By now, most Bitcoin and Blockchain enthusiasts are aware of four looming issues that threaten the conversion of Bitcoin from an instrument of academics, criminal activity, and closed circle communities into a broader instrument that is fungible, private, stable, ubiquitous and recognized as a currency—and not just an investment unit or a transaction instrument.
These are the elephants in the room:
- Unleashing high-volume and speedy transactions
- Governance and the concentration of mining influence among pools, geography or special interests
- Privacy & Anonymity
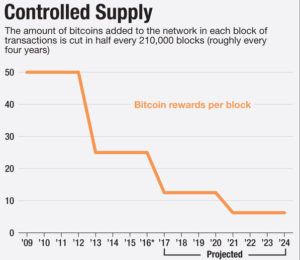
- Dwindling mining incentives (and the eventual end of mining). Bitcoin’s design eventually drops financial incentives for transaction validation. What then?
As an Op-Ed pundit, I value original content. But the article, below, on Bitcoin fungibility, and this one on the post-incentive era, are a well-deserved nod to inspired thinking by other writers on issues that loom over the cryptocurrency community.
This article at Coinidol comes from an unlikely source: Jacob Okonya is a graduate student in Uganda. He is highly articulate, has a keen sense of market economics and the evolution of technology adoption. He is also a quick study and a budding columnist.
What Happens When Bitcoin Mining Rewards Diminish To Zero?
Jacob addresses this last issue with clarity and focus. I urge Wild Ducks to read it. My response, below touches on both issues 3 and 4 in the impromptu list, above.
Sunset mining incentives—and also the absence of supporting fully anonymous transactions—are two serious deficiencies in Bitcoin today.
I am confident that both shortcomings will be successfully addressed and resolved.
Thoughts about Issues #3 and #4: [Disclosure] I sit on the board at CRYPSA and draft whitepapers and position statements.*
Blockchain Building: Dwindling Incentives
 Financial incentives for miners can be replaced by non-financial awards, such as recognition, governance, gaming, stakeholder lotteries, and exchange reputation points. I am barely scratching the surface. Others will come up with more creative ideas.
Financial incentives for miners can be replaced by non-financial awards, such as recognition, governance, gaming, stakeholder lotteries, and exchange reputation points. I am barely scratching the surface. Others will come up with more creative ideas.
Last year, at the 2015 MIT Bitcoin Expo, Keynote speaker Andreas Antonopoulos expressed confidence that Bitcoin will survive the sunset of miner incentives. He proposed some novel methods of ongoing validation incentives—most notably, a game theory replacement. Of course, another possibility is the use of very small transaction fees to continue financial incentives.
Personally, I doubt that direct financial incentives—in the form of microcash payments— will be needed. Ultimately, I envision an ecosystem in which everyone who uses Bitcoin to buy, sell, gift, trade, or invest will avoid fees while creating fluidity—by sharing the CPU burden. All users will validate at least one Blockchain transaction for every 5 transactions of their own.
Today, that burden is complex by design, because it reflects increasing competition to find a diminishing cache of unmined coins. But without that competition, the CPU overhead will be trivial. In fact, it seems likely that a validation mechanism could be built into every personal wallet and every mobile device app. The potential for massive crowd-sourced scrutiny has the added benefit of making the blockchain more robust: Trusted, speedy, and resistant to attack.
Transaction Privacy & Anonymity
Bitcoin’s lack of rock-solid, forensic-thwarting anonymity is a weak point that must ultimately be addressed. It’s not about helping criminals, it’s about liberty and freedoms. Detectives & forensic labs have classic methods of pursuing criminals. It is not our job to offer interlopers an identity, serial number and traceable event for every transaction.
Anonymity can come in one of three ways. Method #3 is least desirable:
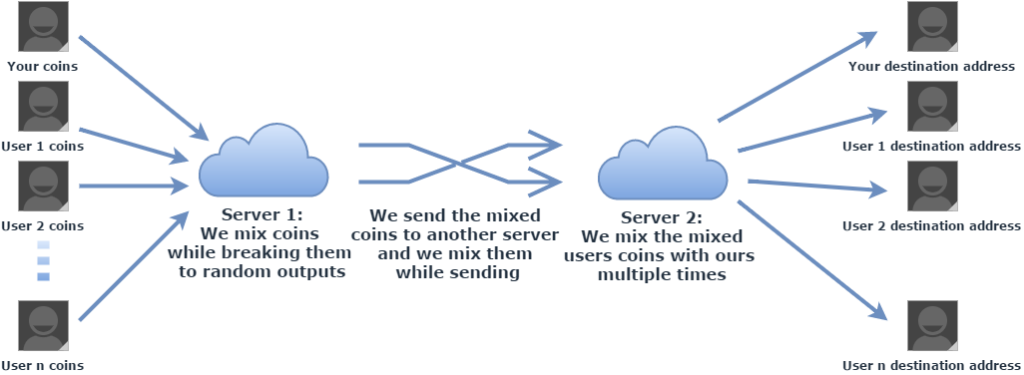
- Add complex, multi-stage, multi-party mixing to every transaction—including random time delays, and parsing out fragments for real purchases and payments. To be successful, mixing must be ubiquitous. That is, it must be active with every wallet and every transaction by default. Ideally, it should even be applied to idle funds. This thwarts both forensic analysis
 and earnest but misguided attempts to create a registry of ‘tainted’ coins.
and earnest but misguided attempts to create a registry of ‘tainted’ coins.
- Fork by consensus: Add anonymizing technology by copying a vetted, open source alt-coin
- Migrate to a new coin with robust, anonymizing tech at its core. To be effective, it must respect all BTC stakeholders with no other ownership, pre-mined or withheld distribution. Of course, it must be open, transparent and permissionless—with an opportunity and incentive for all users to be miners, or more specifically, to be bookkeepers.
That’s my opinion on the sunset of mining incentives and on transaction anonymity.
—What’s yours?
* Philip Raymond is co-chair of the Cryptocurrency Standards
Association. He was host and MC for the Bitcoin Event in New York.

 Financial incentives for miners can be replaced by non-financial awards, such as recognition, governance, gaming, stakeholder lotteries, and exchange reputation points. I am barely scratching the surface. Others will come up with more creative ideas.
Financial incentives for miners can be replaced by non-financial awards, such as recognition, governance, gaming, stakeholder lotteries, and exchange reputation points. I am barely scratching the surface. Others will come up with more creative ideas. and earnest but misguided attempts to create a registry of ‘tainted’ coins.
and earnest but misguided attempts to create a registry of ‘tainted’ coins.