Anyone who has heard of Bitcoin knows that it is built on a mechanism called The Blockchain. Most of us who follow the topic are also aware that Bitcoin and the blockchain were unveiled—together—in a whitepaper by a mysterious developer, under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
That was eight years ago. Bitcoin is still the granddaddy of all blockchain-based networks, and most of the others deal with alternate payment coins of one type or another. Since Bitcoin is king, the others are collectively referred to as ‘Altcoins’.
But the blockchain can power so much more than coins and payments. And so—as you might expect—investors are paying lots of attention to blockchain startups or blockchain integration into existing services. Not just for payments, but for everything under the sun.
Think of Bitcoin as a product and the blockchain as a clever network architecture that enables Bitcoin and a great many future products and institutions to do more things—or to do these things better, cheaper, more robust and more secure than products and institutions built upon legacy architectures.
When blockchain developers talk about permissionless, peer-to-peer ledgers, or decentralized trust, or mining and “the halving event”, eyes glaze over. That’s not surprising. These things refer to advantages and minutiae in abstract ways, using a lexicon of the art. But—for many—they don’t sum up the benefits or provide a simple listing of products that can be improved, and how they will be better.
I am often asked “What can the Blockchain be used for—other than digital currency?” It may surprise some readers to learn that the blockchain is already redefining the way we do banking and accounting, voting, land deeds and property registration, health care proxies, genetic research, copyright & patents, ticket sales, and many proof-of-work platforms. All of these things existed in the past, but they are about to serve society better because of the blockchain. And this impromptu list barely scratches the surface.
I address the question of non-coin blockchain applications in other articles. But today, I will focus on a subtle but important tangent. I call it “A blockchain in name only”…
Question: Can a blockchain be a blockchain if it is controlled by the issuing authority? That is, can we admire the purpose and utility, if it was released in a fashion that is not is open-source, fully distributed—and permissionless to all users and data originators?
Answer: Unmask the Charlatans
Many of the blockchains gaining attention from users and investors are “blockchains” in name only. So, what makes a blockchain a blockchain?
Everyone knows that it entails distributed storage of a transaction ledger. But this fact alone could be handled by a geographically redundant, cloud storage service. The really beneficial magic relies on other traits. Each one applies to Bitcoin, which is the original blockchain implementation:
 ▪Open-source
▪Open-source
▪Fully distributed among all users.
▪ Any user can also be a node to the ledger
▪Permissionless to all users and data originators
▪Access from anywhere data is generated or analyzed
A blockchain designed and used within Santander Bank, the US Post Office, or even MasterCard might be a nifty tool to increase internal redundancy or immunity from hackers. These potential benefits over the legacy mechanism are barely worth mentioning. But if a blockchain pretender lacks the golden facets listed above, then it lacks the critical and noteworthy benefits that make it a hot topic at the dinner table and in the boardroom of VCs that understand what they are investing in.
Some venture financiers realize this, of course. But, I wonder how many Wall Street pundits stay laser-focused on what makes a blockchain special, and know how to ascertain which ventures have a leg up in their implementations.
Perhaps more interesting and insipid is that even for users and investors who are versed in this radical and significant new methodology—and even for me—there is a subtle bias to assume a need for some overseer; a nexus; a trusted party. 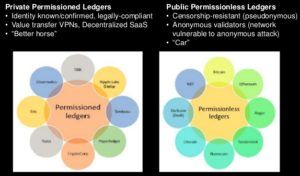 After all, doesn’t there have to be someone who authenticates a transaction, guarantees redemption, or at least someone who enforces a level playing field?
After all, doesn’t there have to be someone who authenticates a transaction, guarantees redemption, or at least someone who enforces a level playing field?
That bias comes from our tendency to revert to a comfort zone. We are comfortable with certain trusted institutions and we feel assured when they validate or guarantee a process that involves value or financial risk, especially when we deal with strangers. A reputable intermediary is one solution to the problem of trust. It’s natural to look for one.
So, back to the question. True or False?…
In a complex value exchange with strangers and at a distance, there must be someone or some institution who authenticates a transaction, guarantees redemption, or at least enforces the rules of engagement (a contract arbiter).
Absolutely False!
No one sits at the middle of a blockchain transaction, nor does any institution guarantee the value exchange. Instead, trust is conveyed by math and by the number of eyeballs. Each transaction is personal and validation is crowd-sourced. More importantly, with a dispersed, permissionless and popular blockchain, transactions are more provably accurate, more robust, and more immune from hacking or government interference.
What about the protections that are commonly associated with a bank-brokered transaction? (For example: right of rescission, right to return a product and get a refund, a shipping guaranty, etc). These can be built into a blockchain transaction. That’s what the Cryptocurrency Standards Association is working on right now. Their standards and practices are completely voluntary. Any missing protection that might be expected by one party or the other is easily revealed during the exchange set up.
For complex or high value transactions, some of the added protections involve a trusted authority.  But not the transaction itself. (Ah-hah!). These outside authorities only become involved (and only tax the system), when there is a dispute.
But not the transaction itself. (Ah-hah!). These outside authorities only become involved (and only tax the system), when there is a dispute.
Sure! The architecture must be continuously tested and verified—and Yes: Mechanisms facilitating updates and scalability need organizational protocol—perhaps even a hierarchy. Bitcoin is a great example of this. With ongoing growing pains, we are still figuring out how to manage disputes among the small percentage of users who seek to guide network evolution.
But, without a network that is fully distributed among its users as well as permissionless, open-source and readily accessible, a blockchain becomes a blockchain in name only. It bestows few benefits to its creator, none to its users—certainly none of the dramatic perks that have generated media buzz from the day Satoshi hit the headlines.
Related:
- Other Blockchain apps will surpass the ubiquity of Bitcoin
- Reuters foresees thousands of blockchain uses
- Tommorow’s Wall Street Journal: Bitcoin is Just the Beginning
Philip Raymond is co-chair of The Cryptocurrency Standards Association,
host & MC for The Bitcoin Event and editor at A Wild Duck.