Coal is a highly polluting and expensive way to generate electricity. This analysis shows that we have economic alternatives to continuing to burn coal for power in the US. Furthermore, analyses such as “The 2035 Report” show that we can fully retire coal, stop building other fossil fuel plants (namely gas), and still reliably meet electricity demand, while providing a host of environmental and societal benefits. There are existing policies that can help policymakers closely examine the cost burden of generation resources used today, procure cheaper and cleaner generation resources going forward, and address current assets on the books. The continuation and intensification of the coal cost crossover demands attention from policymakers and consumers alike.
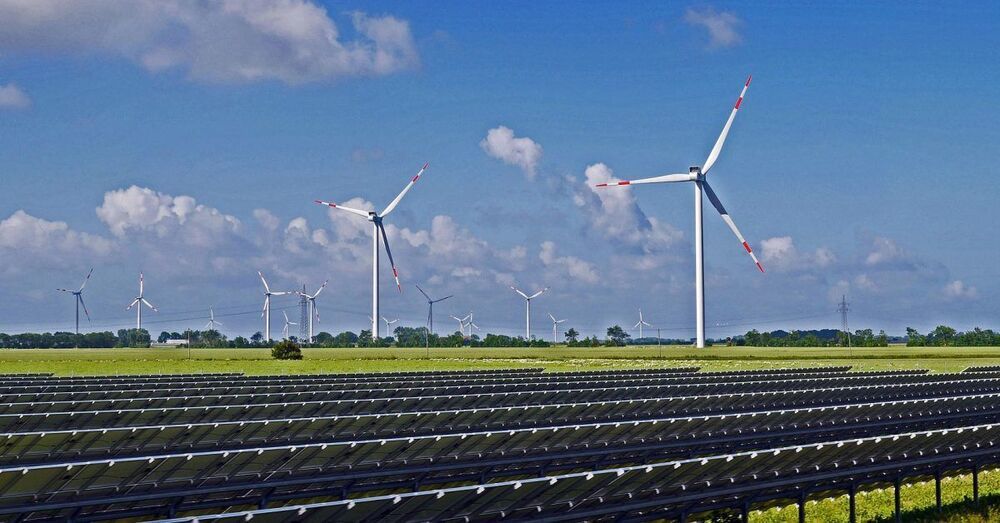
The costs of most existing US coal-fired power plants are now more expensive than the total costs of wind and solar.