Blog — Bundex Film Archives coming to posthuman university.
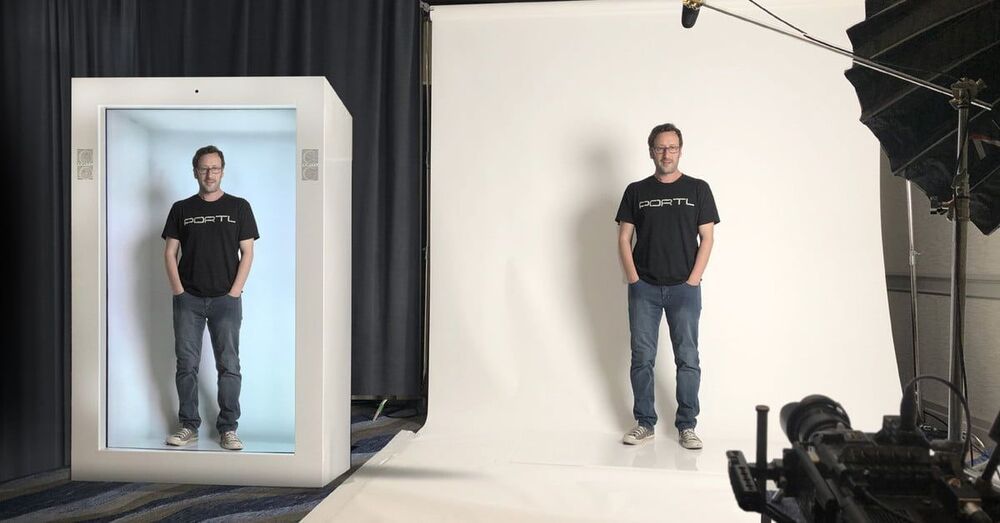
As editor, sound engineer and roadie with director Bunny Dexter’s “Bundex Films”, the three of us (Eugene Smith was cameraman) travelled to various parts of the world making political, environmental and quirky documentaries during the first age of digital video. Bunny was also a judge at some international film festivals, and we actually won an award in Poland for one of our films. At NY film school, Bunny’s teacher was Marty Scorsese, who would call at Bunny’s flat sometimes when in London. We made two versions of a 3D hologram of Marty, of which he has one and I the other. After Bunny’s passing I inherited the huge shoulder-harnress digital camera which remains in my garage and has less capability than a modern smartphone, digital tape-decks and lots footage together with all rights, except for the lost Orson Welles tapes matter and story of his aristocratic Sicilian producer. More about this and other films later. I have boxes to sort through, and am sure I have forgotten some projects which will come as a surprise when I rediscover them. Will post at posthuman university side when sorted, this footage give unique insights from a period of very rapid evolution and transformation in film-making.
Documentaries include the Homeless and their Dogs, Gipsy persecution in Hungary, a study of Tattoo’s and Tattoo artists, Momento Mori – a film of an elderly lady after her death, and our pursuit of Cocoa plant agricultural sabotage in Brazil. There is unseen footage from these and other films, and interviews with Bunny before her death which I will edit together. She had an interesting life including appearances in Andy Warhol movies, and early success with a short film with Hollywood beckoning. Woody Allen was in her NY film school class, and many of her friends went on to become big stars, but B was too much of a socialite, and was unable to get her screen plays produced. At least one political biography that I have is very good, I might update it for sub-Hollywood production in the future. Anyway, Bunny had an interesting “career” and was close friends with Yoko & John Lennon from her guerrilla art days, Jimmy Hendrix, also Graham Chapman and some of the Pythons.