“French members of parliament (MPs) have voted to give the government extra powers to block online communications when the country is under a “state of emergency.””


“French members of parliament (MPs) have voted to give the government extra powers to block online communications when the country is under a “state of emergency.””

“Companies around the world are bracing themselves for an avalanche of cyber security regulation, as governments scramble to introduce rules forcing corporate groups to build stronger defences against catastrophic hacks.”
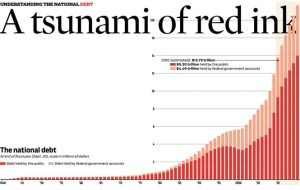
At the end of 2015, the US national debt will be 18.6 trillion dollars. With such a big number, it’s tempting to put it in perspective by comparing it with things more easily envisioned. Alas, I can not think of anything that puts such an oppressive and unfair burden into perspective, except to this:
US debt represents a personal obligation of $60,000 for each American citizen. And it is rising quickly. Most of our GDP is used simply to pay down interest on that debt. Few pundits see a way out of this hole.
 In my opinion, that hole was facilitated in August 1971, when the US modified the Bretton Woods Agreement and unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold. By forcibly swapping every dollar in every pocket and bank account with the promise of transient legislators, individual wealth was suddenly based on fiat instead of something tangible or intrinsic.
In my opinion, that hole was facilitated in August 1971, when the US modified the Bretton Woods Agreement and unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold. By forcibly swapping every dollar in every pocket and bank account with the promise of transient legislators, individual wealth was suddenly based on fiat instead of something tangible or intrinsic.
Feds Meet: No interest rate hike
The benchmark interest rate set by the US Federal Reserve Board is currently between 0 and 0.25%. It has been at or near zero since 2006.
By now, Lifeboat readers know that 20 hours ago, the US Federal Reserve board decided to not hike the benchmark interest rate. The Fed did, however, signal that they still intend to raise interest rates at a future meeting—perhaps in October or December.
The announcement came just after US equity markets closed. But, in what has become a most odd news coverage of a non-event, the immediate reaction was to lift the Asian stock markets, which were still open during the announcement.
I am a frequent contributor to Quora. I field many questions on economics, politics, law, and even physics. You might be inclined to check out my credentials as pundit of macro-economics. Don’t bother…There are none! I am an armchair economist (this is the same as saying: “I am not an economist”). But I certainly follow these things closely, and have an informed opinion.
Today, I was asked this:
What would happen if the fed had raised interest rates?
The question asked specifically about the effect on other interest rates, but a more interesting exercise might be to speculate on the state of the economy. Here then, is a comon-sense response…
If we could freeze all other conditions and avoid the effects of public confidence, likely change in debt, debt rating, etc… If we ignore these things, then the direct result of raising the interest rate for a given national currency is to attract outside money. That is, we would see an increase in foreign conversion into dollars and a movement of US assets from stocks and bonds into currency or currency equivalents. This is a simple result of the higher payout that one would expect after a raise in interest rates.
In theory, the sift of international assets and investment into dollars does four things:
This is all theoretical, of course. In practice, one of the first effects is for individuals and institutions to wonder: “How can the US possibly pay out on debt at an increased rate?”. [possible answer]*
One very obvious effect is that many individuals will further lose confidence in the American economy or the will of American’s to honor the national debt. Because of this, the effect of raising the interest rate (for the first time in 9 years) is not easy to predict. Despite massive uptake on US debt, the Chinese and energy producing nations have limits to what they can believe. A subtle switch in their investment activity (or the determination to move away from a dollar-based reserve) will have massive repercussions, especially for the US.
_____________
* Some pundits argue that US debt and payments can continue to grow, because the ability to accommodate these things are protected by these things:
But, a growing number of economists, investors, analysts, credit bureaus, and citizens don’t buy this argument! They point out that it kicks-the-can down the road and foists untenable debt on future generations. They would prefer that the US reign in spending and pay down debt.
In this regard, being the world’s reserve currency has helped hook the US on debt, and it has ballooned out of control. Transitioning to a firmly capped currency that is not controlled by legislation or a reserve board would help the country avoid massive debts (those that exceed the willingness of bond holders to finance) and to do what it must do.
In my take, the real question is not “What if the Fed has raised interest rates?” The real question is:
Does the U.S. have the courage to link its currency to something durable
— and beyond control of transient political winds and a debt pyramid?”
Sure, we must still honor the excess of the past 40 years. But with gold, or Bitcoin, at least we will have solid underpinnings and incentives to spend within our means.
Philip Raymond is a member the New Money Systems Board
at Lifeboat. He is Co-chair of Cryptocurrency Standards
Association and editor at A Wild Duck.
This short post is not about Bitcoin. It’s about a new method of organizing and arbitrating communications that is at the heart of Bitcoin
We hear a lot about the blockchain. We also hear a lot of misconceptions about its purpose and benefits. Some have said that it represents a threat to banks or to governments. Nonsense! It is time to form a simple, non-political, and non-economic explanation…
What is a Blockchain?
The blockchain is a distributed approach to bookkeeping. It offers an empowering, efficient and trusted way for disparate parties to reach consensus. It is “empowering”, because conclusions built on a blockchain can be constructed in a way that is inherently fair, transparent, and resistant to manipulation.
This is why blockchain-backed systems are generating excitement. Implemented as distributed and permissionless, they take uncertainty out of accounting, voting, legislation or research, and replace it with trust and security. Benefits are bestowed without the need for central authority or arbitration. The blockchain not only solves a fundamental transaction challenge, it addresses communication and arbitration problems that have bedeviled thinkers since the ancient Egyptians.
Related:
—Philip Raymond, CRYPSA Co-chair
Cryptocurrency Standards Association

When my daughter was just starting primary school, she would look inside a book for the pictures before reading the text. She was old enough to read without pictures, but she wanted to get a quick synopsis before diving in. “Look, Dad! a bunny is carrying a giant clock into a rabbit hole.”
This is my first article without pictures. At least none of Bitcoin, because the copper coin metaphors are tired and inaccurate. At the user level, owning bitcoin is simply your stake in a widely distributed ledger. Ownership exists only as strings of secret code and public code. There is no physical coin.
Since the only pictures in this post show a white rabbit with a big clock, let me give you the quick synopsis: The answer is “No”. Bitcoin will not end government, nor its ability to tax, spend—or even enforce compliance.
But there is an irony: Most lawmakers and regulators have not yet figured this out. They perceive a great threat to their national interests. That’s why Andreas M. Antonopoulos runs around the world. He briefs prime ministers, cabinets and legislators with the noble purpose of demystifying and de-boogieing Bitcoin.
Does Bitcoin Help Tax Cheats?
I accept the need for taxpayer reporting, measurement, and compliance initiatives. After all, it’s human nature to dislike paying taxes. Many individuals dodge taxes, if the perceived risk of being caught is low. Sociologists also point out that people are willing to cheat a system, if they perceive it to be sufficiently big or impersonal—i.e that their individual contribution is meaningless.
[ASIDE]: For this reason, Akamai Technologies ends their free-soda-&-snack policy whenever an office grows beyond 30 people (I learned this during a job interview a few years ago). People who would normally respect the policy begin pocketing free sodas for their home or friends, if (a) they no longer know everyone, or (b) they perceive the extra burden is just a drop in the corporate bucket, and not a burden on their office peers.
I suspect that most early proponents of Bitcoin are partially motivated by a desire for low taxes and privacy. While I don’t feel that these individuals are bad for the cause (after all, I am one), I feel that it is unfortunate that they appear to be the overwhelming majority of users & supporters. Let’s dismiss, for the moment, the fraction of voices that want to completely end government and taxation…If you believe in any taxes at all, then government needs compliancy mechanisms, including methods that measure, verify and ultimately arbitrate or prosecute offenders. (Don’t blame me…I’m not even the messenger here. Just an observer).
My point is that in their effort to control a country’s monetary supply (and the interbank loan rate, etc) and in their effort to ensure taxpayer compliance, a great many governments view Bitcoin as a threat. In the past, I felt that my job was to evangelize the public on the benefits of cryptocurrency, and to a great extent, that’s what CRYPSA is all about. But in recent months, I have become confident that Bitcoin will become ubiquitous. It doesn’t need me to be an evangelist. The freight train is now rolling downhill. But…

But as an engineer, author, speaker and occasional consultant, I have found a new calling. Like Andreas Antonopoulos (my idol), I have found a calling in de-boogieing Bitcoin to lawmakers and regulators. I demonstrate that (a) cryptocurrency represents far more of an opportunity than a threat to a national interests, and (b) the future is coming at ya’.
So, either: Stand pat; Get out of the way; or Hop on!
I can give an audience filled with old-school conservatives compelling reasons to “hop on”. Ultimately, blockchain technology coupled with true, permissionless, p2p transactions will shake up established mechanisms and enforcement protocols. They will force new ways of thinking. But cryptocurrency will not end the reign of government—nor even end the ability to tax, enforce and spend. It will simply change the way they do these things. It will also change the way we conduct polls, vote, arbitrate disputes, perform scientific research and much more.
Bitcoin and the blockchain are not just technologies. They transform the way in which many tasks are performed. But it’s not just about efficiency. These technologies offer mechanisms to level the playing field. T hey bring fairness and representation to processes that were opaque and perhaps even relied on the excuse of opaqueness.
hey bring fairness and representation to processes that were opaque and perhaps even relied on the excuse of opaqueness.
Ultimately, Bitcoin may render certain government departments redundant. Nations will begin to question their need to directly control monetary policy. The impact at the department level is no reason to fear Bitcoin. Overall, it represents great opportunity and not a threat. In my opinion, the changes will benefit everyone.
Bitcoin is not an us-against-them instrument. It is win-win. Of course, perception counts. Misunderstanding potential and confusing it for a threat is a fundamental problem. I share CRYPSA’s passion to help make it a very short-term problem.
Philip Raymond is CEO and Co-Chair of CRYPSA,
The Cryptocurrency Standards Association.

Responding to this nugget from Engadget:
Tokyo’s district court has ruled that it’s not possible for people to own bitcoin, and therefore they cannot sue for compensation in the wake of Mt. Gox’s collapse.
The ruling comes days after the head of the world’s largest bitcoin exchange was arrested on charges of fraud. Judge Masumi Kurachi felt that bitcoins do not possess “tangible qualities” to constitute owned property. Mt. Gox held thousands of individual accounts, and so there’s plenty of angry customers looking for compensation.
Here at Lifeboat, we have a long term view of cryptocurrency, and we sense the underpinning of fundamentals that are often overlooked.
My response to the Tokyo court…
A personal stake in Bitcoin is every bit as real (and a bit more tangible) than a personal stake in Yen, Dollars or Euros. Fiat currency is backed by the knowledge that your national government will demand tax payments in kind. But is it tangible? Like any invention of humans, that’s a matter of perception.
a) Dollars / Yen / Euros
 Over the long term, national currency is likely to be debased by debt, social welfare, war, political ambition, and a desire to redistribute fruits of labor, typically to assuage political ambitions. A built in mechanism of inflation forces a hidden tax and enables legislators to spend beyond the consent of their constituents.
Over the long term, national currency is likely to be debased by debt, social welfare, war, political ambition, and a desire to redistribute fruits of labor, typically to assuage political ambitions. A built in mechanism of inflation forces a hidden tax and enables legislators to spend beyond the consent of their constituents.
b) Bitcoin
 Bitcoin on the other hand is backed by math. It is an asset without the potential for inflation or manipulation. It is a pure supply-demand currency and a pure 2-sided network—completely unfettered by the chaff that comes with central banks and national treasuries.
Bitcoin on the other hand is backed by math. It is an asset without the potential for inflation or manipulation. It is a pure supply-demand currency and a pure 2-sided network—completely unfettered by the chaff that comes with central banks and national treasuries.
A stake in Bitcoin rises over the long haul, because the total quantity of currency is capped. As it is adopted for payments and commerce, a fixed pie is sliced thinner and thinner. This results in increased value per unit. Result: A deflationary economy without the baggage of sluggish economics.
Japan has made a foolish pronouncement; one that will ultimately embarrass their courts. Declaring Bitcoin ethereal is laughable when you consider that paper money is no more tangible than an unfulfilled promise. Likewise, declaring the theft or mismanagement of Bitcoin unworthy of recovery or restitution is no different than declaring the theft of art unworthy of restitution. Consider that each Mt. Gox account holder has proof of a real dollar investment position and an appreciation that is reported and tracked by exchanges all over the world.
Wake up Japan. You have so much more to offer the world than a distorted interpretation of a new technology.
Philip Raymond is Co-Chair of CRYPSA,
Cryptocurrency Standards Association
One of the biggest existential challenges that transhumanists face is that most people don’t believe a word we’re saying, however entertaining they may find us. They think we’re fantasists when in fact we’re talking about a future just over the horizon. Suppose they’re wrong and we are right. What follows? Admittedly, we won’t know this until we inhabit that space ‘just over the horizon’. Nevertheless, it’s not too early to discuss how these naysayers will be regarded, perhaps as a guide to how they should be dealt with now.
So let’s be clear about who these naysayers are. They hold the following views:
1) They believe that they will live no more than 100 years and quite possibly much less.
2) They believe that this limited longevity is not only natural but also desirable, both for themselves and everyone else.
3) They believe that the bigger the change, the more likely the resulting harms will outweigh the benefits.
Now suppose they’re wrong on all three counts. How are we to think about such beings who think this way? Aren’t they the living dead? Indeed. These are people who live in the space of their largely self-imposed limitations, which function as a self-fulfilling prophecy. They are programmed for destruction – not genetically but intellectually. Someone of a more dramatic turn of mind would say that they are suicide bombers trying to manufacture a climate of terror in humanity’s existential horizons. They roam the Earth as death-waiting-to-happen. This much is clear: If you’re a transhumanist, ordinary people are zombies.
Zombies are normally seen as either externally revived corpses or bodies in a state between life and death – what Catholics call ‘purgatory’. In both cases, they remain on Earth beyond their will. So how does one deal with zombies, especially when they are the majority of the population? There are three general options:
1) You kill them, once and for all.
2) You avoid them.
3) You enable them to be fully alive.
The decision here is not as straightforward as it might seem because the prima facie easiest option (2) requires that there are no resource implications. But of course, zombies require living humans (i.e. potential transhumans) in order to exist in the manner they do, which in turn makes the zombies dangerous; hence (1) has always proved such an attractive option for dealing with zombies. After all, it is difficult to dedicate the resources needed to secure the transhumanist goal of indefinite longevity, if there are zombies trying to anchor your existential horizons in the present to make their own lives as easy as possible.
This kind of problem normally arises in the context of ecological sustainability as ‘care for future generations’: Our greedy habits of mass consumption blind us to the long-term damage it does to the environment. However, the relevant sense of ‘care’ in the transhumanist case relates to sustaining the investment base needed to reach a state of indefinite longevity. It may require diverting public resources from seemingly more pressing needs, such as having a strong national defence — as the US Transhumanist Party presidential candidate Zoltan Istvan thinks. It is certainly true that if people routinely lived indefinitely, then the existential character of ‘the horror of war’ would be considerably reduced, which may in turn decrease both the likelihood and cost of war. Well, maybe…
So what about option (3), which is probably the one that most of us would find most palatable, at least in principle?
Here there is a serious public relations problem, one not so different from development aid workers trying to persuade ‘underdeveloped’ peoples that their lives would be appreciably improved by allowing their societies to be radically re-structured so as to double their life expectancy from 40 to 80. While such societies are by no means perfect and may require significant change to deliver what they promise their members, nevertheless the doubling of life expectancy would mean a radical shift in the rhythm of their individual and collective life cycles – which could prove quite threatening to their sense of identity.
Of course, the existential costs suggested here may be overstated, especially in a world where even poor people have decent access to more global trends. Nevertheless the chequered history of development aid since the formal end of Imperialism suggests that there is little political will – at least on the part of Western nations — to invest the human and financial capital needed to persuade people in developing countries that greater longevity is in their own long-term interest, and not simply a pretext to have them work longer for someone else.
The lesson for us lies in the question: How can we persuade people that extending their lives is qualitatively different from simply extending their zombiehood?
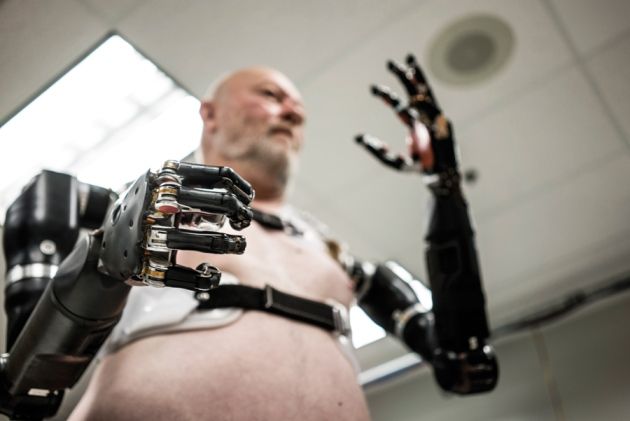

“The Biological Technologies Office (BTO), which opened in April 2014, aims to support extremely ambitious — some say fantastical — technologies ranging from powered exoskeletons for soldiers to brain implants that can control mental disorders. DARPA’s plan for tackling such projects is being carried out in the same frenetic style that has defined the agency’s research in other fields.” Read more
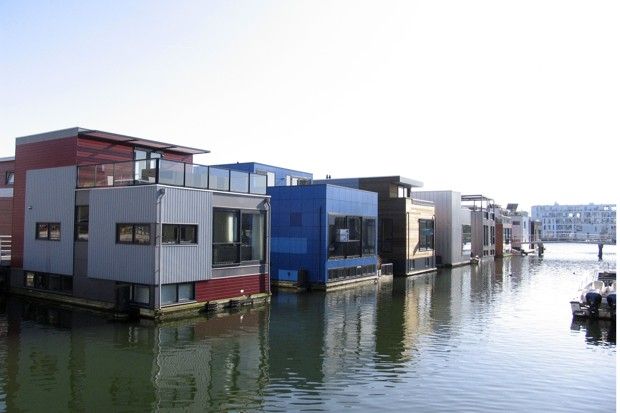

“Instead of treating Amsterdam as complete and starting again elsewhere, the IJburg plan has managed to find more space in a city that thought it had no more left.”