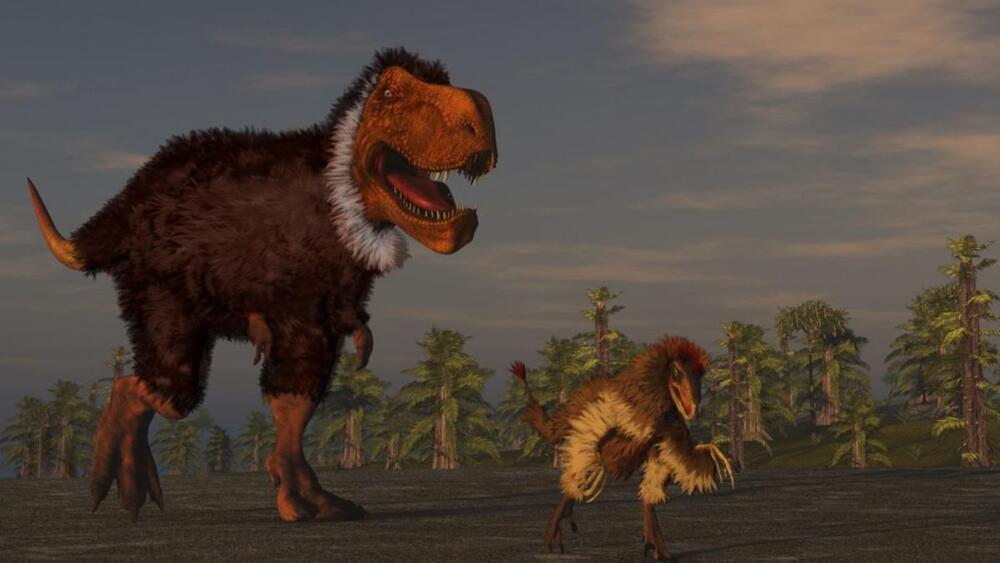
We thought that all the dinosaurs went extinct when an asteroid hit the earth some 65 million years ago until recently. Now we know that some of the dinosaur species, mostly avians, survived and become birds. Scientists are trying to tweak chicken DNA to produce atavistic, dinosaur-like, traits that are embedded in the genes of birds for years.
A research team led by Yale paleontologist and developmental biologist Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar and Harvard developmental biologist Arhat Abzhanov conducted the first successful reversion of a bird’s skull features back in 2015. The team replicated ancestral molecular development to transform chicken embryos in a laboratory to turn its beak into a snout and palate configuration similar to that of small dinosaurs such as Velociraptor and Archaeopteryx.
“I wanted to know what the beak was skeletally, functionally and when this major transformation occurred from a normal vertebrate snout to the very unique structures used in birds,” Bhullar said.