Elon Musk wants to connect all corners of the planet via space, but his thousands of orbiting routers may pose a risk to satellites and to science.


Elon Musk wants to connect all corners of the planet via space, but his thousands of orbiting routers may pose a risk to satellites and to science.

Harun Šiljak, Trinity College Dublin
Google reported a remarkable breakthrough towards the end of 2019. The company claimed to have achieved something called quantum supremacy, using a new type of “quantum” computer to perform a benchmark test in 200 seconds. This was in stark contrast to the 10,000 years that would supposedly have been needed by a state-of-the-art conventional supercomputer to complete the same test.
Despite IBM’s claim that its supercomputer, with a little optimisation, could solve the task in a matter of days, Google’s announcement made it clear that we are entering a new era of incredible computational power.

China Launches 6G Satellite and Nokia seals the deal with NASA for 4G moon network.
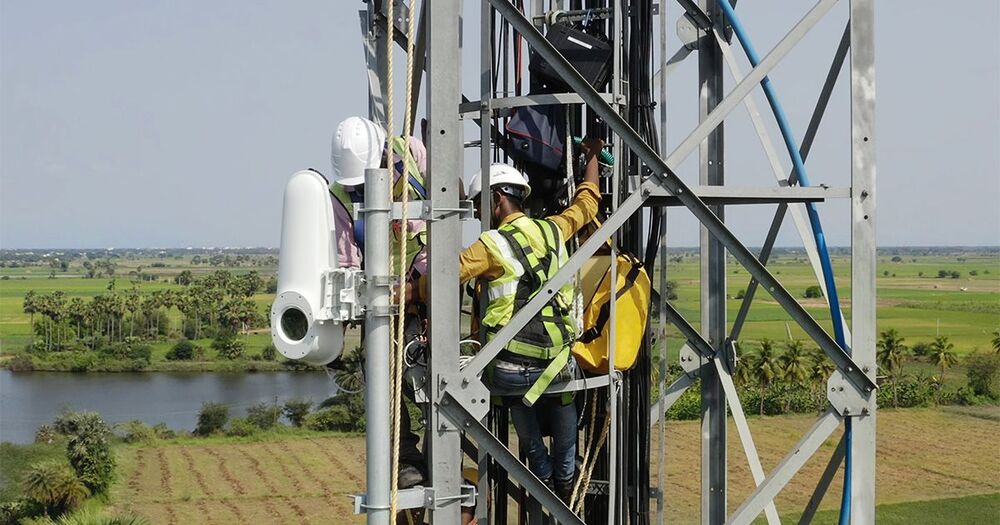


The Internet of Things can create tiny efficiencies that amount to a lot of money. Ben Fahy reports on how the IoT is changing the way businesses work.
Back in the 1830s, a depressed minister from Massachusetts named Lorenzo Langstroth got into beekeeping as therapy. His hobby eventually led him to develop the moveable comb hive, an innovation that allowed honey to be harvested without destroying the colony of bees. Since then, the art of beekeeping hasn’t changed much, but Bruce Trevarthen, the founder and CEO of the LayerX group, thinks some smart technology and a bit of connectivity might be the next big bee-based breakthrough.
ModuSense, a division of the Hamilton-based tech company/incubator, focuses on providing industrial Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, particularly for the primary sector. But when it kicked off around four years ago, Trevarthen felt that target was still too broad, so he decided to focus on improving the productivity of one sector in particular: apiculture.

Korean electronics giant LG, along with two California computing startups, Renovo and Savari, are demonstrating use cases for 5G-connected vehicles as Verizon and Amazon expand the wireless computing availability to multiple U.S. cities.

What we pay attention to shapes our opinions and views and our opinions and views shape our actions—well beyond clicks and taps on a screen.
But this is only the beginning. The internet and its enabling tools were the last great generation of technology. New generations are already making their presence known. In coming decades, technology will more compellingly seduce our attention, will escape its silicon-and-glass cage, will animate the inanimate, and even shape our biology.
The answer isn’t to do away with technology. There’s no putting the genie back in the bottle—nor should we want to. Besides negative outcomes, technology remains a powerful tool for good too. But as individuals, as a society, we need to become far more aware of how we interact with technology, to keep a closer eye on business incentives, and to consciously employ our tools in ways that firmly align with our goals.
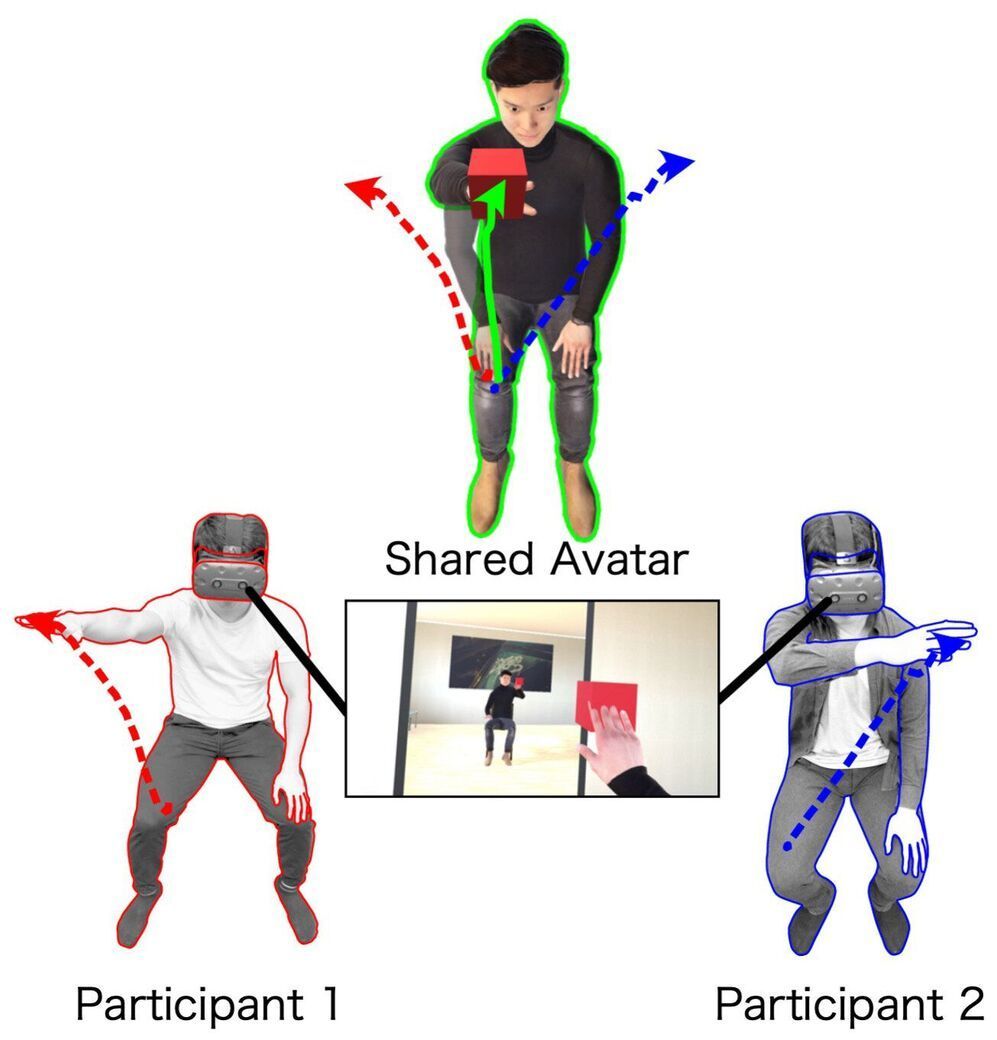
The COVID-19 crisis has led to a significant increase in the use of cyberspace, enabling people to work together at distant places and interact with remote environments and individuals by embodying virtual avatars or real avatars such as robots. However, the limits of avatar embodiment are not clear. Furthermore, it is not clear how these embodiments affect the behaviors of humans.
Therefore, a research team comprising Takayoshi Hagiwara (graduate student) and Professor Michiteru Kitazaki from Toyohashi University of Technology; Dr. Ganesh Gowrishankar (senior researcher) from UM-CNRS LIRMM; Professor Maki Sugimoto from Keio University; and Professor Masahiko Inami from The University of Tokyo aimed to develop a novel collaboration method with a shared avatar, which can be controlled concurrently by two individuals in VR, and to investigate human motor behaviors as the avatar is controlled in VR.
Full body movements of two participants were monitored via a motion-capture system, and movements of the shared avatar were determined as the average of the movements of the two participants. Twenty participants (10 dyads) were asked to perform reaching movements with their right hand towards target cubes that were presented at various locations. Participants exhibited superior reaction times with the shared avatar than individual reaction times, and the avatar’s hand movements were straighter and less jerky than those of the participants. The participants exhibited a sense of agency and body ownership towards the shared avatar although they only formed a part of the shared avatar.

The ocean is home to more than 700,000 miles of submarine cables that carry the internet worldwide. This crucial infrastructure is at the center of a development race between the big tech companies amidst geopolitical rivalries between the world’s most powerful nations. CNBC’s Tom Chitty explains.
–
Like our Facebook page:
https://www.facebook.com/cnbcinternational
Follow us on Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/cnbcinternational/

Starlink is a global satellite system being deployed by SpaceX to provide high-speed broadband Internet access to locations where it was unreliable, unreasonably expensive or completely inaccessible. All over the world, even in well-developed countries, there are many remote regions that are lagging far behind in the speed of digital development, and Germany is no exception. Nevertheless, good news awaits the residents of the country, because, according to a representative of Starlink, the company will enter the German market this year.
In Frankfurt am Main, the groundwork has been laid for the Starlink universal Internet offering. According to the relevant trade register entry, Starlink Germany GmbH must offer Internet connection services and the sale or rental of the necessary accessories.
“If everything goes according to plan, we will start this year in Germany,” said VP Build and Flight Reliability at SpaceX Hans Königsmann to Wirtschaftswoche. “Our mission is to provide fast Internet access to remote corners of the world.”