Machine learning is helping doctors diagnose things like genetic disorders, Alzheimer’s, and autism faster than ever before.
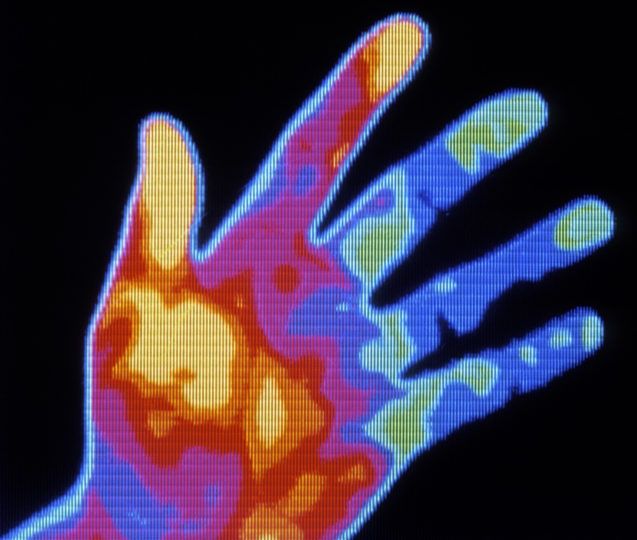


More data for caloric restriction and health benefits.
The long-term response to calorie restriction has long been of interest to the aging research community, and particularly in the past few decades as the tools of biotechnology allowed for a more detailed analysis of the metabolic changes that accompany a reduced calorie intake. A restricted diet extends healthy life spans in near all species tested to date, though to a much greater extent in short-lived species than in long-lived species such as our own. Considerable effort is presently devoted to the development of drugs that can replicate some fraction of calorie restriction — more effort than is merited in my opinion, given that the optimal result for extension of human life span achieved via calorie restriction mimetics will be both hard to achieve safely and very limited in comparison to the gains possible through rejuvenation therapies after the SENS model. Repairing damage within the existing system should be expected to outdo attempts to change the system in order to slow the accumulation of damage, in both efficiency and size of result.
Not everyone is interested in the long term, however. The short term health benefits of calorie restriction appear quickly and are surprisingly similar in mice and humans, given that calorie restriction in mice results in significantly extended life and calorie restriction in humans does not. The beneficial adjustments to metabolism and organ function are for the most part larger and more reliable than similar gains presently achievable through forms of medicine. That is more a case of medical science having a long way to go yet than calorie restriction being wondrous, however. Still, the short term benefits are coming to the attention to wider audience within the research and medical community.

Interesting approach.
Families who rely on food stamps may not be left out of the future of grocery shopping after all.
The pilot, which will run for two years, will launch on Shop.safeway.com in August.
The other retailers include Amazon, testing the program in New York, New Jersey and Maryland; Safeway, testing it in Maryland, Oregon and Washington; delivery service FreshDirect, testing in New York; and other regional and local grocers testing the program in New York and other East Coast states. As with the core program, SNAP participants will be able to use their benefits only to purchase eligible items online, not to pay for service or delivery charges. “Allowing consumers to use their SNAP benefits in the same way you would also use a credit or debit card to purchase groceries will lead to lower prices and greater options for consumers in every corner of this city and state”, said Diaz “I want to thank Congressman Maloney and our NY delegation, our partners in business and the health and hunger advocates who understood the need for this pilot program and joined our efforts to bring this important new program to NY”. “With the SNAP Pilot, we look forward to bringing the online purchasing option to SNAP clients and positively impacting all the communities that we serve”.

Another example where we will see a convergence of tech and bio especially as we emerge QC forward and synbio technology such as gene/ cell circuitry. We are finding so many synergies between Quantum and bio including the brain/ neuro networking, cell technology, human framework and pathways, etc. My guess when we mature these fields along with the minerals fiend we will began to wonder why we didn’t figure this out sooner.
New technique illuminates role of previously inaccessible proteins involved in health and disease.

My grandparents taught me the importance of a power nap; and it does help.
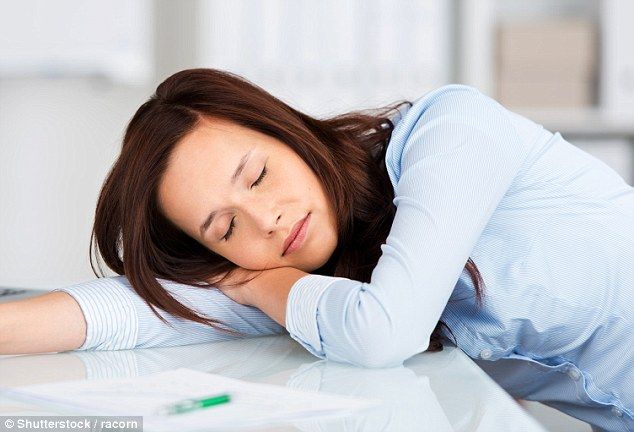
We’re not sure what the boss would have to say about it if you suddenly downed tools and made a decision to have a little sleep, but new research has found that taking an hour’s nap after lunch can have a number of health benefits, including preventing brain ageing.
The study conducted among the older Chinese men by a team of worldwide researchers concentrated mainly on post-lunchtime napping and its impact on the health of elderly people.
Do you hesitate to take a sleep after having your lunch, now you should not.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=DnYUNQVcVnI
I like this article as it highlights some of the major discoveries made in 2016 that will launch many areas forward in 2017.
IBM is taking steps to make the world a better place.
The company has unveiled its annual ‘Five in Five’ list today, which lays out some of the most important and groundbreaking scientific innovations that, in the next five years, could have the potential to drastically alter the way people work, live and interact.
This year’s overarching theme is “making the invisible visible,” with IBM highlighting artificial intelligence (AI), hyperimaging, macroscopes, chip technology, and smart sensors as technologies that could have a big impact on life as we know it.

More evidence to support that excess fat ages the body and is linked with inflammation and senescent cells.
Excess visceral fat tissue is very bad for long-term health. Being obese is by some measures as harmful as a smoking habit when it comes to remaining life expectancy. Even modest amounts of excess weight have a measurable negative impact on the future trajectory of health and longevity. There is an enormous mountain of data to support these points, ranging from large human studies to simple but compelling experiments in which the surgical removal of fat from mice leads to extended life spans. Unfortunately we evolved in an environment of scarcity and so find it a challenge to stay slim in an environment of plenty; this is a high class problem to have in exchange for an end to unavoidable famine and malnutrition, but a problem nonetheless.
One of the contributing causes of degenerative aging is the growing presence of senescent cells in tissues. While investigating the effects of changes in the amount of fat tissue in mice, researchers here find evidence to suggest that some portion of the damage done by fat tissue occurs because it hosts many more senescent cells than would otherwise be present in the body. These cells produce a mix of inflammatory signals, and may well be a sizable cause of the well-known link between visceral fat and increased inflammation. Chronic inflammation alone drives a faster progression of most of the common fatal age-related conditions, and that is without considering all of the other damage done due to the signaling produced by senescent cells.

Let’s show them we appreciate! smile
Removing senescent cells could help reduce age-related diseases and improve health. You have the power to help shape the future of medicine by supporting the CellAge campaign at lifespan.io check it out on the link below:
https://www.lifespan.io/campaigns/cellage-targeting-senescent-cells-with-synthetic-biology/
Philadelphia, PA, USA / Moscow, Russia — Bioquark, Inc., (http://www.bioquark.com) a life sciences company focused on the development of novel bio-products for regeneration, disease reversion, and healthy aging, announced the commercial approval of naturally derived Bioquantine food ingredients in the Eurasian Customs Union (formerly known as the Customs Union of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia). Moscow based, Lakmus LLC, a diversified investment company with business interests in pharmacies, restaurants, and real estate, collaborated with Bioquark Inc. on the regulatory approvals.
“We are very excited about this successful regulatory approval,” said Ira S. Pastor, CEO, Bioquark Inc. “The commercialization of Bioquantine food ingredients, including functional foods, drinks, and dietary supplements, represents another important step in our continued evolution as a company focused on a broad range of products and services in the regenerative healthcare space.”
Throughout the 20th century, natural products formed the basis for a majority of all pharmaceuticals, biologics, and consumer healthcare products used by patients around the globe, generating trillions of dollars of wealth. However, many scientists believe we have only touched the surface with what the natural world, and its range of organisms, which from a health and wellness perspective are much further advanced than human beings, has to teach us.
The integration of a complex set of newer research disciplines, including interkingdom signaling, semiochemical communication, and evolutionary biology, as well as significant recent activity in the areas of the microbiome and virome, are highlighting a myriad of new ways that non-human bio-products can affect the human genome for positive transitions in health and wellness dynamics.
“Bioquark has spent several years studying the natural ability of many species to turn back biological time in order to maintain health, fitness, and survival,” said Dr. Sergei Paylian, Founder, CSO, and President, Bioquark Inc. “This Eurasian initiative is one more step in the path in allowing humans to recapture these capabilities to effectively counter our unfortunate progression into aging, disease and degeneration.”
About Bioquark, Inc.
Bioquark Inc. is focused on the development of natural biologic based products, services, and technologies, with the goal of curing a wide range of diseases, as well as effecting complex regeneration. Bioquark is developing both biological pharmaceutical candidates, as well as products for the global consumer health and wellness market segments.
Link to Press — http://www.prweb.com/releases/2017/01/prweb13955162.htm

In Brief
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 285 million people are visually impaired, with 39 million living with blindness and the other 246 million having low vision.
In a world of modern technological advancements, visual impairment has been the subject of much medical research. Perhaps the most notable among these are those that use artificial intelligence (AI), specifically through machine learning. Google’s DeepMind has been working with the UK’s National Health Service to do ophthalmology research.