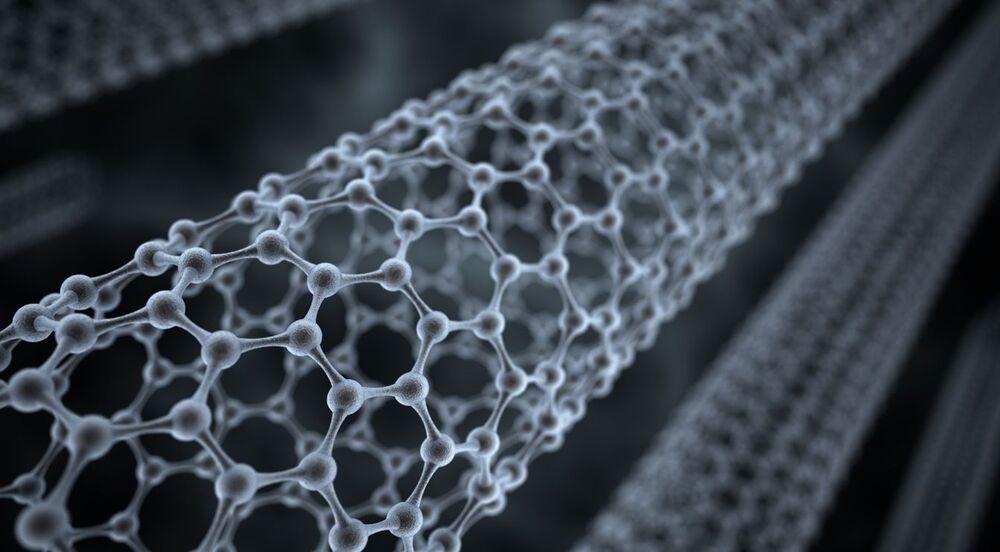
By grinding up nanotubes and dipping them in special solvents, the team showed it’s possible to generate enough current to run important electrochemical reactions, and maybe one day to power super-small devices.
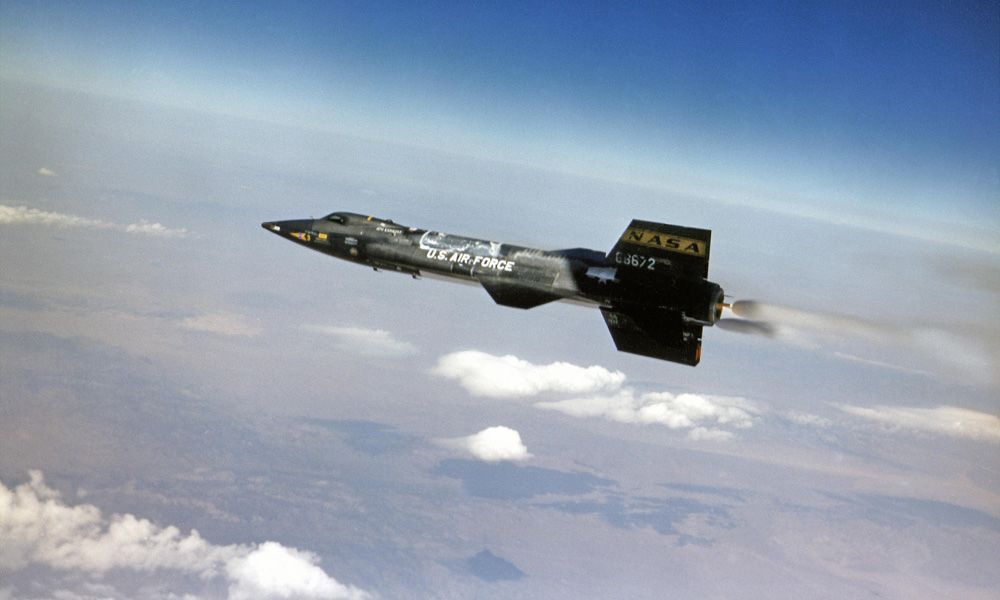


Because it was, 62 years ago, the first fully reusable space vehicle, two stages, both reusable. The same concept of Virgin Galactic SpaceShipTwo.
X15 made 200 flights at suborbital altitude, 100 km.
Of course X15 was a military spaceplane, nothing like a civilian passengers transportation vehicle, yet the concept is important.
The first project of the Space Shuttle (Krafft Ehricke, early 70’s) was based on the same concept. But then such project was abandoned, in favor of a partially reusable machine, realized in 5 unic pieces.
We could have reusable launch vehicles since 40 years, at least.
Civilization could be well on its way of expansion in the solar system: Earth orbit industries, cislunar economy, asteroid materials use, producing fuel in space… topics for an ucronian novel?
Or a topic for reflection, that technology is not an obstacle (as Branson and Musk finally demonstrated), while short-sighted policies and lobbies were huge and heavy burdens for human progress…
History of NASA: $22.99 at Magazines Direct
Discover the story of how and why NASA was created, its greatest triumphs, darkest days, and of the times it exceeded all possible hopes. A tale of adventure, heroism and resourcefulness, learn of the space agency’s greatest achievements and how — over six decades — the organization has consistently and tirelessly devoted itself to its founding principle: that “activities in space should be devoted to peaceful purposes for the benefit of all humankind”. View Deal.

The bike’s powertrain uses a fuel cell to turn gaseous hydrogen into electrical energy.
The engine setup holds its own, too. The Apex H2 will feature a hybrid powertrain that will convert gaseous hydrogen into electrical energy via a special fuel cell, reports New Atlas. Ninebot says the hydrogen-electric setup will be able to generate over 80 horsepower and rocket the bike from zero to 60 mph in less than four seconds. Considering that the original Segway—yes, the infamous two-wheel personal transporter favored by mall cops—topped out at 10 mph, that’s pretty impressive, even if it is slower than the Apex concept’s quoted top speed of 124 mph. Of course, there’s one key difference between the two bikes: The Apex H2 will be one of the rare concept vehicles you’ll be able to buy.
Ninebot says the bike will go into production in 2023, with deliveries expected to begin that same year. When the H2 does finally go on sale, the bike will join a varied Segway lineup that includes a Wall-E-esque motorized chair on wheels and a high-performance, Lamborghini-approved go-kart that can go 25 mph. You do you, Segway.

Flying taxis, more technically known as electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) vehicles, might actually — finally — become a feasible technology thanks to a new development in battery technology.
Ironically, the hardest part of designing and building eVTOLs isn’t the vehicle itself. Instead, it’s solving the challenging energy situation that eVTOLs face: Any battery that’s powerful enough to lift the thing is almost certainly too heavy and slow-charging to make a trip worthwhile. But a team of Pennsylvania State University engineers tested new batteries that can both recharge in a matter of minutes and survive thousands of charge cycles, according to research published Monday in the journal Joule, making eVTOLs seem a whole lot more realistic.
The energy-dense lithium-ion batteries represent a major leap forward in electric vehicle energy tech, according to The Independent. Both could be charged for a 50-mile journal in under ten minutes, making eVTOLs far more economically viable because each vehicle could take more trips per day.
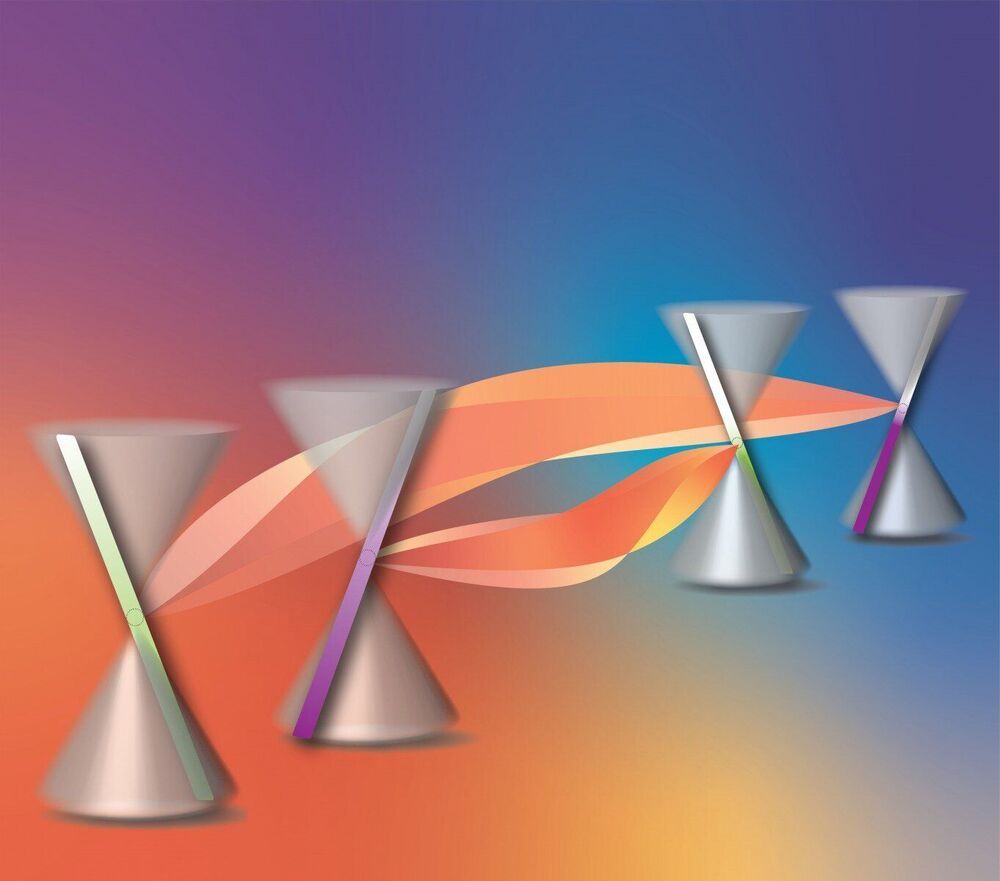

Researchers have discovered a new electronic property at the frontier between the thermal and quantum sciences in a specially engineered metal alloy—and in the process identified a promising material for future devices that could turn heat on and off with the application of a magnetic “switch.”
In this material, electrons, which have a mass in vacuum and in most other materials, move like massless photons or light—an unexpected behavior, but a phenomenon theoretically predicted to exist here. The alloy was engineered with the elements bismuth and antimony at precise ranges based on foundational theory.
Under the influence of an external magnetic field, the researchers found, these oddly behaving electrons manipulate heat in ways not seen under normal conditions. On both the hot and cold sides of the material, some of the electrons generate heat, or energy, while others absorb energy, effectively turning the material into an energy pump. The result: A 300% increase in its thermal conductivity.

Scientists in South Korea have made a breakthrough in battery research that could help us bust through a key bottleneck in energy storage. The team’s advance overcomes a technical issue that has held back highly promising lithium-metal battery architecture and could pave the way for batteries with as much as 10 times the capacity of today’s devices.
The reason lithium-metal batteries hold so much promise is because of the excellent energy density of pure lithium metal. Scientists hope to swap out the graphite used for the anode in today’s lithium batteries for this “dream material,” though this comes with some complicated problems to solve.
One of the key issues relates to needle-like structures called dendrites, which form on the anode surface as the battery is charged. These penetrate the barrier between the anode and the battery’s other electrode, the cathode, and quickly cause the battery to short-circuit, fail, or even catch fire.
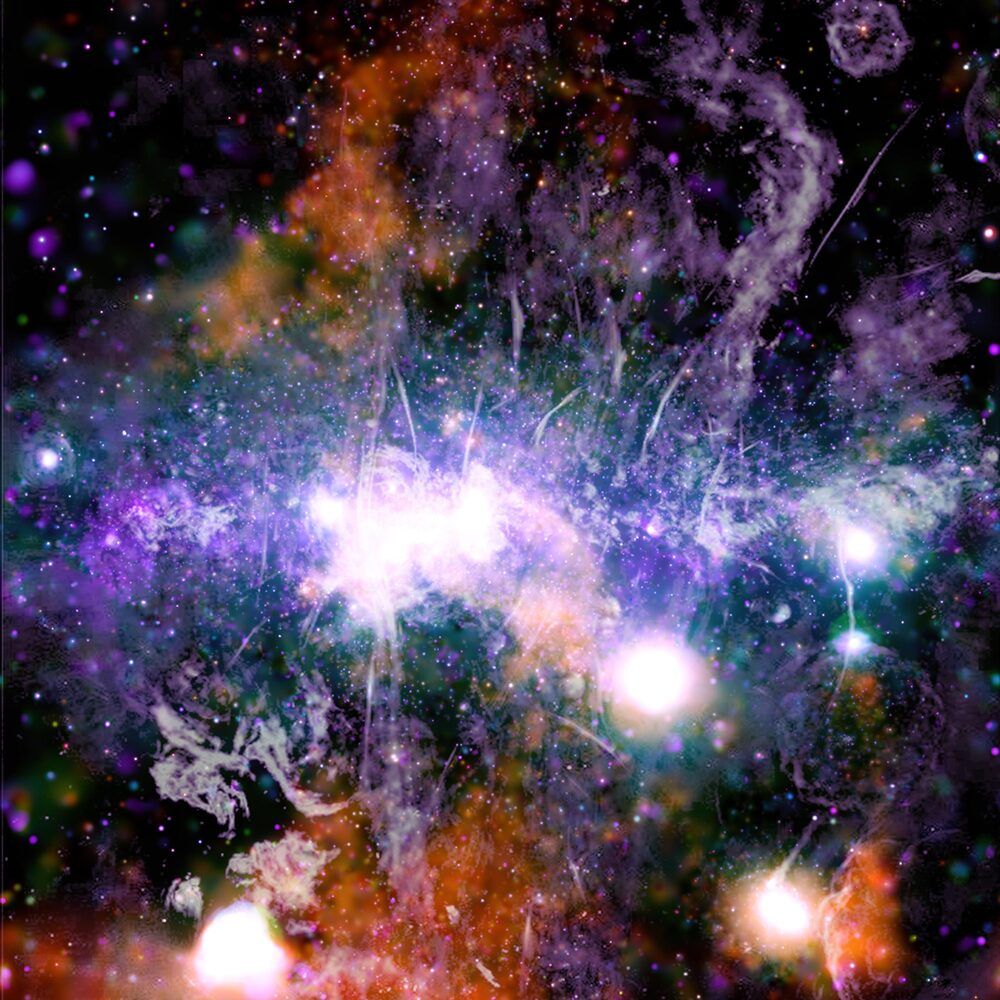

New image made using NASA ’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory hints at previously unknown interstellar energy source at the Milky Way center.
New research by University of Massachusetts Amherst astronomer Daniel Wang reveals, with unprecedented clarity, details of violent phenomena in the center of our galaxy. The images, published recently in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, document an X-ray thread, G0.17–0.41, which hints at a previously unknown interstellar mechanism that may govern the energy flow and potentially the evolution of the Milky Way.
“The galaxy is like an ecosystem,” says Wang, a professor in UMass Amherst’s astronomy department, whose findings are a result of more than two decades of research. “We know the centers of galaxies are where the action is and play an enormous role in their evolution.” And yet, whatever has happened in the center of our own galaxy is hard to study, despite its relative proximity to Earth, because, as Wang explains, it is obscured by a dense fog of gas and dust. Researchers simply can’t see the center, even with an instrument as powerful as the famous Hubble Space Telescope. Wang, however, has used a different telescope, NASA’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory, which “sees” X-rays, rather than the rays of visible light that we perceive with our own eyes. These X-rays are capable of penetrating the obscuring fog — and the results are stunning.
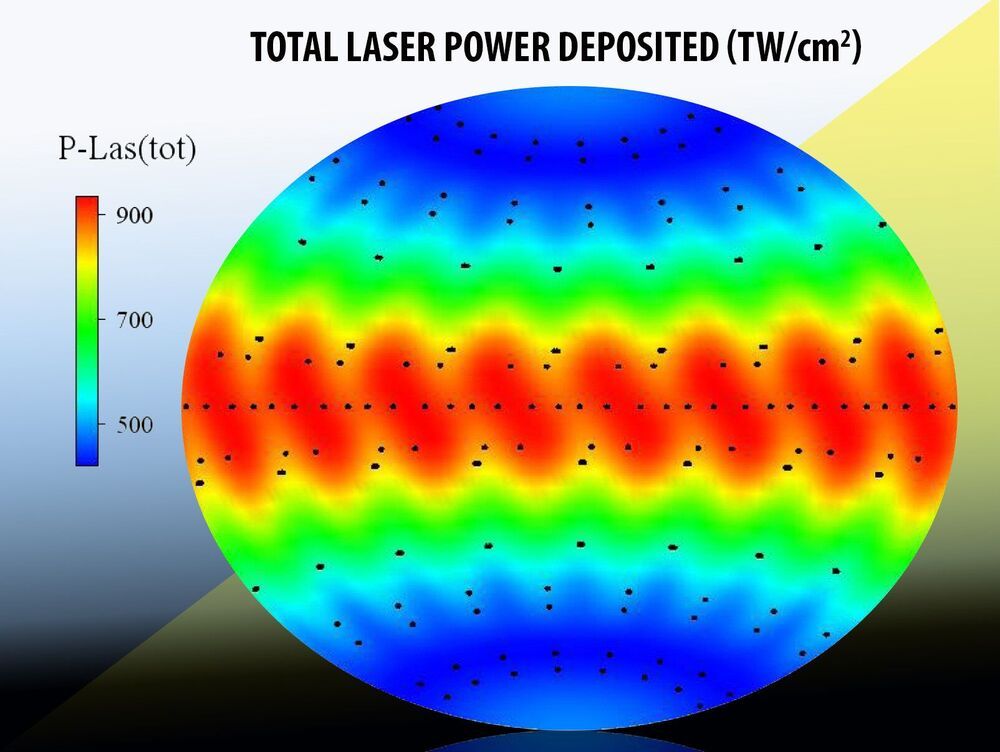
Scientists have examined the performance of pure boron, boron carbide, high-density carbon and boron nitride ablators—the material that surrounds a fusion fuel and couples with the laser or hohlraum radiation in an experiment—in the polar direct drive exploding pusher (PDXP) platform, which is used at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). The platform uses the polar direct drive configuration to drive high ion temperatures in a room-temperature capsule and has potential applications for plasma physics studies and as a neutron source.
The key findings of the work, featured in High Energy Density Physics, show that these alternate ablators do not improve the symmetry of the PDXP implosion, according to lead author Heather Whitley, associate program director for High Energy Density Science in the Fundamental Weapon Physics section at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL).
“While our simulations predict that the platform is not amenable to the electron-ion coupling measurements due to a lack of implosion symmetry, the alternate materials do enable better coupling between the laser and capsule,” she said. “We plan to test those predicted impacts on future neutron source experiments.”

While the remaining supersonic contenders duke it out to bring faster jets to market, private jet operators are doing their best to address the business traveler’s appetite for speed with aircraft that are as close to the sound barrier as they can be without actually breaking it, which poses all kinds of environmental issues.
With the news that supersonic planemaker Aerion has unexpectedly folded, is the dream of a successor to Concorde running out of fuel?
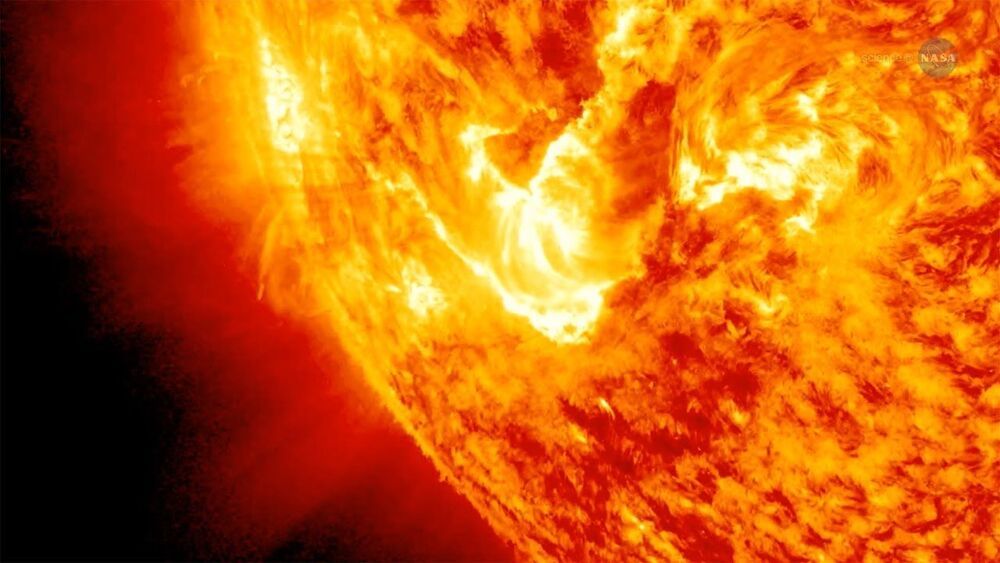

Everything is weird on the Sun, where things are not where you’d expect.
This spike in temperature, despite the increased distance from the Sun’s main energy source, has been observed in most stars and represents a fundamental puzzle that astrophysicists have mulled over for decades.
In 1942, the Swedish scientist Hannes Alfvén proposed an explanation. He theorized that magnetized waves of plasma could carry huge amounts of energy along the Sun’s magnetic field from its interior to the corona, bypassing the photosphere before exploding with heat in the Sun’s upper atmosphere.
The theory had been tentatively accepted — but we still needed proof, in the form of empirical observation, that these waves existed. Our recent study has finally achieved this, validating Alfvén’s 80-year-old theory and taking us a step closer to harnessing this high-energy phenomenon here on Earth.