Calculations involving a higher dimension are guiding physicists toward a misstep in Stephen Hawking’s legendary black hole analysis.
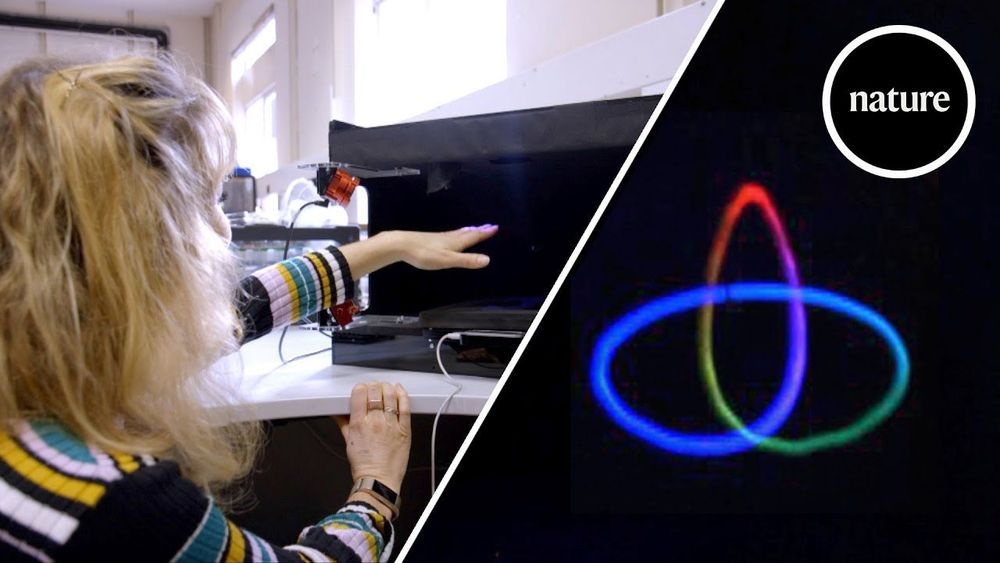


The use of ultrasound waves allows the device to produce audible noise as well as a physical sensation.
“Even if not audible to us, ultrasound is still a mechanical wave and it carries energy through the air,” researcher Diego Martinez Plasencia said in the press release. “Our prototype directs and focuses this energy, which can then stimulate your ears for audio, or stimulate your skin to feel content.”
The researchers envision future versions of the device making use of multiple beads to create even more detailed holograms. And perhaps even more exciting than the prototype itself is the fact that, unlike many cutting-edge technologies, this one might not have too much difficulty making the leap to consumer product.
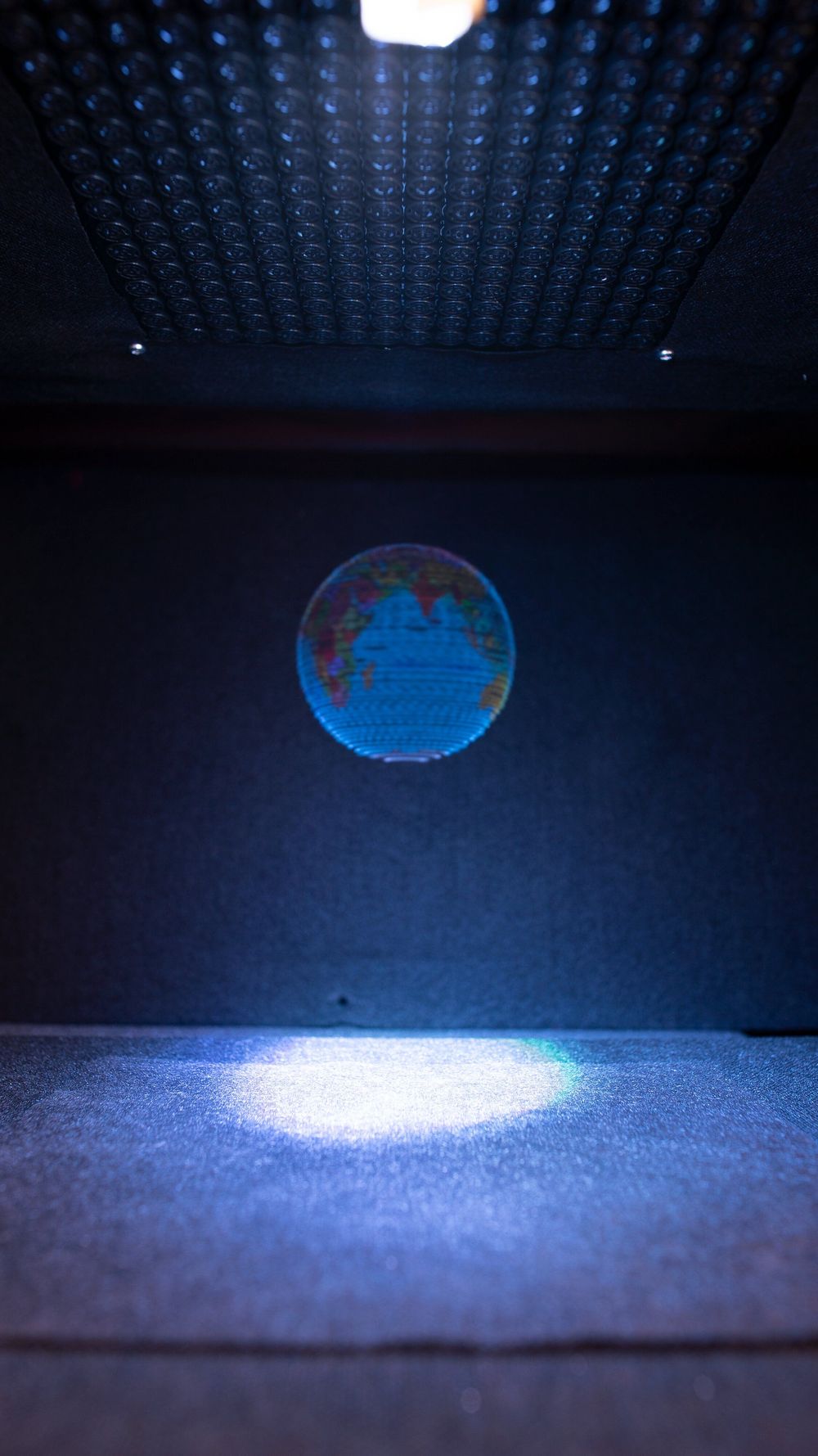

Walking, talking holograms have been a staple of sci-fi films since Princess Leia was magically brought to life in “Star Wars”.
Now scientists in Britain say they can make even more realistic 3D versions—a butterfly, a globe, an emoji—which can be seen with the naked eye, heard and even felt without the need for any virtual reality systems.
Writing in the journal Nature, a team at the University of Sussex in southern England, said technology currently in use can create 3D images but they are slow, short-lived and “most importantly, rely on operating principles that cannot produce tactile and auditive content as well”.

Researchers have developed a new printer that produces digital 3D holograms with an unprecedented level of detail and realistic color. The new printer could be used to make high-resolution color recreations of objects or scenes for museum displays, architectural models, fine art or advertisements that do not require glasses or special viewing aids.
“Our 15-year research project aimed to build a hologram printer with all the advantages of previous technologies while eliminating known drawbacks such as expensive lasers, slow printing speed, limited field of view and unsaturated colors,” said research team leader Yves Gentet from Ultimate Holography in France. “We accomplished this by creating the CHIMERA printer, which uses low-cost commercial lasers and high-speed printing to produce holograms with high-quality color that spans a large dynamic range.”
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Applied Optics, the researchers describe the new printer, which creates holograms with wide fields of view and full parallax on a special photographic material they designed. Full parallax holograms reconstruct an object so that it is viewable in all directions, in this case with a field of view spanning 120 degrees.
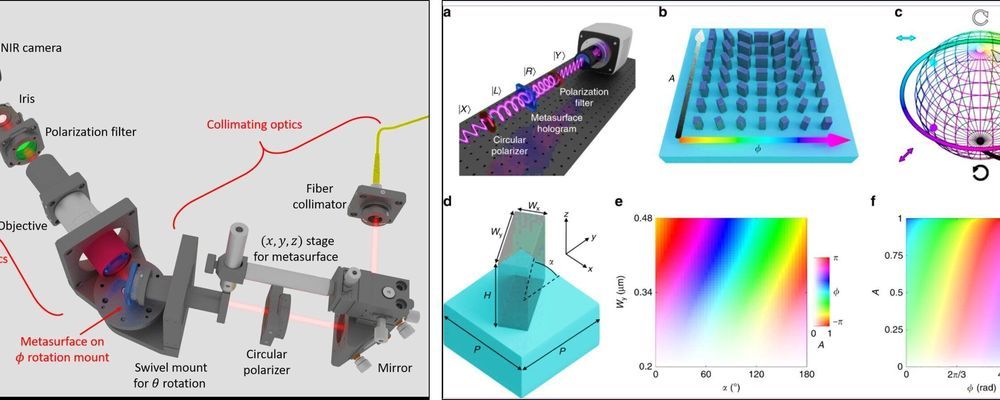
Metasurfaces are optically thin metamaterials that can control the wavefront of light completely, although they are primarily used to control the phase of light. In a new report, Adam C. Overvig and colleagues in the departments of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics at the Columbia University and the Center for Functional Nanomaterials at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, U.S., presented a novel study approach, now published on Light: Science & Applications. The simple concept used meta-atoms with a varying degree of form birefringence and angles of rotation to create high-efficiency dielectric metasurfaces with ability to control optical amplitude (maximum extent of a vibration) and phase at one or two frequencies. The work opened applications in computer-generated holography to faithfully reproduce the phase and amplitude of a target holographic scene without using iterative algorithms that are typically required during phase-only holography.
The team demonstrated all-dielectric metasurface holograms with independent and complete control of the amplitude and phase. They used two simultaneous optical frequencies to generate two-dimensional (2-D) and 3D holograms in the study. The phase-amplitude metasurfaces allowed additional features that could not be attained with phase-only holography. The features included artifact-free 2-D holograms, the ability to encode separate phase and amplitude profiles at the object plane and encode intensity profiles at the metasurface and object planes separately. Using the method, the scientists also controlled the surface textures of 3D holographic objects.
Light waves possess four key properties including amplitude, phase, polarization and optical impedance. Materials scientists use metamaterials or “metasurfaces” to tune these properties at specific frequencies with subwavelength, spatial resolution. Researchers can also engineer individual structures or “meta-atoms” to facilitate a variety of optical functionalities. Device functionality is presently limited by the ability to control and integrate all four properties of light independently in the lab. Setbacks include challenges of developing individual meta-atoms with varying responses at a desired frequency with a single fabrication protocol. Research studies previously used metallic scatterers due to their strong light-matter interactions to eliminate inherent optical losses relative to metals while using lossless dielectric platforms for high-efficiency phase control—the single most important property for wavefront control.
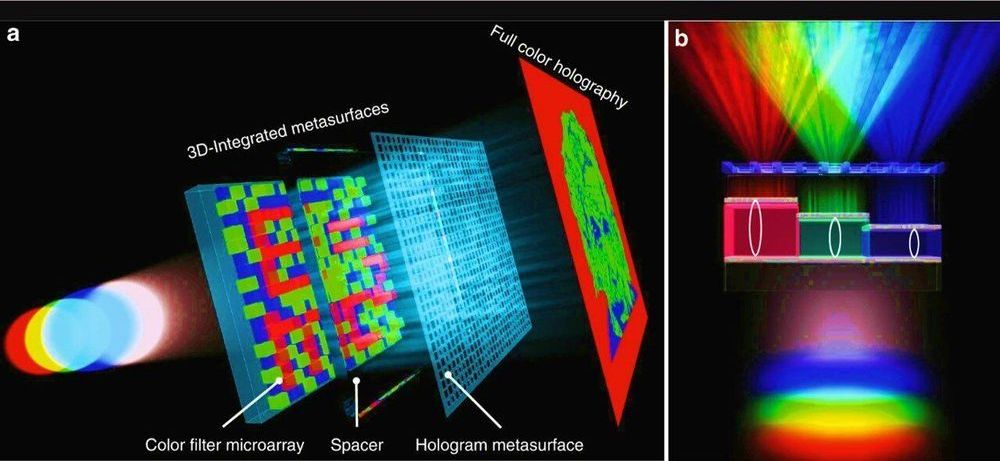
Physicists and materials scientists have developed a compact optical device containing vertically stacked metasurfaces that can generate microscopic text and full-color holograms for encrypted data storage and color displays. Yueqiang Hu and a research team in Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body in the College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering in China implemented a 3D integrated metasurface device to facilitate miniaturization of the optical device. Using metasurfaces with ultrathin and compact characteristics, the research team designed optical elements by engineering the wavefront of light at the subwavelength scale. The metasurfaces possessed great potential to integrate multiple functions into the miniaturized optoelectronic systems. The work is now published on Light: Science & Applications.
Since existing research on multiplexing in the 2-D plane remains to fully incorporate capabilities of metasurfaces for multi-tasking, in the present work, the team demonstrated a 3D integrated metasurface device. For this, they stacked a hologram metasurface on a monolithic Fabry-Pérot (FP) cavity-based color filter microarray to achieve simultaneous cross-talk, polarization-independent and highly efficient full-color holography and microprint functions. The dual function of the device outlined a new scheme for data recording, security, encryption color displays and information processing applications. The work on 3D integration can be extended to establish flat multi-tasking optical systems that include a variety of functional metasurface layers.
Metasurfaces open a new direction in optoelectronics, allowing researchers to design optical elements by shaping the wavefront of electromagnetic waves relative to size, shape and arrangement of structures at the subwavelength. Physicists have engineered a variety of metasurface-based devices including lenses, polarization converters, holograms and orbital angular momentum generators (OAM). They have demonstrated the performance of metasurface-based devices to even surpass conventional refractive elements to construct compact optical devices with multiple functions. Such devices are, however, withheld by shortcomings due to a reduced efficiency of plasmonic nanostructures, polarization requirements, large crosstalk and complexity of the readout for multiwavelength and broadband optical devices. Research teams can therefore stack 3D metasurface-based devices with different functions in the vertical direction to combine the advantages of each device.

When ordinary light, whether it comes from science fiction projectors or a magic spell, seems to have (or really does have) actual substance, it’s Hard Light. Hard light objects behave like any other object — chairs support weight, bullets kill, razors shave, and so forth. An illusory person made of Hard Light can pick up real things and interact physically with real people, even though they don’t technically exist.
Strictly speaking, hard light is not holography. A hologram is a sort of three-dimensional projection. It is not solid. If something is solid, it is, by definition, not a hologram.
That said, it’s easy to imagine holography being used in tandem with some other technology (Deflector Shields, perhaps) to produce a projection which seems solid to observers. The Holographic Terminal in its “real world” form comes to mind.

In the past, a trip to the circus was nothing without seeing some exotic animals doing impressive tricks. But as we become more aware of human impact on the world, and more inclined to be careful about how we interact with other species on earth, the simple pleasure no longer seems so pure. In fact, using other animals for our enjoyment seems deeply unethical, and, for many, precludes any circus-related enjoyment.
But one innovative circus has come up with a solution to this problem. Wanting to enchant visitors with traditional shows of the past without having to make shady ethical calls, they’ve gone for a different approach. Instead of performing these tricks with living beings, they’ve used technical advancements to achieve beautiful effects — and the internet is loving it.
Black holes are some of the most powerful and fascinating phenomena in our Universe, but due to their tendency to swallow up anything nearby, getting up close to them for some detailed analysis isn’t possible right now.
Instead, scientists have put forward a proposal for how we might be able to model these massive, complex objects in the lab — using holograms.
While experiments haven’t yet been carried out, the researchers have put forward a theoretical framework for a black hole hologram that would allow us to test some of the more mysterious and elusive properties of black holes — specifically what happens to the laws of physics beyond its event horizon.

Hologram messaging is a sci-fi staple that has captured people’s collective imaginations for years.
The new finding could lead to technology straight out of sci-fi.