BMI is an area that will only explode when the first set of successful tests are presented to the public. I suggest investors, technologists, and researchers keep an eye on this one because it’s own impact to the world is truly inmense especially when you realize BMI changes everything in who we view how we process and connect with others, business, our homes, public services, transportation, healthcare, etc.
Implantable brain-machine interfaces (BMI) that will allow their users to control computers with thoughts alone will soon going to be a reality. DARPA has announced its plans to make such wetware. The interface would not be more than two nickels placed one on the other.
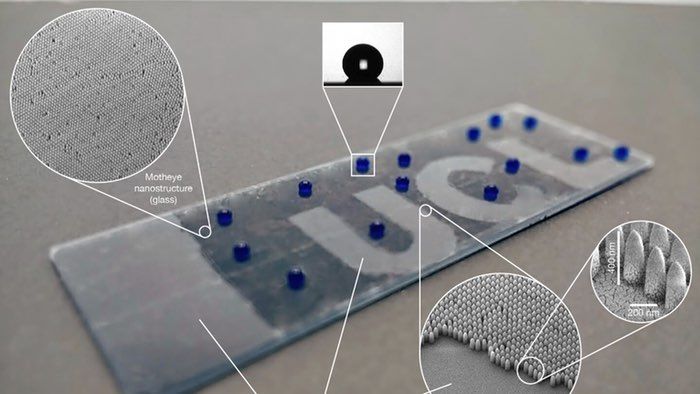
These implantable chips as per the DARPA will ‘open the channel between the human brain and modern electronics’. Though DARPA researchers have earlier also made few attempts to come up with a brain-machine interface, previous versions were having limited working.
The wetware is being developed a part of the Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program. The device would translate the chemical signals in neurons into digital code. Phillip Alvelda, the NESD program manager, said, “Today’s best brain-computer interface systems are like two supercomputers trying to talk to each other using an old 300-baud modem. Imagine what will become possible when we upgrade our tools to really open the channel between the human brain and modern electronics”.