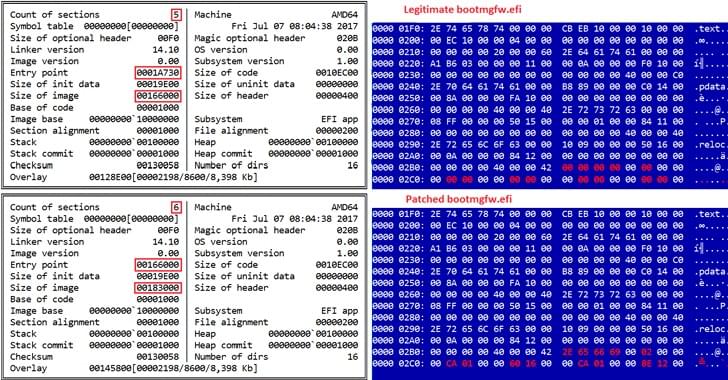
Amazon (AMZN) owned video game livestreaming service Twitch has confirmed on Twitter that a massive data breach has occurred. The leaked data, reportedly posted as a 125GB torrent link…



The cybersecurity world is evolving rapidly — perhaps more quickly than at any other time in its history. It would be easy to attribute the cyber hiccups that many businesses face to the fact that they are simply unable to keep up with bad actors.
The facts are more complicated. While it’s true that new threats are emerging every day, more often than not, breaches result from long-standing organizational issues, not a sudden upturn in the ingenuity of cybercriminals.
Full Story:
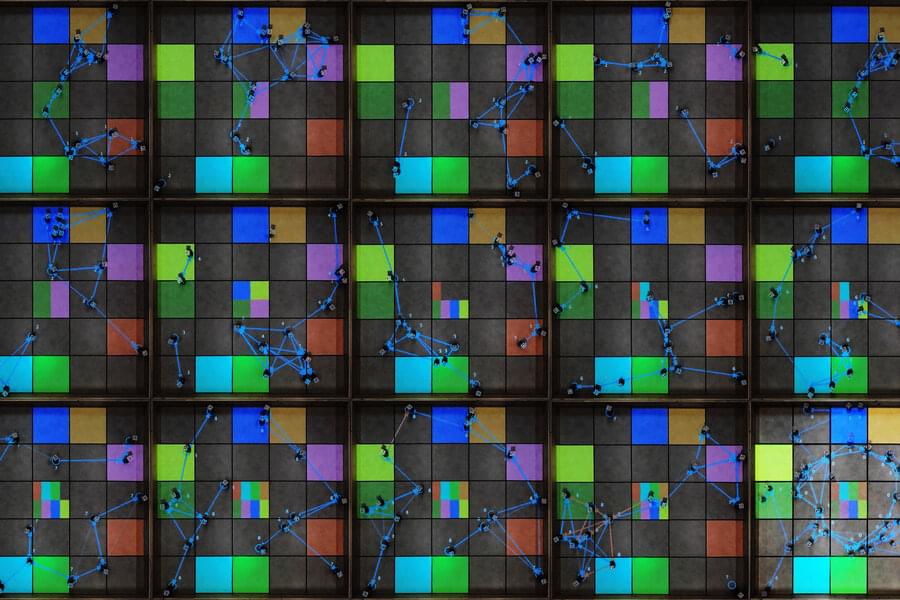
The transaction-based communications system ensures robot teams achieve their goal even if some robots are hacked.
Imagine a team of autonomous drones equipped with advanced sensing equipment, searching for smoke as they fly high above the Sierra Nevada mountains. Once they spot a wildfire, these leader robots relay directions to a swarm of firefighting drones that speed to the site of the blaze.
But what would happen if one or more leader robots was hacked by a malicious agent and began sending incorrect directions? As follower robots are led farther from the fire, how would they know they had been duped?
The use of blockchain technology as a communication tool for a team of robots could provide security and safeguard against deception, according to a study by researchers at MIT and Polytechnic University of Madrid, which was published today in IEEE Transactions on Robotics. The research may also have applications in cities where multirobot systems of self-driving cars are delivering goods and moving people across town.


“Right now, organizations see a twofold gain from consolidating around a platform player in cybersecurity,” Nichols said. The first is, “to increase efficiency” but the other, he pointed out, is legislation. With more regulatory oversight in how companies are handling their cybersecurity challenges, the pressure is on them to make their systems more resilient, and having too many components becomes a challenge to manage for that reason, too.
“Joining One Identity provides us with the ability to further accelerate our growth and provide additional value for both of our customers,” added Brad Brooks, CEO of OneLogin, in a statement. “With OneLogin’s robust unified platform for both workforce and CIAM, combining forces with One Identity’s suite of products including their PAM solution will allow new and existing customers, on a global scale, to tap into the market’s only unified identity security platform.” consolidation is afoot in the world of cybersecurity, specifically around services to help organizations manage identity and access. Today, One Identity — which provides tools for managing “zero trust” access to systems, as well as running log management and other governance services for enterprises — announced that it has acquired OneLogin, a rival to companies like Okta, Ping and others in the area of secure sign-on services for end users.
Terms of the acquisition — which officially closed last week, on October 1 — are not being disclosed, but we are trying to find out.

Traditional networks are unable to keep up with the demands of modern computing, such as cutting-edge computation and bandwidth-demanding services like video analytics and cybersecurity. In recent years, there has been a major shift in the focus of network research towards software-defined networks (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV), two concepts that could overcome the limitations of traditional networking. SDN is an approach to network architecture that allows the network to be controlled using software applications, whereas NFV seeks to move functions like firewalls and encryption to virtual servers. SDN and NFV can help enterprises perform more efficiently and reduce costs. Needless to say, a combination of the two would be far more powerful than either one alone.

Traditional networks are unable to keep up with the demands of modern computing, such as cutting-edge computation and bandwidth-demanding services like video analytics and cybersecurity. In recent years, there has been a major shift in the focus of network research towards software-defined networks (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV), two concepts that could overcome the limitations of traditional networking. SDN is an approach to network architecture that allows the network to be controlled using software applications, whereas NFV seeks to move functions like firewalls and encryption to virtual servers. SDN and NFV can help enterprises perform more efficiently and reduce costs. Needless to say, a combination of the two would be far more powerful than either one alone.
In a recent study published in IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, researchers from Korea now propose such a combined SDN/NFV network architecture that seeks to introduce additional computational functions to existing network functions. “We expect our SDN/NFV-based infrastructure to be considered for the future 6G network. Once 6G is commercialized, the resource management technique of the network and computing core can be applied to AR/VR or holographic services,” says Prof. Jeongho Kwak of Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Korea, who was an integral part of the study.
The new network architecture aims to create a holistic framework that can fine-tune processing resources that use different (heterogeneous) processors for different tasks and optimize networking. The unified framework will support dynamic service chaining, which allows a single network connection to be used for many connected services like firewalls and intrusion protection; and code offloading, which involves shifting intensive computational tasks to a resource-rich remote server.

Crypto exchange Coinbase disclosed that a threat actor stole cryptocurrency from 6,000 customers after using a vulnerability to bypass the company’s SMS multi-factor authentication security feature.
Coinbase is the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency exchange, with approximately 68 million users from over 100 countries.
In a notification sent to affected customers this week, Coinbase explains that between March and May 20th, 2,021 a threat actor conducted a hacking campaign to breach Coinbase customer accounts and steal cryptocurrency.
More than 6,000 Coinbase users had funds stolen from their accounts after hackers used a vulnerability in Coinbase’s SMS-based two-factor authentication system to breach accounts.
The intrusions took place earlier this year, between March and May, the exchange said in a data breach notification letter it has filed with US state attorney general offices.
“The third party took advantage of a flaw in Coinbase’s SMS Account Recovery process in order to receive an SMS two-factor authentication token and gain access to your account,” Coinbase said.