Category: life extension

Sleep-Disordered Breathing Tied to Accelerated Aging
SAN ANTONIO — Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB), and the disruption in nightly sleep it causes, speeds up the aging process, according to preliminary research.
SDB is a common disorder that results in oxidative stress and inflammation and is associated with several age-related health disorders. However, it hasn’t been well studied with respect to epigenetic aging.
“To our knowledge, this study is the first empirical study that has linked sleep-disordered breathing with epigenetic age acceleration,” Xiaoyu Li, ScD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News.

Judith Campisi — Senolytics for Healthy Aging
Is an American biochemist and cell biologist. She is a professor of biogerontology at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. She is also a member of the SENS Research Foundation Advisory Board and an adviser at the Lifeboat Foundation. She is co-editor in chief of the Aging Journal, together with Mikhail Blagosklonny and David Sinclair, and founder of the pharmaceutical company Unity Biotechnology. She is listed in Who’s Who in Gerontology.
She is widely known for her research on how senescent cells influence aging and cancer — in particular the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
Judy Campisi, The Buck Institute for Research on Aging, presenting at Undoing Aging 2019.
#senolytics #biotech #anti-aging #antiaging #undoingaging #longevity
Many thanks for watching!
Consider supporting SciFuture by:
a) Subscribing to the SciFuture YouTube channel: http://youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=TheRationalFuture b) Donating
- Bitcoin: 1BxusYmpynJsH4i8681aBuw9ZTxbKoUi22
- Etherium: 0xd46a6e88c4fe179d04464caf42626d0c9cab1c6b
- Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/scifuture c) Sharing the media SciFuture creates: http://scifuture.org

New evidence that optimists live longer
Exceptional longevity: the hunt for associated factors has concentrated on #genomics and biomarkers. What has been missed? Optimism. And it’s dose-dependent.
Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM), National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare System and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, have found that individuals with greater optimism are more likely to live longer and to achieve “exceptional longevity,” that is, living to age 85 or older.
Optimism refers to a general expectation that good things will happen, or believing that the future will be favorable because we can control important outcomes. Whereas research has identified many risk factors that increase the likelihood of diseases and premature death, much less is known about positive psychosocial factors that can promote healthy aging.
The study was based on 69,744 women and 1,429 men. Both groups completed survey measures to assess their level of optimism, as well as their overall health and health habits such as diet, smoking and alcohol use. Women were followed for 10 years, while the men were followed for 30 years. When individuals were compared based on their initial levels of optimism, the researchers found that the most optimistic men and women demonstrated, on average, an 11 to 15 percent longer lifespan, and had 50–70 percent greater odds of reaching 85 years old compared to the least optimistic groups. The results were maintained after accounting for age, demographic factors such as educational attainment, chronic diseases, depression and also health behaviors, such as alcohol use, exercise, diet and primary care visits.
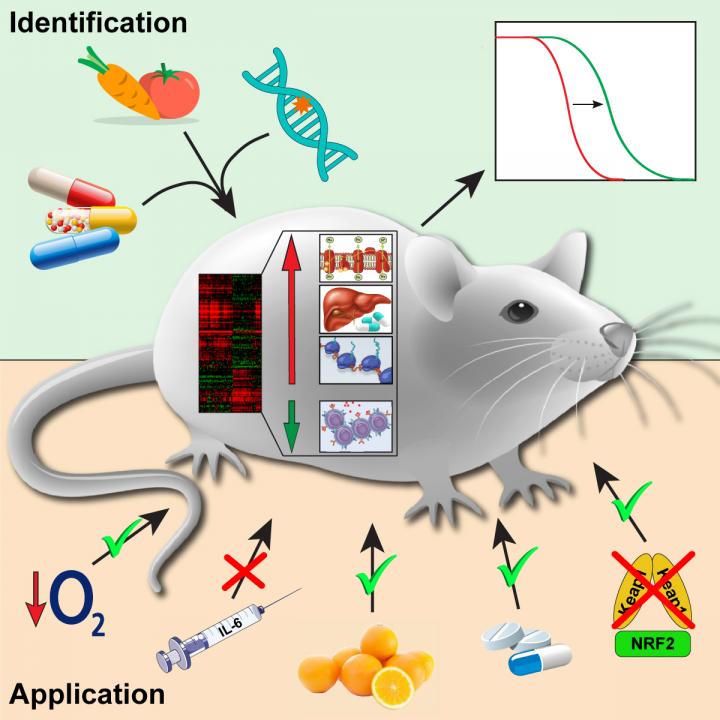
Scientists have found longevity biomarkers
An international group of scientists studied the effects of 17 different lifespan-extending interventions on gene activity in mice and discovered genetic biomarkers of longevity. The results of their study were published in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Nowadays, dozens of interventions are known that extend the lifespan of various living organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. They include chemical compounds (e.g. rapamycin), genetic interventions (e.g. mutations associated with disruption of growth hormone synthesis), and diets (e.g. caloric restriction). Some targets of these interventions have been discovered. However, there is still no clear understanding of the systemic molecular mechanisms leading to lifespan extension.
A group of scientists from Skoltech, Moscow State University and Harvard University decided to fill this gap and identify crucial molecular processes associated with longevity. To do so, they looked at the effects of various lifespan-extending interventions on the activity of genes in a mouse, a commonly used model organism closely related to humans.
Reducing Gut Dysbiosis Partially Alleviates Alzheimer’s Symptoms
In a recent study, a team from the Neurobiota Research Center in Korea has discovered that reducing gut dysbiosis partially alleviates the cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s disease. This may seem puzzling, as the gut and the brain are separate and relatively distant organs, but this research makes sense in the context of chronic inflammation.
Inflammaging
Under normal circumstances, inflammation is a short-term measure in response to infection: immune cells are directed towards the inflamed area and handle the infection, and then the inflammation dies down. However, chronic inflammation causes harm to our organs; it is the main form of altered intercellular communication, which is one of the hallmarks of aging. The protein complex NF-kB, the master regulator of inflammation, is the main culprit of inflammaging, and it is specifically discussed in this paper.

‘Extraordinary’ Breakthroughs In Anti-Aging Research ‘Will Happen Faster Than People Think’
How about some life extension optimism to start your day?
People 50 and older have a lot to look forward to, according to Juvenescence’s Greg Bailey—mainly that we won’t be aging as fast or poorly as our parents. “Science fiction has become science,” said the UK-based anti-aging biotech’s CEO about the company’s completing its $100 million Series B round of financing last week. “I think the world is going to be shocked,” he said in an interview. In total, Juvenescence has now raised $165 million in just 18 months to fund longevity projects with the lofty goal of extending human lifespans to 150 years.

A Multidimensional Systems Biology Analysis of Cellular Senescence in Ageing and Disease
Cellular senescence, a permanent state of replicative arrest in otherwise proliferating cells, is a hallmark of ageing and has been linked to ageing-related diseases like cancer. Senescent cells have been shown to accumulate in tissues of aged organisms which in turn can lead to chronic inflammation. Many genes have been associated with cell senescence, yet a comprehensive understanding of cell senescence pathways is still lacking. To this end, we created CellAge (http://genomics.senescence.info/cells), a manually curated database of 279 human genes associated with cellular senescence, and performed various integrative and functional analyses. We observed that genes promoting cell senescence tend to be overexpressed with age in human tissues and are also significantly overrepresented in anti-longevity and tumour-suppressor gene databases. By contrast, genes inhibiting cell senescence overlapped with pro-longevity genes and oncogenes. Furthermore, an evolutionary analysis revealed a strong conservation of senescence-associated genes in mammals, but not in invertebrates. Using the CellAge genes as seed nodes, we also built protein-protein interaction and co-expression networks. Clusters in the networks were enriched for cell cycle and immunological processes. Network topological parameters also revealed novel potential senescence-associated regulators. We then used siRNAs and observed that of 26 candidates tested, 19 induced markers of senescence. Overall, our work provides a new resource for researchers to study cell senescence and our systems biology analyses provide new insights and novel genes regarding cell senescence.
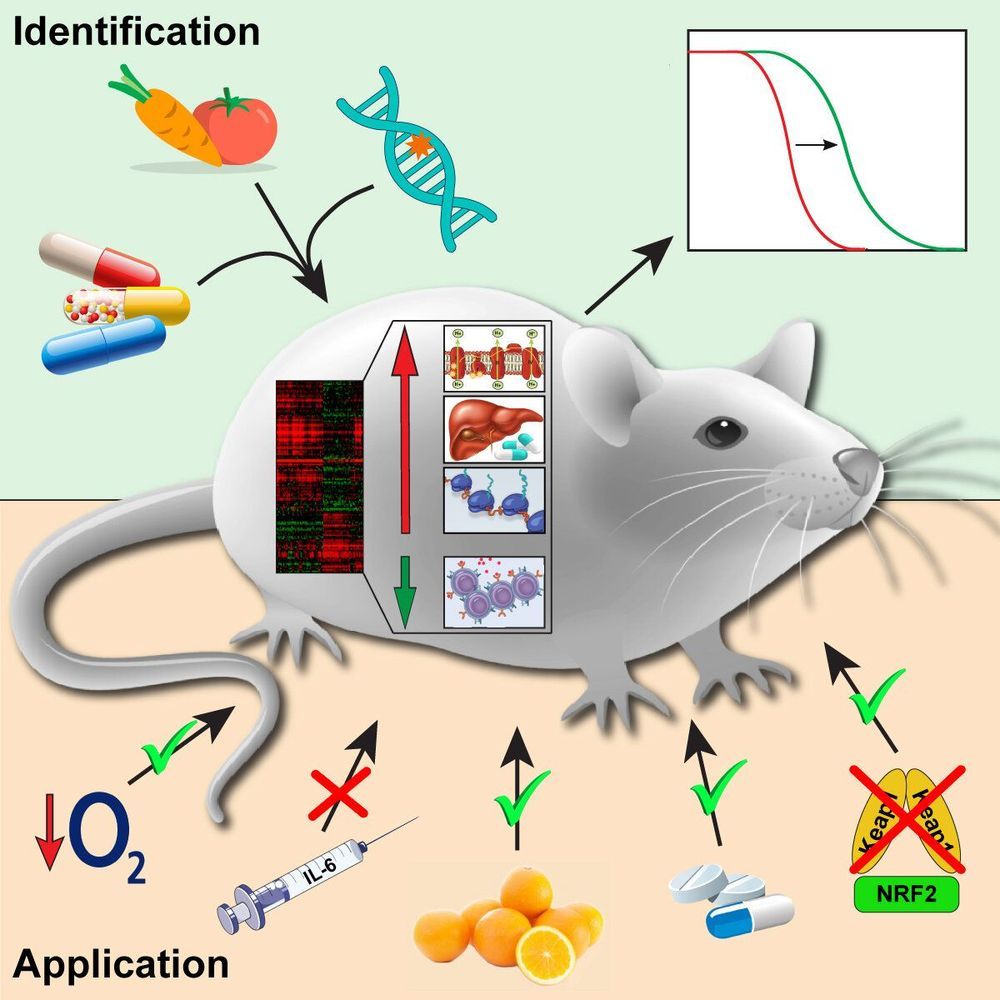
Scientists find longevity biomarkers
An international group of scientists studied the effects of 17 lifespan-extending interventions on gene activity in mice and discovered genetic biomarkers of longevity. The results of their study were published in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Nowadays, dozens of interventions are known that extend the lifespan of various living organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. They include chemical compounds (e.g. rapamycin), genetic interventions (e.g. mutations associated with disruption of growth hormone synthesis), and diets (e.g. caloric restriction). Some targets of these interventions have been discovered. However, there is still no clear understanding of the systemic molecular mechanisms leading to lifespan extension.
A group of scientists from Skoltech, Moscow State University and Harvard University decided to fill this gap and identify crucial molecular processes associated with longevity. To do so, they looked at the effects of various lifespan-extending interventions on the activity of genes in a mouse, a commonly used model organism closely related to humans.

Rejuvenation Research Is Now a Mainstream Topic
It is a sure sign that the tide has turned when mainstream news outlets and magazines start publishing positive articles about aging research and the prospects of rejuvenation.
A refreshing change
Today, I want to highlight an article in MIT Technology Review in which the author, David Adam, gives a sensible and measured overview of what is happening in the field and manages to sidestep the usual negativity and misconceptions that often plague popular science pieces.