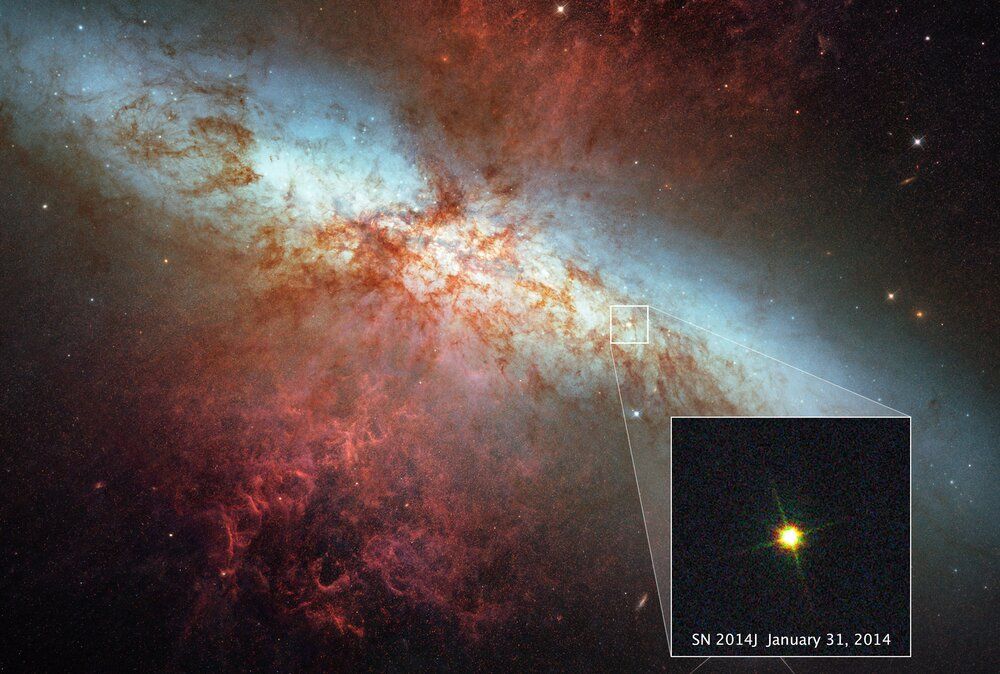
A pair of researchers with Indiana University and Illinois University, respectively, has developed a theory that suggests crystalizing uranium “snowflakes” deep inside white dwarfs could instigate an explosion large enough to destroy the star. In their paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters, C. J. Horowitz and M. E. Caplan describe their theory and what it could mean to astrophysical theories about white dwarfs and supernovas.
White dwarfs are small stars that have burned up most of their nuclear fuel—they are typically much cooler than they once were and are very dense. In this new effort, Horowitz and Caplan used data from the Gaia space observatory to theorize that sometimes small grains of uranium could begin to crystalize (due to enriched actinides), forming what they describe as snowflakes. They suggest this could happen because of the differing melting points of the material involved. They further suggest that if this were to occur, it could lead to splitting of atomic nuclei, resulting in a series of fission reactions as the solids become enriched in actinides. And if such reactions were to raise the temperature of the interior of the star by igniting carbon, the result would likely be merging of atomic nuclei and eventually a very large fusion reaction that would result in a large explosion—likely large enough to destroy the star.