The COVID-19 crisis has led to a significant increase in the use of cyberspace, enabling people to work together at distant places and interact with remote environments and individuals by embodying virtual avatars or real avatars such as robots. However, the limits of avatar embodiment are not clear. Furthermore, it is not clear how these embodiments affect the behaviors of humans.
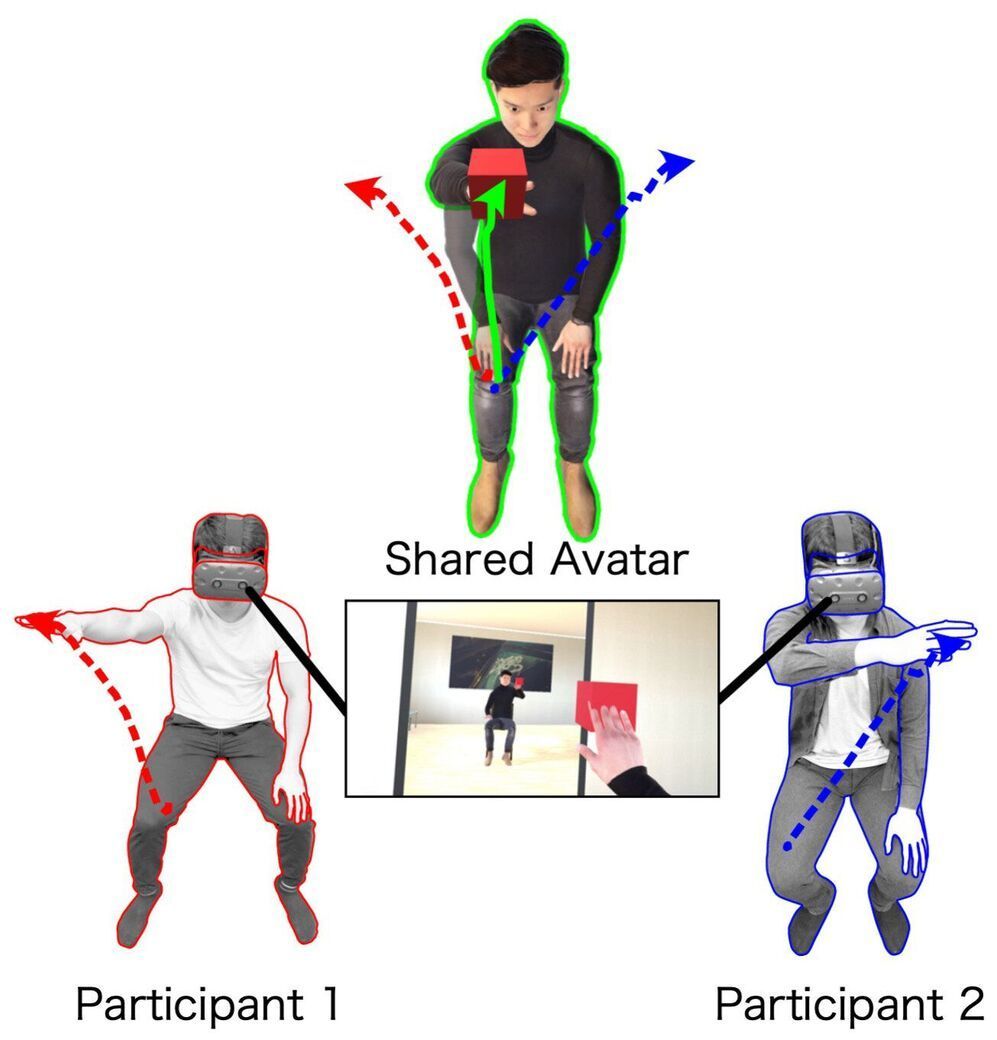
Therefore, a research team comprising Takayoshi Hagiwara (graduate student) and Professor Michiteru Kitazaki from Toyohashi University of Technology; Dr. Ganesh Gowrishankar (senior researcher) from UM-CNRS LIRMM; Professor Maki Sugimoto from Keio University; and Professor Masahiko Inami from The University of Tokyo aimed to develop a novel collaboration method with a shared avatar, which can be controlled concurrently by two individuals in VR, and to investigate human motor behaviors as the avatar is controlled in VR.
Full body movements of two participants were monitored via a motion-capture system, and movements of the shared avatar were determined as the average of the movements of the two participants. Twenty participants (10 dyads) were asked to perform reaching movements with their right hand towards target cubes that were presented at various locations. Participants exhibited superior reaction times with the shared avatar than individual reaction times, and the avatar’s hand movements were straighter and less jerky than those of the participants. The participants exhibited a sense of agency and body ownership towards the shared avatar although they only formed a part of the shared avatar.