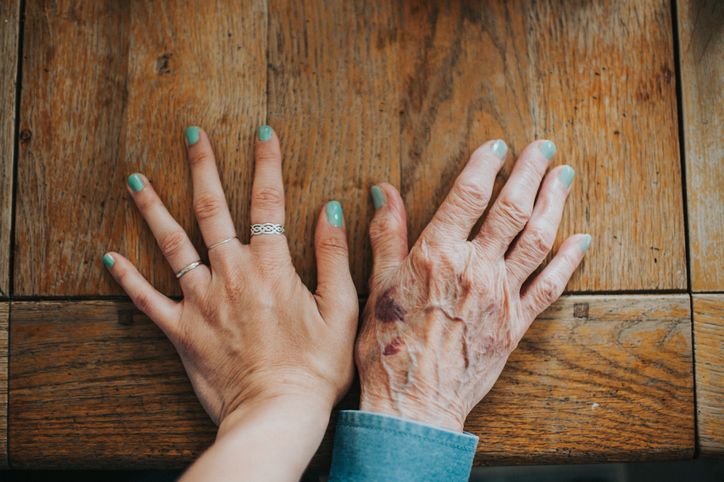
Study shows changes to gene activity that occur with age can be turned back.



Having a healthy gut should always be a priority when dealing with any health-related issues. It’s connected to various problems like IBS, asthma, thyroid disorders, and even diabetes. A new study, however, is giving us another reason to promote gut health—and we’re excited about it.
Using mice, an international research team has discovered a specific microorganism living in the gut that may affect the aging process.
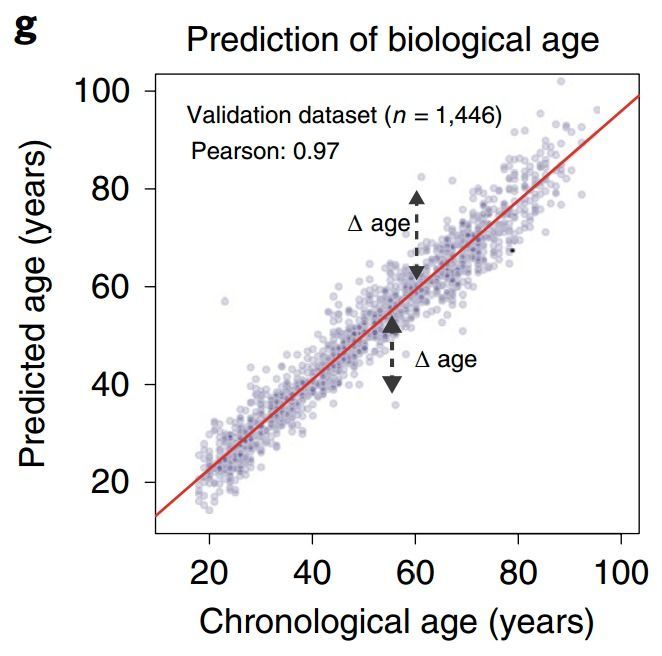
Methylation clocks are far and away the most accurate markers of a person’s age, and so are a promising tool for evaluating anti-aging interventions, but they are a bit of a black box. We know from statistics that certain places on chromosomes become steadily methylated ( or demethylated ) with age, but we often don’t know what effect that has on expression of particular genes.
For the first time, a clock has been devised based on proteins in the blood that is comparable in accuracy to the best methylation clocks. This has the advantage of being downstream of epigenetics, so it is less of a black box. What can we learn from the proteins that are increased ( and decreased ) with age?
I’ve written often and enthusiastically about the utility of methylation clocks for evaluation of anti-aging interventions [ blog, blog, blog, journal article ]. This technology offers a way to promptly identify small age-reversal successes (perhaps not in individuals, but averaged over a cohort of ~50 to 100 subjects). Before these tests were available, we had no choice but to wait — usually 10 years or more — for enough experimental subjects to die that we could be sure the intervention we were evaluating affected life expectancy. (This is the plan of the worthy but ridiculously expensive TAME trial promoted by Nir Barzilai.)
Promising news- very primitive proof of concept for cryonics.
Scientists (and sci-fi fans) have been talking about suspended animation for years. The idea that the functions of the human body can somehow be put on “pause” while life-saving medical procedures are performed (or a person is sent into space, a la Alien) has long seemed untenable — until now. According to New Scientist, doctors have successfully placed humans in suspended animation for the first time, in a trial that could have an enormous influence on the future of emergency room surgery.
Read our full story on Engadget: https://www.engadget.com/2019/11/20/human-patient-put-in-suspended-animation-for-the-first-time/
Get More Engadget:
• Like us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/engadget
• Follow us on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/engadget
• Follow us on Instagram: http://www.instagram.com/engadget
•

You heard about reversing the epigenetic clock 2.5 years? Living drugs? CAR T cells? Fight cancer? Here ya go.
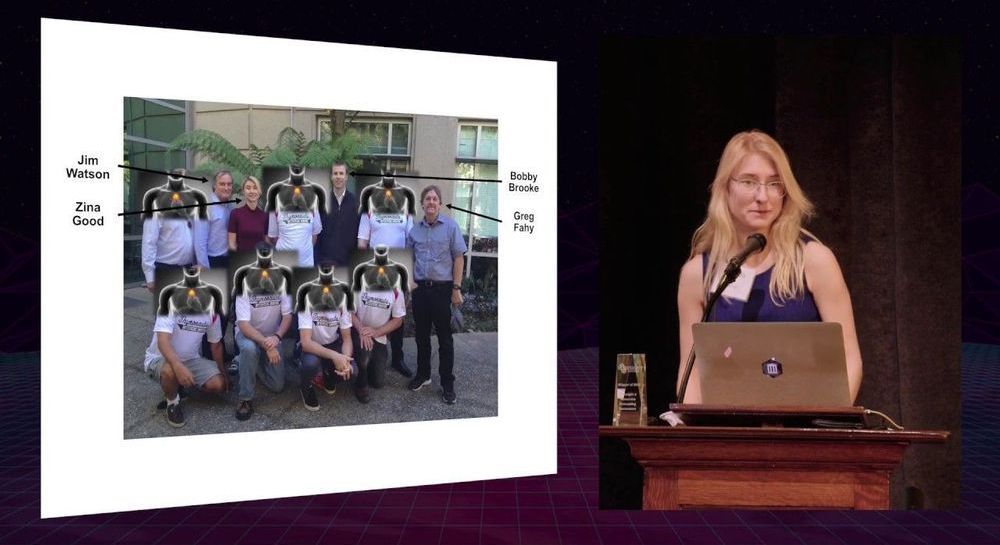
Vision Weekend is the annual member gathering of Foresight Institute, a non-profit for advancing beneficial technologies for the long-term flourishing of life.
More info on speakers and program: https://foresight.org/vision-weekend-2019/.
Join Foresight Institute’s community: www.bit.ly/foresightnews

Intermittent fasting means interspersing periods of abstaining from food with periods of eating regularly. You could skip breakfast and eat a late lunch, for example, or fast all day long, once or twice a week.
The research suggests that intermittent fasting is a simple, effective life hack for solving many age-related problems, but the evidence is far from conclusive.
“There really is no one weird trick for the perfect diet for everyone,” John Newman, geriatrician at the University of California, San Francisco told Inverse. Science is leading us toward the idea of maintaining some flexibility in our body’s metabolism, he said.

Transhumanism can mean uploading one’s mind into cyberspace. But some transhumanists hope to slowly morph into “immortal cyborgs” with endlessly replaceable parts.
Five years ago, we were told, we were all turning into cyborgs:
Did you recently welcome a child into the world? Congratulations! An upstanding responsible parent such as yourself is surely doing all you can to prepare your little one for all the pitfalls life has in store. However, thanks to technology, children born in 2014 may face a far different set of issues than you ever had to. And we’re not talking about simply learning to master a new generation of digital doohickeys, we’re talking about living in a world in which the very definition of “human” becomes blurred.

From insilico meddicine — the beginning of an AI healthcare revolution.
Poly Mamoshina on Machine Learning for small molecule drug discovery and the beginning of an AI healthcare revolution — interviewed at the Undoing Aging conference in Berlin 2019!
Polina Mamoshina is a senior research scientist at Insilico Medicine, Inc (www.insilico.com), a Baltimore-based bioinformatics and deep learning company focused on reinventing drug discovery and biomarker development and a part of the computational biology team of Oxford University Computer Science Department. Polina graduated from the Department of Genetics of the Moscow State University. She was one of the winners of GeneHack a Russian nationwide 48-hour hackathon on bioinformatics at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology attended by hundreds of young bioinformaticians. Polina is involved in multiple deep learning projects at the Pharmaceutical Artificial Intelligence division of Insilico Medicine working on the drug discovery engine and developing biochemistry, transcriptome, and cell-free nucleic acid-based biomarkers of aging and disease. She recently co-authored seven academic papers in peer-reviewed journals.
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=YrLgl8gAAAAJ&hl=en
https://uk.linkedin.com/in/polymamoshina
https://cogx.co/speakers/polina-mamoshina/
Many thanks for watching!
Consider supporting SciFuture by:
a) Subscribing to the SciFuture YouTube channel: http://youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=TheRationalFuture
b) Donating
- Bitcoin: 1BxusYmpynJsH4i8681aBuw9ZTxbKoUi22
- Etherium: 0xd46a6e88c4fe179d04464caf42626d0c9cab1c6b
- Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/scifuture
c) Sharing the media SciFuture creates: http://scifuture.org
Kind regards.
Adam Ford
- Science, Technology & the Future.

A new study shows that short-term treatment with the common organ rejection drug rapamycin reverses periodontal bone loss, attenuates inflammation, and makes the oral microbiome revert to a more youthful state in old mice.
What is rapamycin?
Rapamycin (also known as sirolimus) is a macrolide, a class of antibiotics that includes Biaxin (Clarithromycin), Zithromax (Azithromycin), Dificid (Fidoximycin), and Erythromycin. Macrolides inhibit the growth of bacteria and are often used in the treatment of common bacterial infections.